Protocol independent multicast-sparse mode, Bsr candidate summary – Dell POWEREDGE M1000E User Manual
Page 716
714
Configuring IP Multicast
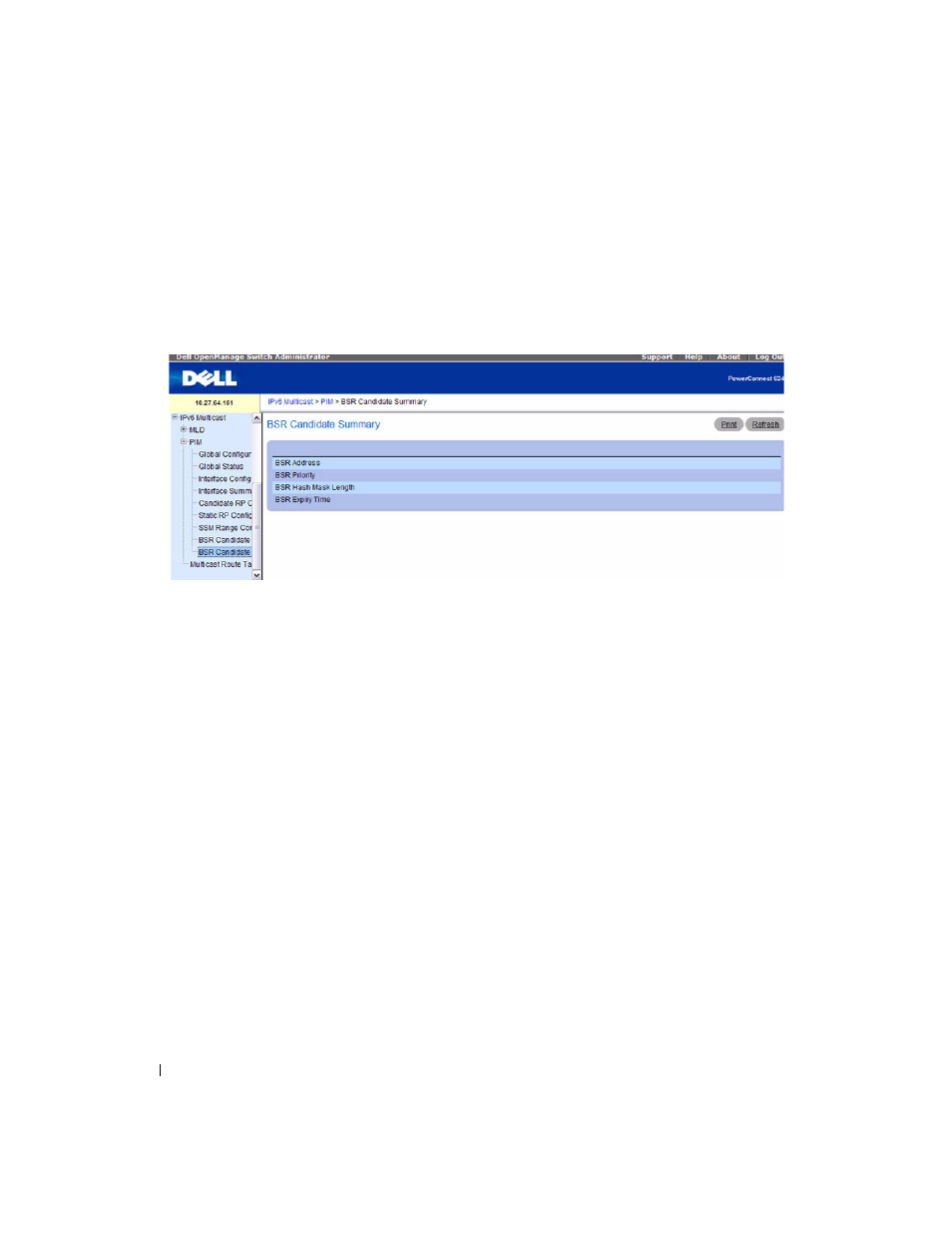
BSR Candidate Summary
Use this page to display information about the configured BSR candidates. To display this page, click
IPv4 Multicast > PIM > BSR Candidate Summary or IPv6 Multicast > PIM > BSR Candidate
Summary.
Figure 12-45. BSR Candidate Summary
The BSR Candidate Summary page contains the following fields:
• BSR Address — Displays the IP address of the elected bootstrap router (BSR).
•
BSR Priority — Displays the priority value of the elected BSR.
• BSR Hash Mask Length — Displays the mask length of the elected BSR.
•
BSR Expiry Time — Time (in hours, minutes, and seconds) in which the learned elected BootStrap
Router (BSR) expires.
Viewing the BSR Candidate Summary using the CLI Commands
For information about the CLI commands that perform this function, see the following chapter in the
CLI Reference Guide:
• PIM Commands
Protocol Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode
Protocol Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM) is used to efficiently route multicast traffic to
multicast groups that may span wide area networks and where bandwidth is a constraint. PIM-SM uses
shared trees by default and implements source-based trees for efficiency. This data threshold rate is used
to toggle between trees. PIM-SM assumes that no hosts want the multicast traffic unless they specifically
ask for it. It creates a shared distribution tree centered on a defined rendezvous point (RP) from which
source traffic is relayed to the receivers. Senders first send the multicast data to the RP, which in turn
