Neurowire slave mode – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 104
94
Serial I/O Models
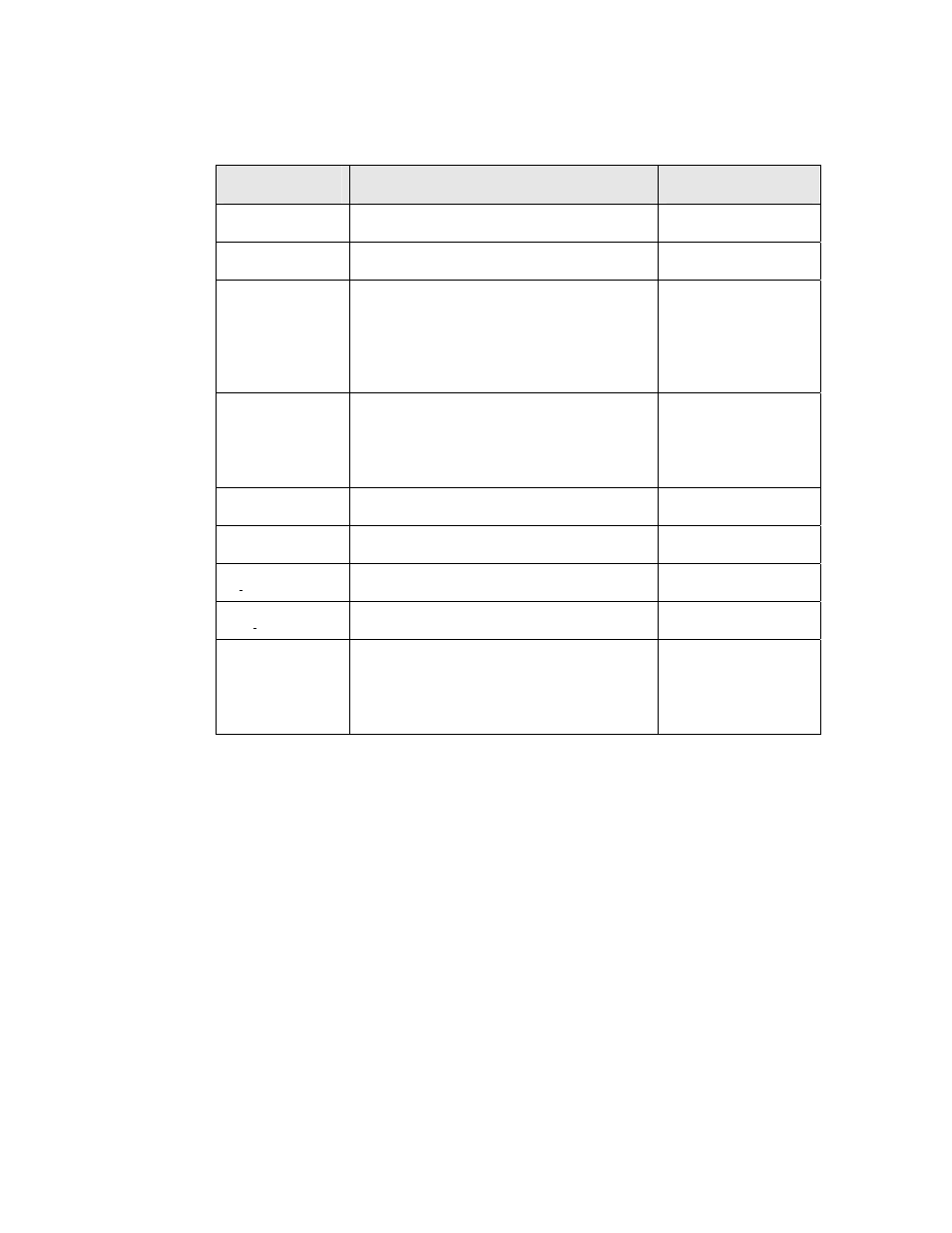
Table 35. Neurowire Master Output Latency Values for Series 3100 Devices
Symbol
Description
Typical at 10 MHz
t
fin
Function call to CS~ active
69.9 μs
t
ret
Return from function
7.2 μs
t
hold
Active clock edge to sampling of input
data
20 kbps bit rate
10 kbps bit rate
1 kbps bit rate
11.4 μs
53.4 μs
960.6 μs
t
high
Period, clock high (active clock edge = 1)
20 kbps bit rate
10 kbps bit rate
1 kbps bit rate
25.8 μs
67.8 μs
975.0 μs
t
low
Period, clock low (active clock edge = 1)
33.0 μs
t
setup
Data output stable to active clock edge
5.4 μs
t
cs clock
Select active to first active clock edge
91.2 μs
t
clock cs
Last clock transition to select inactive
81.6 μs
f
Clock frequency = 1/(t
high
+ t
low
)
20 kbps bit rate
10 kbps bit rate
1 kbps bit rate
17.0 kHz
9.92 kHz
992 Hz
Neurowire Slave Mode
In Neurowire slave mode, pin IO8 is the clock (driven by the external master),
IO9 is the serial data output, and IO10 is the serial data input. Serial data is
clocked out on pin IO9 at the same time as data is clocked in from pin IO10.
Data is clocked by the rising edge of the clock signal (default), which can be up to
18 kbps for a Series 3100 device at 10 MHz. This data rate scales with Smart
Transceiver input clock rate. One of the IO0 – IO7 pins can be designated as a
timeout pin. A logic 1 level on the timeout pin causes the Neurowire slave I/O
operation to be terminated before the specified number of bits has been
transferred. This prevents the Smart Transceiver watchdog timer from resetting
the chip in the event that fewer than the requested number of bits are
transferred by the external clock.
