Programming considerations – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 110
100
Serial I/O Models
START
START
ST
OP
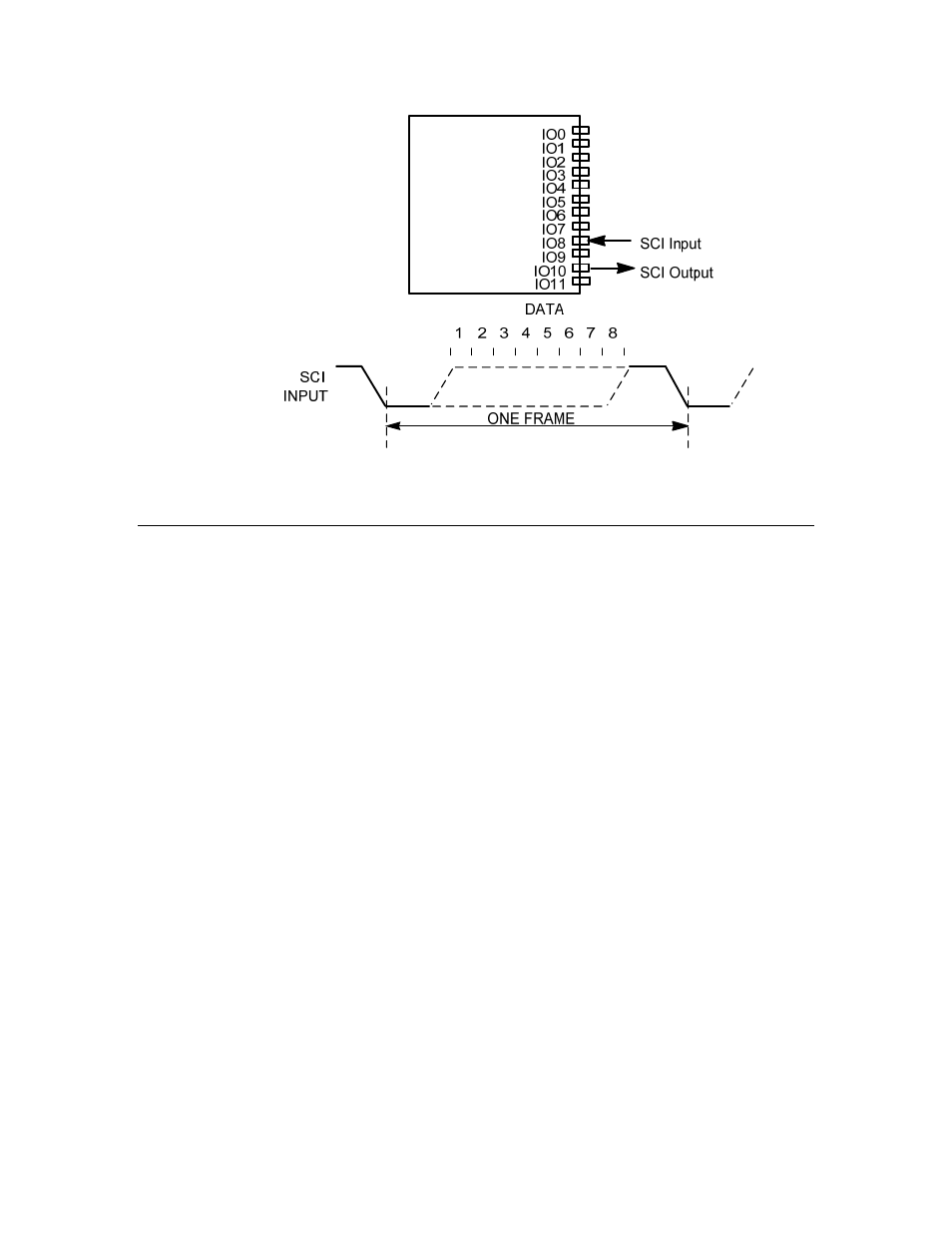
Figure 36. SCI I/O and Timing
Programming Considerations
You can enable and disable SCI interrupts. For example, you can turn off
interrupts when going offline, or to assure that other time-critical application
functions are not disturbed by SCI interrupts. The SCI interrupt signal is used
by the firmware driver for the SCI I/O object. It is not directly accessible by the
application program.
The SCI interrupt is enabled by default. For Series 3100 devices, the io_idis()
function disables I/O interrupts. The function has the following signature:
void io_idis(void);
For Series 3100 devices, the io_iena() function enables I/O interrupts. The
function has the following signature:
void io_iena(void);
For Series 5000 devices, you cannot disable the SCI interrupt.
To cancel an SCI operation currently in progress, use the sci_abort() function
rather than disabling interrupts.
When using hardware SCI I/O, the Neuron C application must specify the clock
frequency that drives the on-chip SCI UART. To specify this frequency, the I/O
clock rate, use the following compiler directive:
#pragma specify_io_clock
clock-rate
The
clock-rate
value must be one of the following quoted strings: “20 MHz”, “10
MHz”, “6.5536 MHz”, “5 MHz”, or “2.5 MHz”. If the pragma-specified clock rate
does not match the Series 3100 physical clock frequency or the Series 5000
system clock rate, the Neuron Exporter component of the NodeBuilder FX
Development Tool reports an error to prevent generation of an incorrect
communications bit rate.
