3 stp status, Figure 26 view: stp status, Table 17 view: stp status – ZyXEL Communications Version 1.03 User Manual
Page 60
Chapter 5 View
NetAtlas Workgroup User’s Guide
60
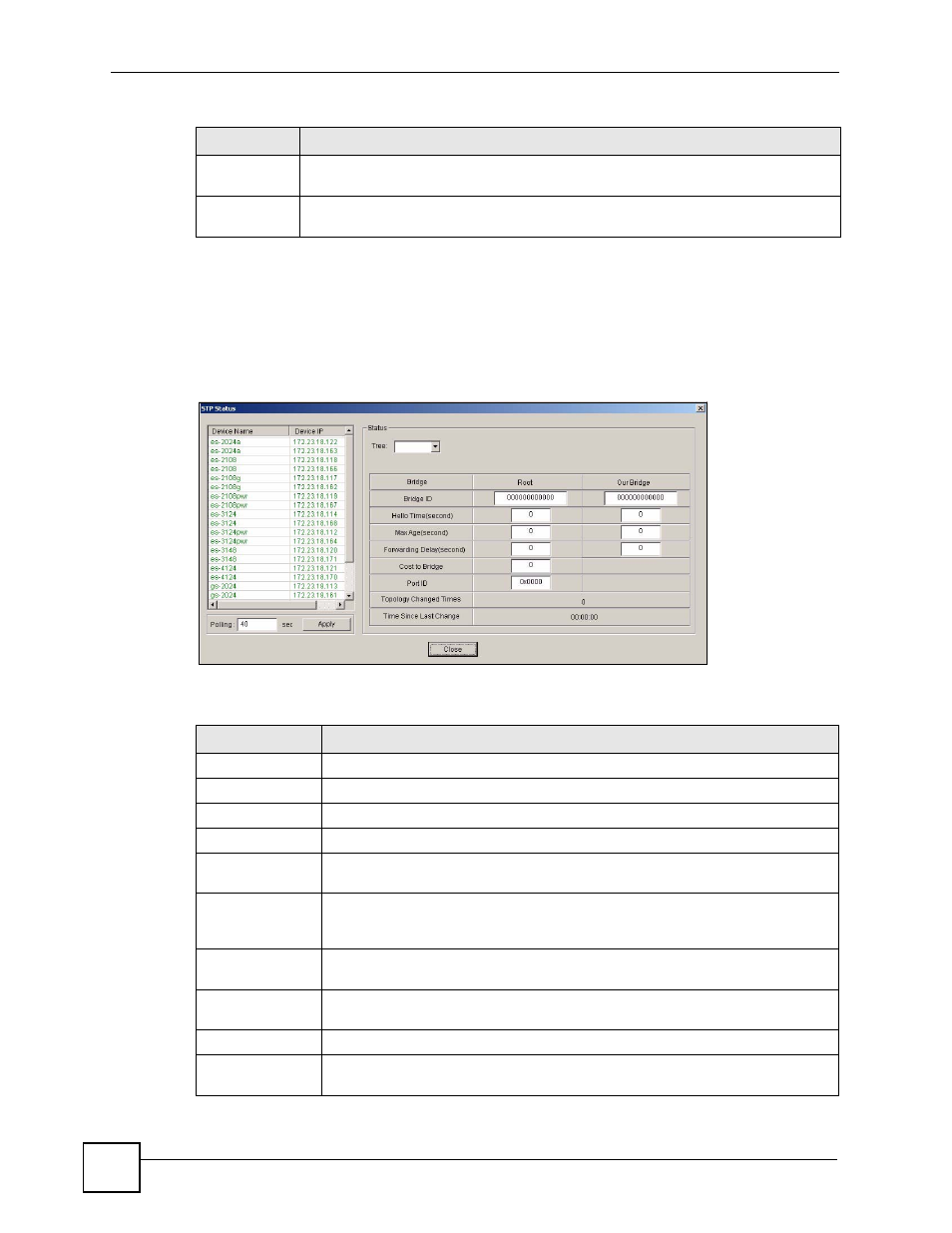
5.2.3 STP Status
View current STP information in the STP Status screen. Click Status > STP Status and select
a switch from the device list located on the left-hand side of the screen. The STP status
displays in the table on the right.
Figure 26 View: STP Status
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Learning
All BPDUs are received and processed. Information frames are submitted to the
learning process but not forwarded.
Forwarding
All BPDUs are received and processed. All information frames are received and
forwarded.
Table 16 STP Port States
PORT STATE
DESCRIPTION
Table 17 View: STP Status
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Device Name
This field displays the descriptive name of a device.
Device IP
This field displays the IP address of a device
Tree
Select the index number of the spanning tree whose status you want to display.
Bridge
Root refers to the base of the spanning tree (the root bridge).
Bridge ID
This is the unique identifier for this bridge, consisting of bridge priority plus MAC
address.
Hello Time
(second)
This is the time interval (in seconds) at which the root device transmits a
configuration message. The root bridge determines Hello Time, Max Age and
Forwarding Delay
Max Age (second) This is the maximum time (in seconds) a switch can wait without receiving a
configuration message before attempting to reconfigure.
Forwarding Delay
(second)
This is the time (in seconds) the root switch will wait before changing states (that
is, listening to learning to forwarding).
Cost to Bridge
This is the path cost from the root port on this switch to the root switch.
Port ID
This is the priority and number of the port on the switch through which this switch
must communicate with the root of the spanning tree.
