3 selecting network connections, Network connection types, Ip networks – HP 3PAR Operating System Software User Manual
Page 23: Remote copy links
3 Selecting Network Connections
1.
Review possible network connections.
• “IP Networks” (page 23)
• “Fibre Channel Networks” (page 24)
• “Fibre Channel over IP Networks” (page 24)
2.
Review general network information for remote copy.
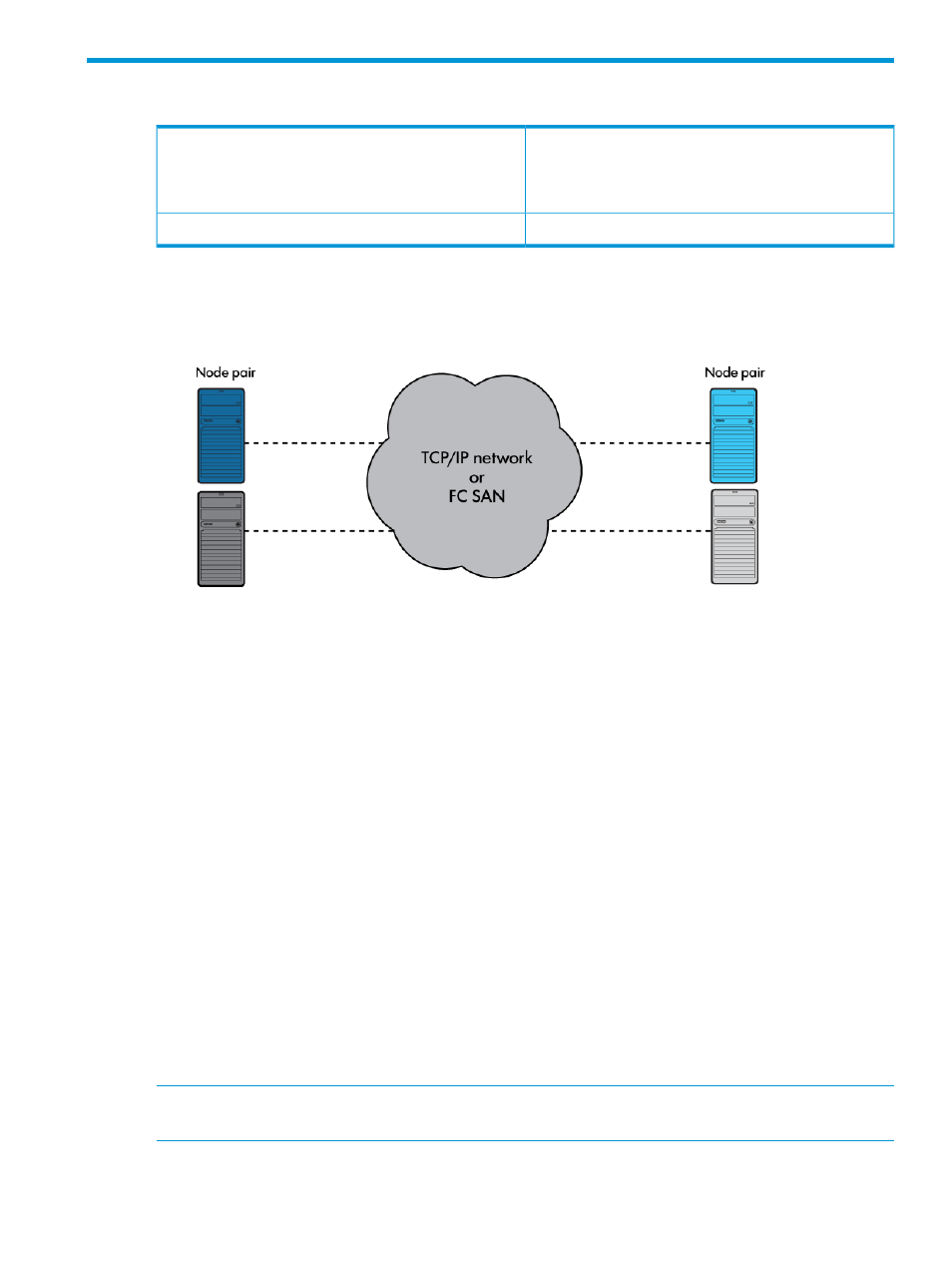
Storage systems in a remote-copy pair are connected through a dedicated link or through a network,
as illustrated in
Figure 7 Remote Copy Links
Network Connection Types
RCFC uses a proprietary HP 3PAR remote-copy protocol that optimizes synchronous replication,
eliminating the need to implement proprietary write-acceleration optimization into the network
(which might require additional licenses and administration).
FCIP is RCFC that is extended over a long-distance wide area network (WAN) using FCIP routers.
Where latency and bandwidth are concerns, and where the anticipated amount of data to be
replicated is high, FCIP can be a better choice than RCIP over native GigE. FCIP allows asynchronous
periodic data replication over longer distances, without introducing GigE into the SAN.
IP Networks
The GigE interface and the management Ethernet port of an HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage system
controller node must be on different IP subnets. The remote-copy subnet can be shared with other
I/O traffic, but a guaranteed amount of bandwidth must be dedicated to remote copy on shared
subnet.
If you configure the interface and port on the same subnet, remote-copy packets might go over the
management port and would no longer be available to the HP 3PAR Remote Copy Software.
Hosts that access the HP 3PAR StoreServ Storage systems for management purposes must not be
on the same subnet as the RCIP ports.
If you add host computers to the remote-copy subnet, IP packets might arrive through the
management interfaces and leave through the RCIP interfaces.
NOTE:
Be sure you understand the IP network that will be used to connect the storage systems.
Industry-standard rules governing IP networks apply.
Network Connection Types
23
