Vlan, 1 introduction to vlans, 2 configuring 802.1q vlan – ZyXEL Communications Version 1.03 User Manual
Page 157: Chapter 15 vlan, Figure 110 selecting a vlan type, Vlan (157)
NetAtlas Workgroup User’s Guide
157
C
H A P T E R
15
VLAN
This chapter describes how to view VLAN status, add and edit VLANs and how to use the
VLAN template. The type of screen you see here depends on the VLAN Type you selected in
the Switch Setup screen.
15.1 Introduction to VLANs
A VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) allows a physical network to be partitioned into
multiple logical networks. Devices on a logical network belong to one group. A device can
belong to more than one group. With VLAN, a device cannot directly talk to or hear from
devices that are not in the same group(s); the traffic must first go through a router.
In MTU (Multi-Tenant Unit) applications, VLAN is vital in providing isolation and security
among the subscribers. When properly configured, VLAN prevents one subscriber from
accessing the network resources of another on the same LAN, thus a user will not see the
printers and hard disks of another user in the same building.
VLAN also increases network performance by limiting broadcasts to a smaller and more
manageable logical broadcast domain. In traditional switched environments, all broadcast
packets go to each and every individual port. With VLAN, all broadcasts are confined to a
specific broadcast domain.
Note that VLAN is unidirectional; it only governs outgoing traffic.
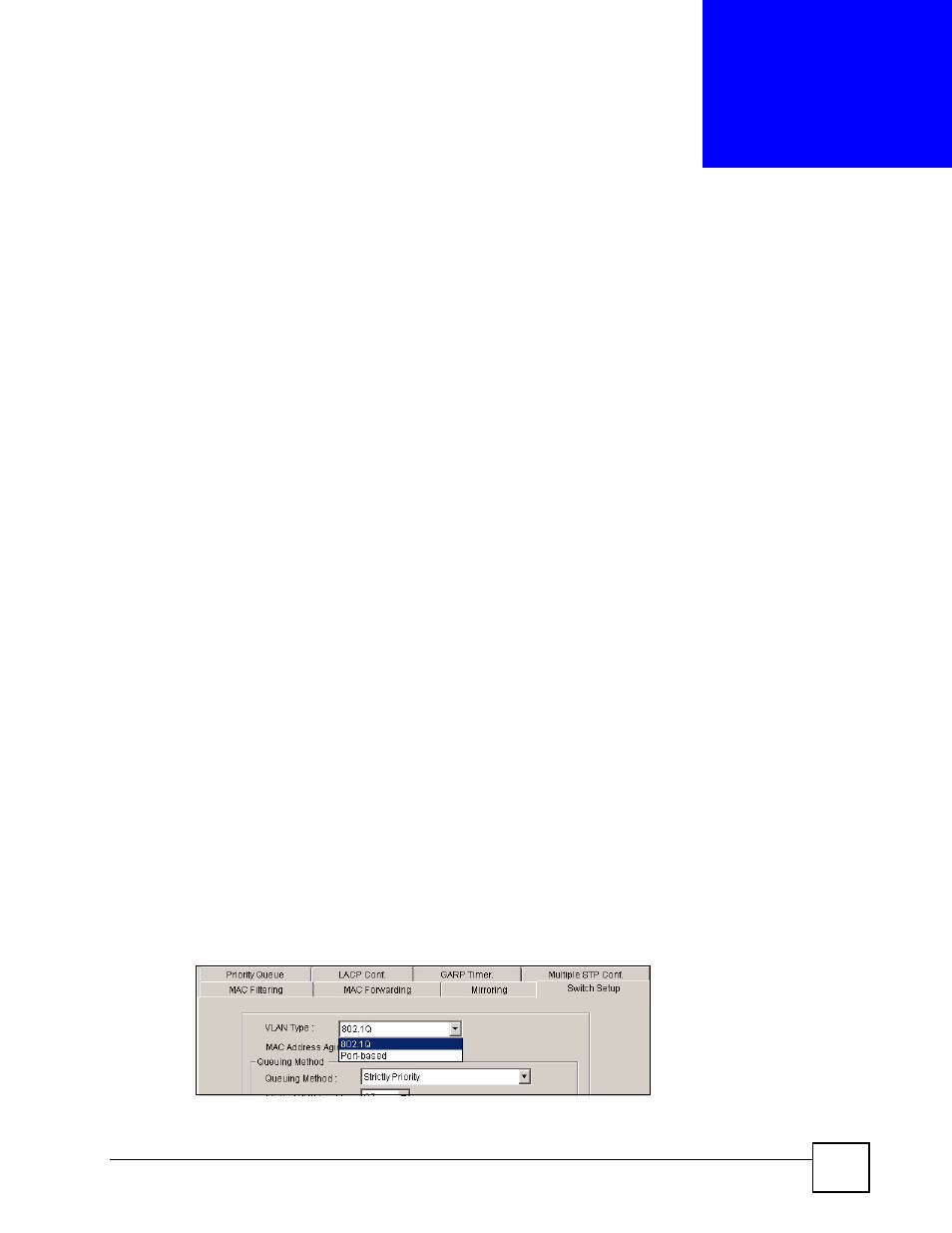
15.2 Configuring 802.1Q VLAN
Follow the steps below to set the 802.1Q VLAN Type on the switch.
1 In the Device Panel list, select a device and then right-click.
2 Click Configuration > Switch Configuration > Switch Setup.
3 Select 802.1Q as the VLAN Type and then click Apply.
Figure 110 Selecting a VLAN Type
4 Click Configuration > VLAN Configuration to display the configuration screen.
