System a - 100 wasp filter, A-124, Basics – Doepfer A-100(~ 40 MB) User Manual
Page 287: Doepfer, Vcf 5)
doepfer
System A - 100
Wasp Filter (
VCF 5)
A-124
3
3. Basics
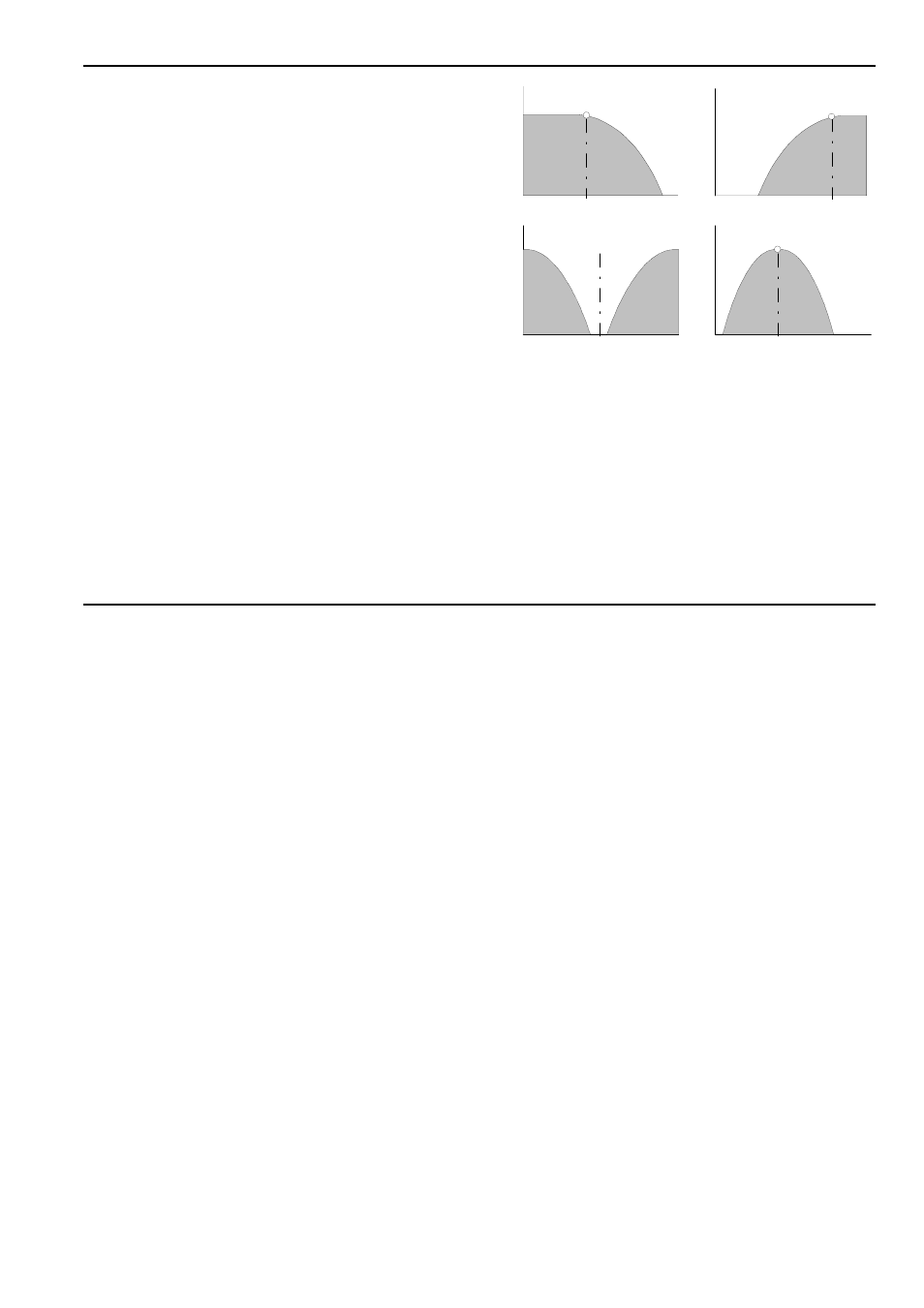
Module A-124 contains three filter types: low-pass,
high-pass and band-pass. Low-pass and high-pass
signals are internally mixed and appear as the mixed
LP/HP output %. The mix control 5 governs the
relative amounts of low-pass and high-pass.
With the mix control fully counterclockwise, at "LP",
the mix output forms a pure low-pass. This is the
most common type of filter in analogue sound produc-
tion, which filters out the higher parts of the sound
spectrum, and lets the lower frequencies pass un-
changed. Cut-off frequency f
C
determines the fre-
quency at which this occurs (see Fig. 1).
With the mix control fully clockwise, at ”HP”, the mix
output is a pure high-pass. The high-pass filter is a
mirror-image of the low-pass filter: while it lets fre-
quencies that are higher than the cut-off frequency f
C
through, it attenuates frequencies below the cut-off
point (see Fig. 1).
With the mix control in its middle position, the result is
a symmetrical notch filter, letting through the upper
and lower end of the frequency spectrum, but rejec-
ting a band in the middle. If the mid-frequency
is
modulated by an LFO, the result sounds very similar
to phasing.
Fig. 1: Typical response curves of the four filter types.
When the mix control deviates from the middle posi-
tion the notch is asymmetrical, i.e. the low-pass or
high-pass share predominates.
In the band-pass filter, which has its own output, both
ends of the frequency spectrum are attenuated (see
Fig. 1), and the cut-off frequency f
C
becomes the mid
frequency. It gives you the ability to highlight a
particular frequency band.
fc
Out
Freq.
Out
Freq.
Low Pass
High Pass
fc
fc
Freq.
Freq.
Out
Out
fc
Band Pass
Notch
