Programming considerations, Syntax – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 124
114
Serial I/O Models
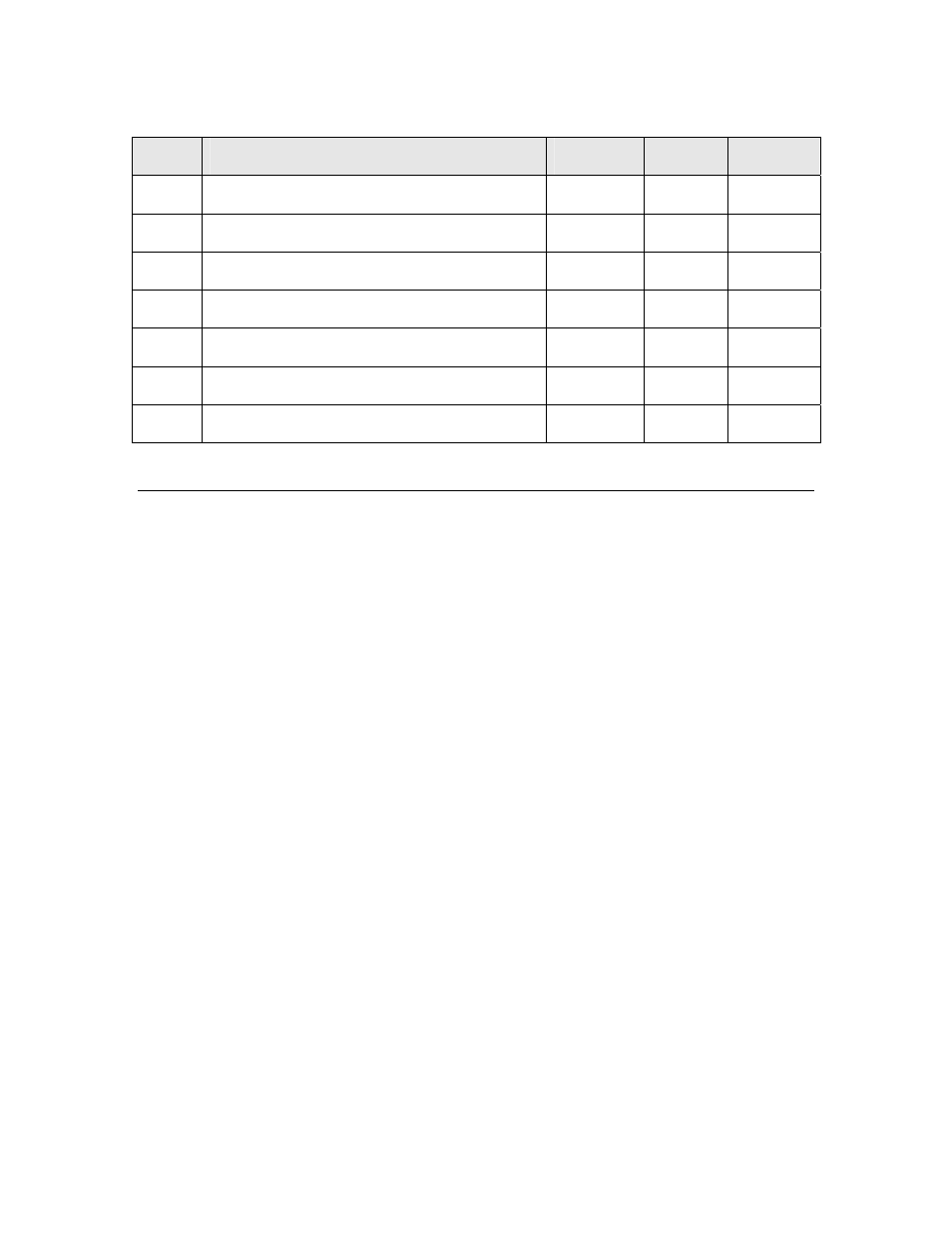
Table 45. SPI Slave Mode I/O Latency Values for Series 3100 Devices
Symbol Description
Minimum
Typical
Maximum
T
ck
Clock cycle (user specified)
—
—
1.25
T
sc
Select low to Clock transition
220 μs — —
T
doc
Data out to Clock (1st bit of invert mode)
440 ns
—
—
T
cdo
Clock to data out
—
—
45 ns
T
dis
Data in setup
10 ns
—
—
T
dih
Data in hold
10 ns
—
—
T
sdz
Select high to data in high impedance
—
—
220 ns
Programming Considerations
You can enable and disable SPI interrupts. For example, you can turn off
interrupts when going offline, or to assure that other time-critical application
functions are not disturbed by background interrupts. The SCI interrupt signal
is used by the firmware driver for the SCI I/O model. It is not directly accessible
by the application program.
The SPI interrupt is enabled by default. For Series 3100 devices, the io_idis()
function disables I/O interrupts. The function has the following signature:
void io_idis(void);
For Series 3100 devices, the io_iena() function enables I/O interrupts. The
function has the following signature:
void io_iena(void);
For Series 5000 devices, you cannot disable the SPI interrupt.
To cancel an SPI operation currently in progress, use the spi_abort() function
rather than disabling interrupts.
Syntax
IO_8 spi master|slave [select(IO_7)] [clock(
const-expr
)] [invert]
[clockedge(+|-)] [neurowire]
io-object-name
;
master|slave
Determines whether the hardware is in master or slave mode. When using a
Neuron C device in SPI master mode, no other masters can be used in the
same bus.
