Programming considerations, Syntax – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 44
34
Direct I/O Models
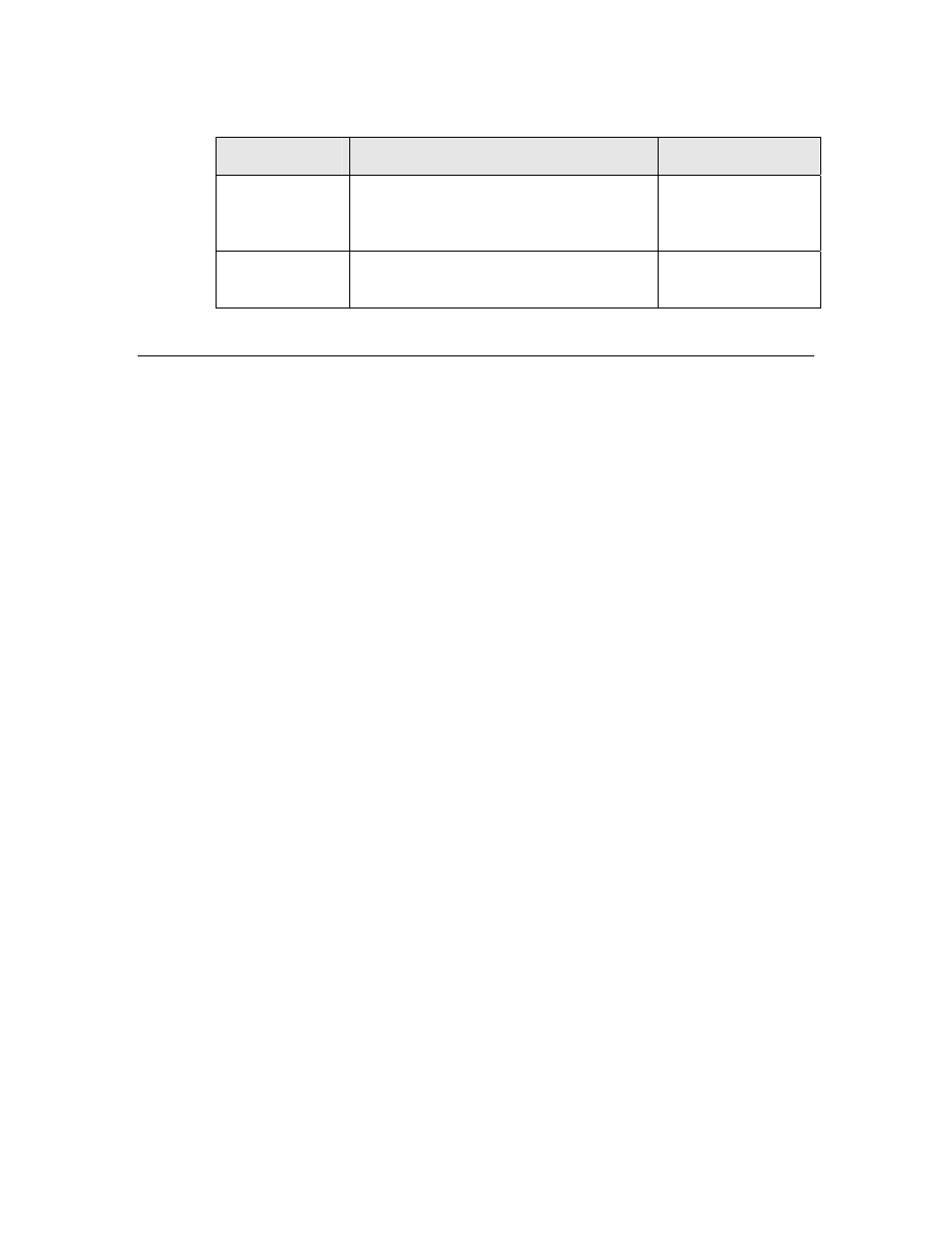
Table 12. Bit Output Latency Values for Series 3100 Devices
Symbol
Description
Typical at 10 MHz
t
fout
Function call to update
IO3 – IO5, IO11
All others
69 μs
60 μs
t
ret
Return from function
IO0 – IO11
5 μs
Programming Considerations
For bit input, the data type of the return value for io_in( ) is an unsigned short.
For bit output, the output value is treated as a Boolean value, so any non-zero
value is treated as a 1.
The bit input and output models are both direct I/O models. Thus, bit input
objects are sampled at the time of the io_in() call, and bit output objects are
driven at the time of the io_out() call.
Although this I/O model is suitable for many simple use-cases, such as driving an
LED or a single relay, many control applications require a synchronized reading
and writing of various bit input and output devices. Applications that require a
synchronized process image should consider using the byte or nibble models
instead.
For Series 3100 devices, add a #pragma enable_io_pullups directive to enable the
Neuron Chip or Smart Transceiver's built-in pull-up resistors on pins IO4
through IO7 and IO11.
IO11 is only available on PL 3120, PL 3150, PL 3170, and Series 5000 chips.
Syntax
pin
input bit
io-object-name
;
pin
output bit
io-object-name
[=
initial-output-level
];
pin
Specifies one of the twelve I/O pins, IO_0 through IO_11. Bit input/output
can be used on any pin.
io-object-name
A user-specified name for the I/O object, in the ANSI C format for variable
identifiers.
initial-output-level
A constant expression, in ANSI C format for initializers, used to set the state
of the output pin of the I/O object at initialization. The initial state can be 0
or 1. The default is 0.
