Programming considerations, Syntax, Usage – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 47: Byte input example
I/O Model Reference
37
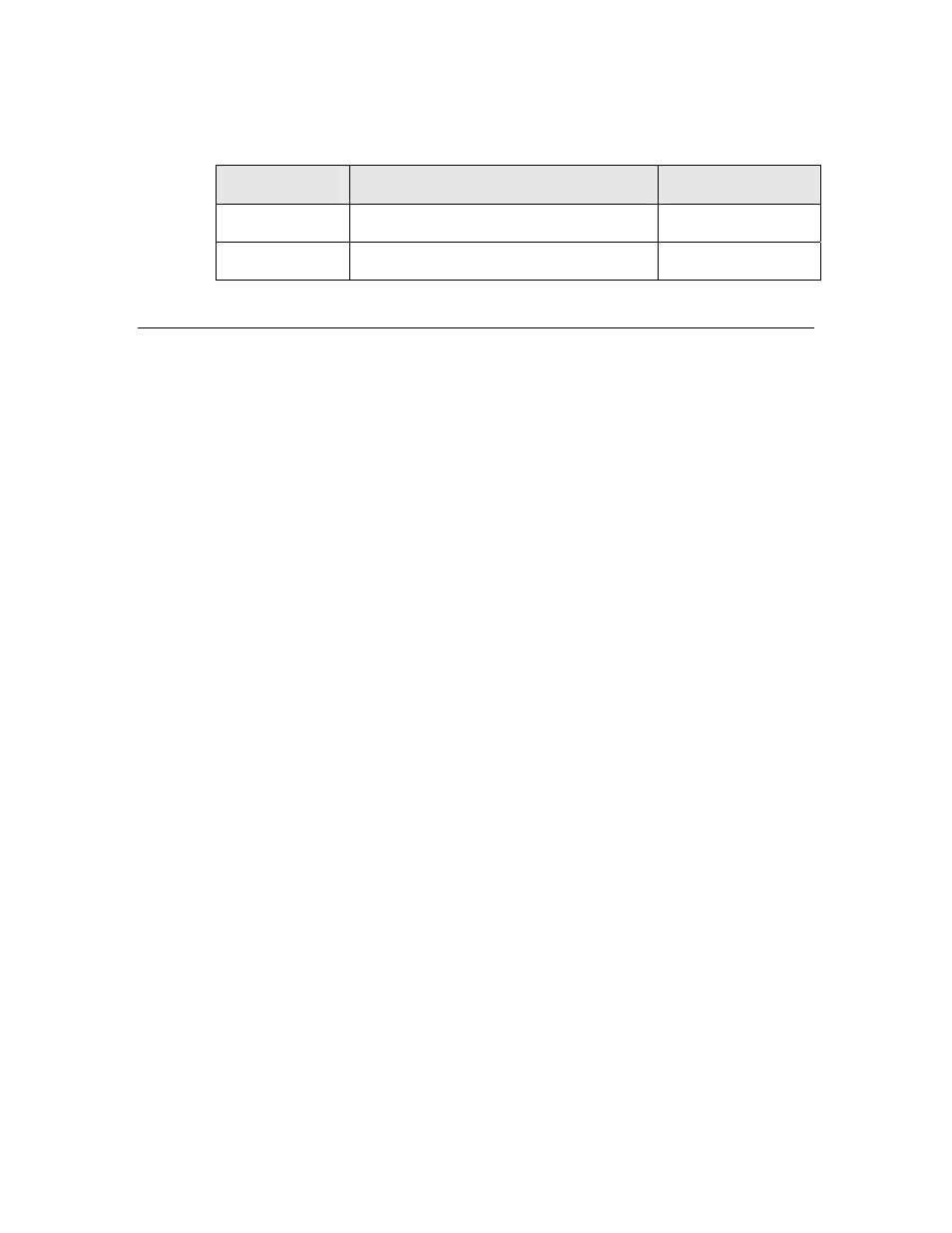
Table 14. Byte Output Latency Values for Series 3100 Devices
Symbol
Description
Typical at 10 MHz
t
fout
Function call to update
57 μs
t
ret
Return from function
5 μs
Programming Considerations
For byte input/output, the data type of the return value for io_in( ), and the data
type of the output value for io_out( ), is an unsigned short.
Syntax
IO_0 input byte
io-object-name
;
IO_0 output byte
io-object-name
[=
initial-output-level
];
IO_0
Specifies pin IO_0 as the least significant bit of the byte. Byte input/output
uses pins IO_0 through IO_7. The pin specification denotes the lowest
numbered pin of the set and must be IO_0.
io-object-name
A user-specified name for the I/O object, in the ANSI C format for variable
identifiers.
initial-output-level
A constant expression, in ANSI C format for initializers, used to set the state
of the output pin of the I/O object at initialization. The initial state can be
from 0 to 255. The default is 0.
Usage
unsigned int
input-value
;
unsigned int
output-value
;
input-value
= io_in(
io-object-name
);
io_out(
io-object-name
,
output-value
);
Byte Input Example
IO_0 input byte ioKeyboard;
unsigned int character;
...
when (reset) {
io_change_init(ioKeyboard);
