Principle of operation – Toshiba Tohsiba Electromagnetic Flowmeter Converter L5232 User Manual
Page 164
6F8A0917
- 163 -
14. Principle of Operation
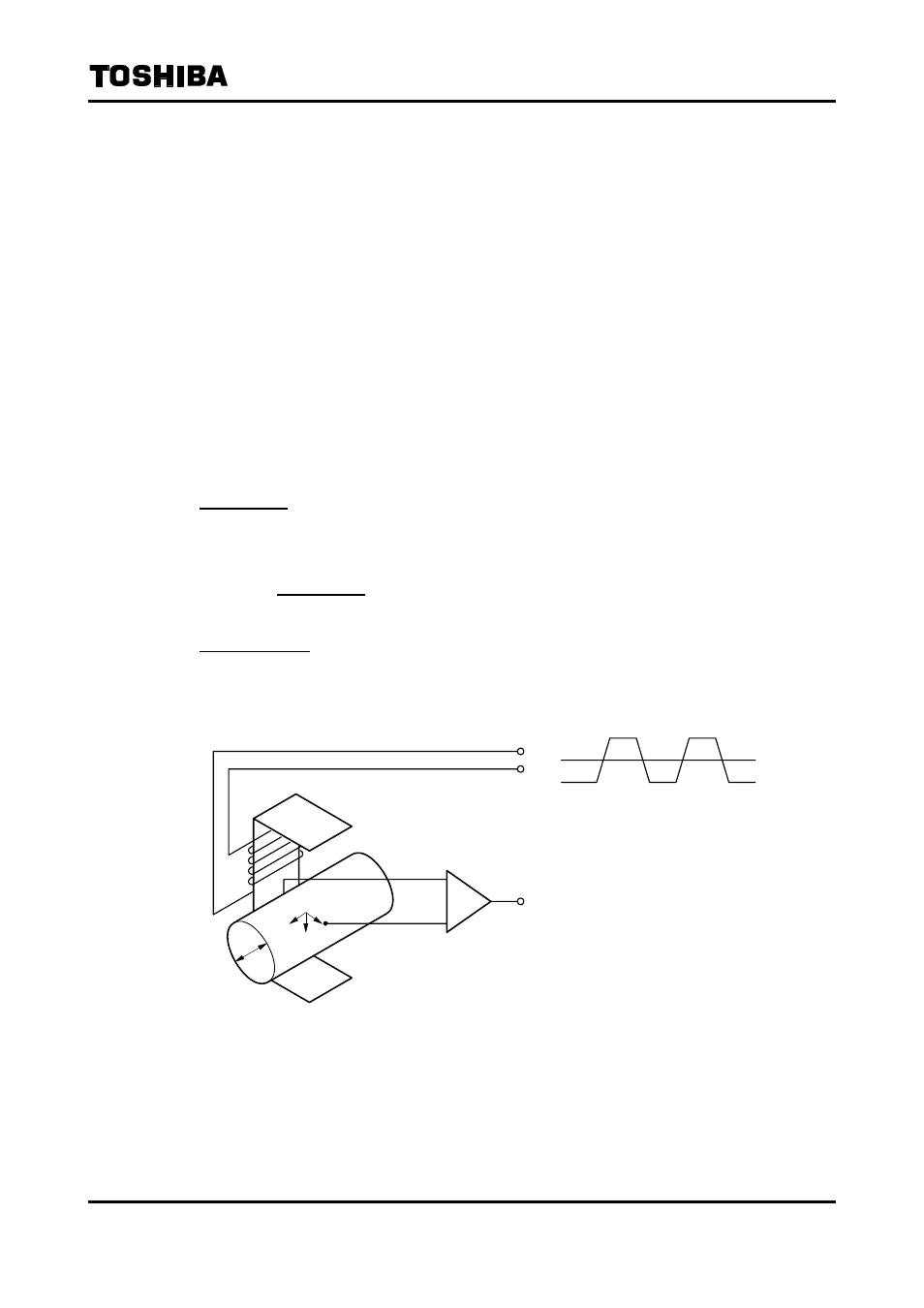
The operating principle of the electromagnetic flowmeter is based on Faraday's Law of
electromagnetic induction. The principle of operation is that an insulated pipe with inner diameter D is
placed vertically to the direction of a magnetic field with flux density B (see Figure 14.1). When an
electrically conductive fluid flows in the pipe, an electromotive force signal E is induced between a
pair of electrodes placed at right angles to the direction of magnetic field. The electromotive force
signal E is directly proportional to the average fluid velocity V and this voltage signal is detected.
The following expression is applicable to the voltage.
E = K × B × D × V [V] ····································· (Eq. 14.1) E: Electromotive force signal [V]
K: Constant
B: Magnetic flux density [T]
D: Meter pipe inner diameter [m]
V: Fluid velocity [m/s]
Volumetric flow rate Q [m
3
/s] of fluid is:
π × D
2
Q =
4
× V ··········································(Eq. 14.2)
Thus, we can obtain the equation below using Eq.14.1 and Eq.14.2,
4
E = K × B × D
π × D
2
× Q
4 × K × B
E =
π × D
× Q·····································(Eq. 14.3)
Therefore, the electromotive force signal E proportional to the flow rate can be obtained.
D
E
V
B
Square-Wave Excitation Method
Figure 14.1 Principle of Operation
The LF232 electromagnetic flowmeter converter uses the square-wave excitation method, which
provides long-term stable operations without being affected by electrostatic and electromagnetic
interferences.
