Printronix PrintNet Enterprise User Manual
Page 291
Viewing Telemetry Data
291
NOTE:
The hex values listed above reflect single failures.
Multiple failures will create additional hex values based on the binary
weighting shown.
For example, the hex value
0042
(or binary
0000 0000 0100 0010
)
represents both the Encodation and Decodeability failures.
RFID
This is the hex value assigned for an RFID failure.
0 = no RFID failure
1 = RFID failure
7. Failure Message
Bar Code
Failure data is grouped into different types of failure, each of which defines a
bar code problem.
•
Checksum:
This occurs when the bar code is not properly encoded with
checksum digits.
•
Decodeability:
This occurs when the difference between wide and
narrow elements is too close to reliably discern. This is generally an
indication of an improperly set heat, speed, or pressure combination, or
the loss of heating element.
•
Defects:
This is a measure of unexpected dark spots in spaces or light
spots in bars. It is generally an indication of a poor ribbon or media
combination, a burnt pixel, or the printhead needs cleaning.
•
Encodation:
This occurs when the bar code is not properly encoded. For
example, a checksum is incorrect, a required number of characters is not
met, or required terminator characters are missing. This is usually an
indication of poor form or host application design.
•
Internal Data Format Error:
The bar code data format is invalid.
•
PDF 417 Gap:
This occurs when there are large gap damages (such as
ribbon wrinkle, voids, spots, etc.) within the PDF 417 data body code.
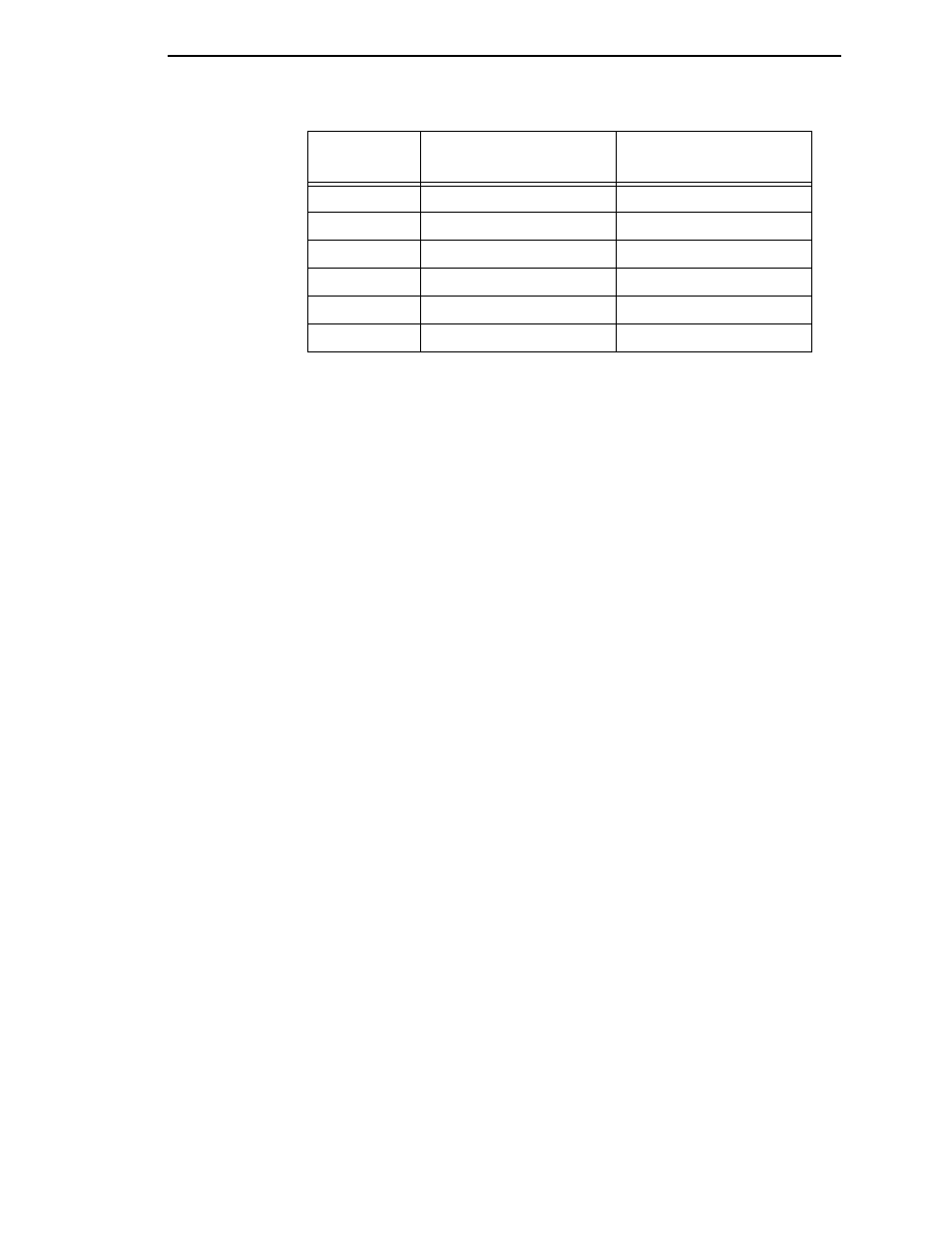
0400
xxxx x1xx xxxx xxxx
Internal Data Format Error
0800
xxxx 1xxx xxxx xxxx
Modulation
1000
xxx1 xxxx xxxx xxxx
Minimum Reflectance
2000
xx1x xxxx xxxx xxxx
Minimum Edge Contrast
4000
x1xx xxxx xxxx xxxx
Future use
8000
1xxx xxxx xxxx xxxx
Future use
Failure Code
(Hex)
Failure Code
(Binary)
Failure Message
