Syntax, Usage – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 82
72
Parallel I/O Models
Syntax
IO_0 parallel slave | slave_b | master
io-object-name
;
IO_0
Parallel input/output requires eleven pins and must specify pin IO_0. Table
29 shows how the pins are used.
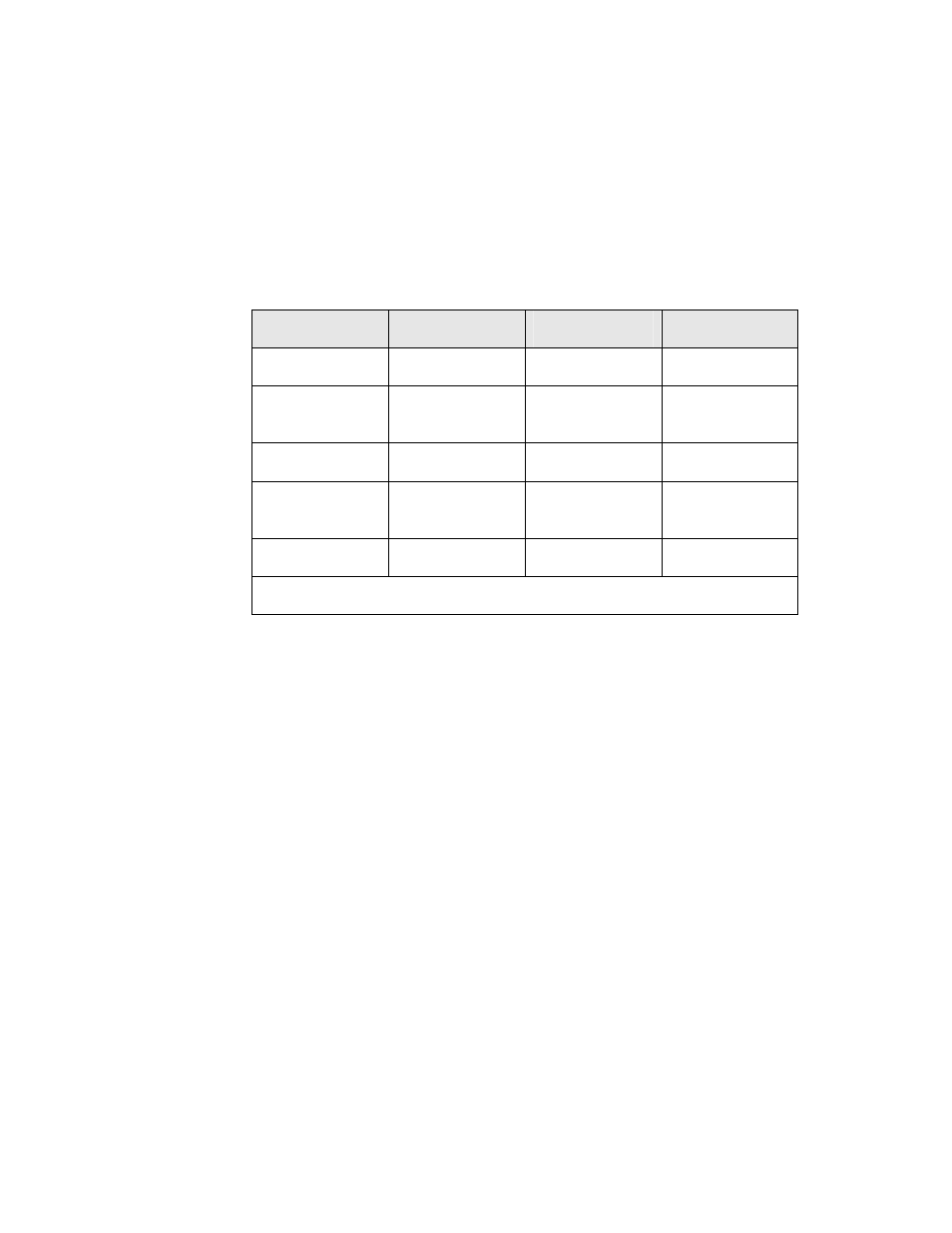
Table 29. Pins for Parallel I/O Object
Pin
Master
Slave A
Slave B
IO_0 thru IO_7
Data Bus
Data Bus
Data Bus
IO_8 Chip
select
output
Chip select
input
Chip select
input
IO_9
RD/~WR output RD/~WR input
RD/~WR input
IO_10 HANDSHAKE
input
HANDSHAKE
input
A0 input
IO_11 N/A N/A IRQ
Note: IO_11 as IRQ is only available for Series 5000 devices.
slave | slave_b | master
Specifies slave A, slave B, or master mode. For master and slave A modes,
IO_10 is a handshake signal. For slave B mode, IO_10 becomes an address
line input, A0, and the handshake signal appears on the data bus on pin IO_0
when A0=1. When A0=0, the data appears on the data bus. This mode is
used to allow a Neuron Chip or Smart Transceiver to reside on a
microprocessor bus with the data at one address location and the handshake
signal at another.
io-object-name
A user-specified name for the I/O object, in the ANSI C format for variable
identifiers.
Usage
struct parallel_io_interface {
unsigned int length;
unsigned int data[
data-size
];
} piofc
;
io_in(
io-object-name
, &piofc);
io_request(
io-object-name
);
io_out(
io-object-name
, &piofc);
