Sgct and snubber circuit – Rockwell Automation 7000L PowerFlex Medium Voltage AC Drive (C Frame) - Classic Control User Manual
Page 368
6-24
Component Definition and Maintenance
7000L-UM300I-EN-P – June 2013
7000 “C” Frame
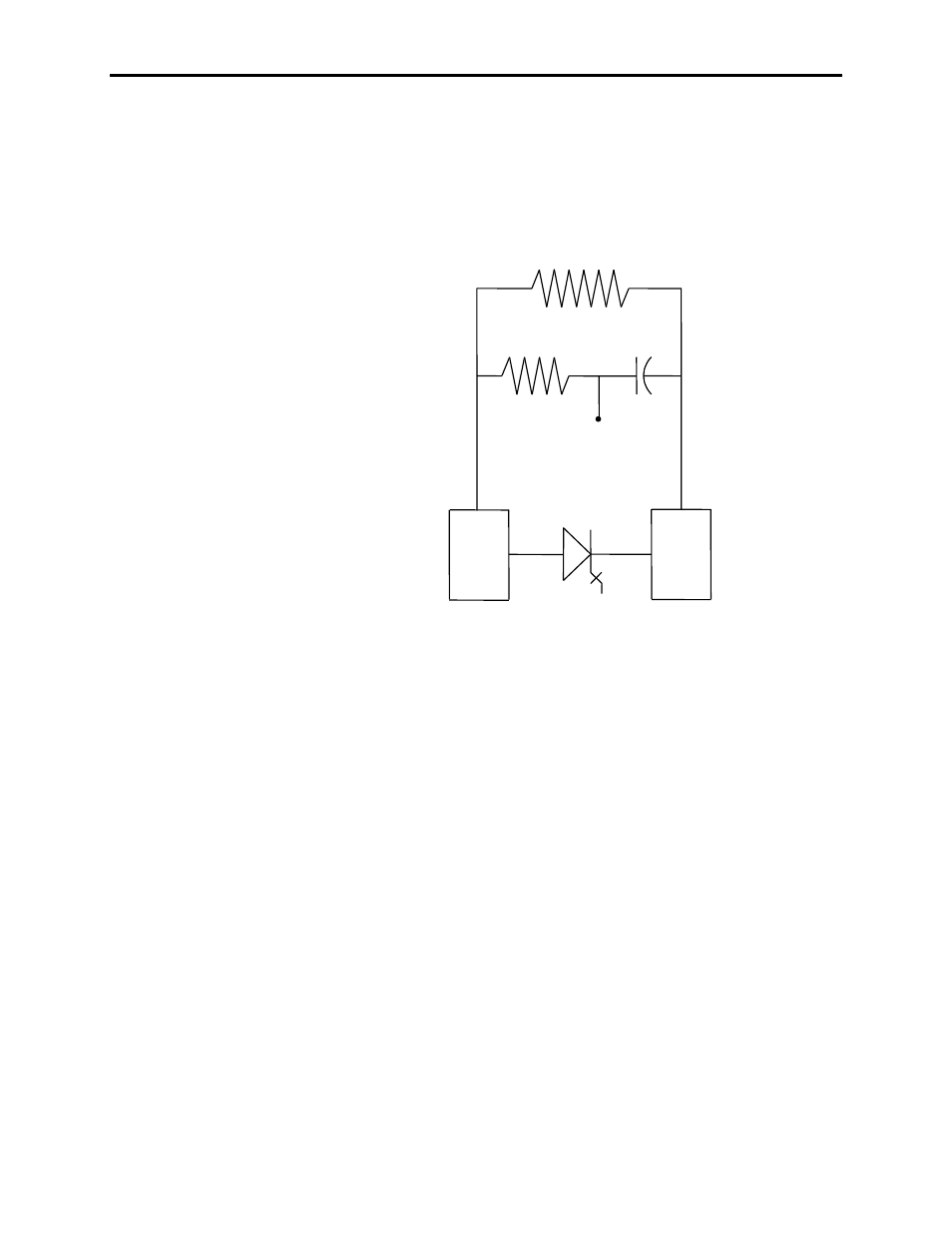
SGCT and Snubber Circuit
Similar to all power-conductors or thyristors, the SGCT must have a
snubber circuit. The snubber circuit for the SGCT is comprised of a
snubber resistor in series with a snubber capacitor.
Sharing
Resistor
Snubber
Resistor
Snubber
Capacitor
Test
Point
SGCT
Chill
Block
Chill
Block
Figure 6.18 – SGCT and Snubber Circuit
In addition to the snubber circuit, a sharing resistor is connected in
parallel with the SGCT. The function of the sharing resistor is to
ensure the voltage is shared equally among the SGCTs when
connected in series. SGCTs are connected in series to increase the
total reverse voltage blocking (PIV) capacity as seen by the electrical
circuit. A single SGCT has a PIV rating of 6.5 kV. At 4.16 kV, 2
SGCTs must be connected in series to provide a net PIV of 13 kV to
achieve the necessary design margin. Similarly, three SGCTs must
be connected in series at 6.6 kV.
The cooling requirements of the SGCT are achieved by placing the
SGCT between two liquid cooled chill blocks – one chill block on
the anode and the other chill block on the cathode. The force placed
on the SGCTs differs with the size of the device. A 63-mm device
(1500A) requires 20 kN. The clamp assembly on the right hand side
of the inverter module generates these forces.
