Programming considerations, Neuron c resources – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 141
I/O Model Reference
131
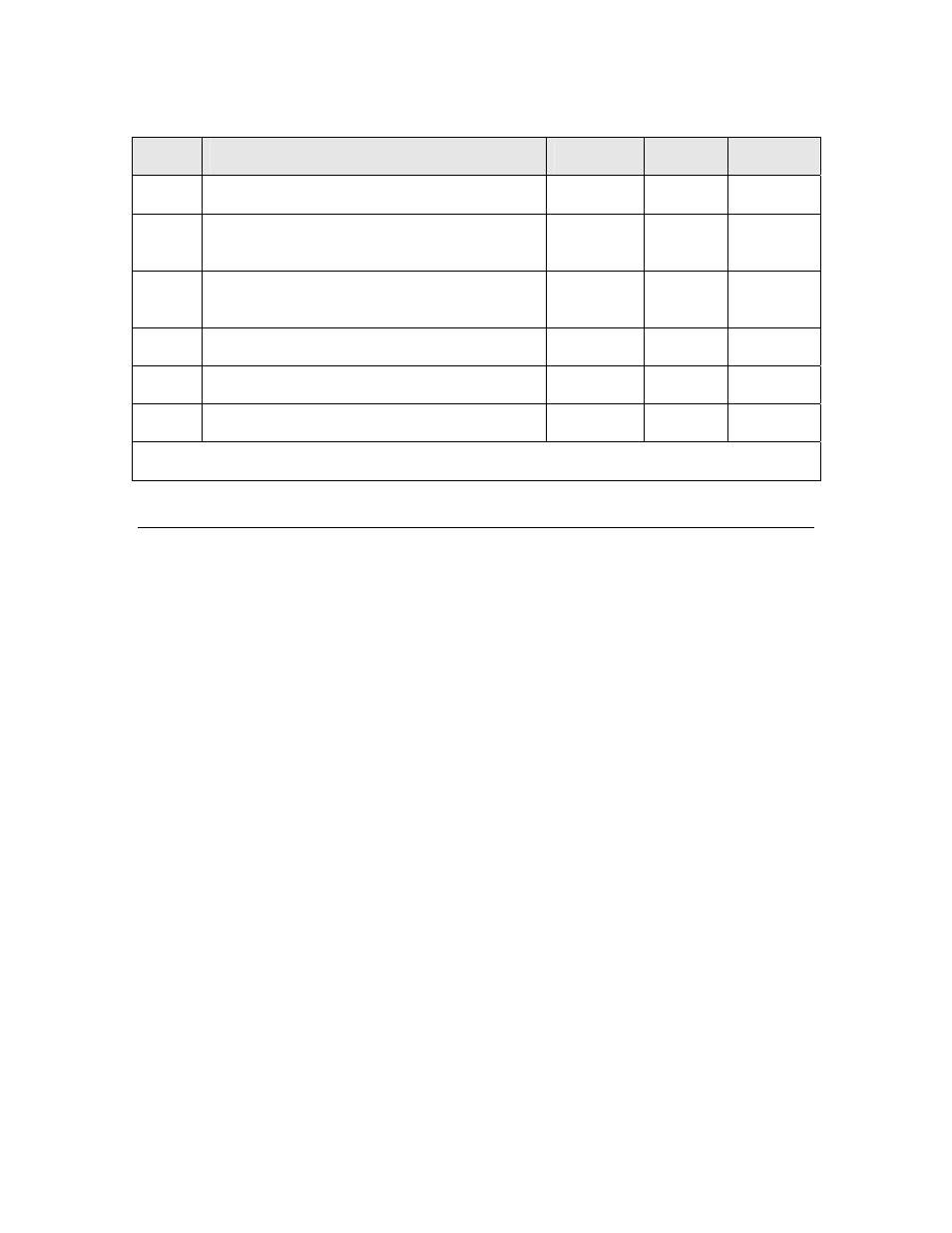
Table 50. Edgelog Input Latency Values for Series 3100 Devices
Symbol Description
Minimum
Typical
Maximum
t
setup
Input data setup
0
—
—
t
win
Input
pulse
width
1
T/C clk
—
65534
T/C
clks
t
hold
io_in() call to data input edge for inclusion of
that pulse
26.4 μs —
—
t
wtcp
Two consecutive pulse widths
104 μs — —
t
oret
Return
on
overflow
—
42.6
μs —
t
ret
Return on count termination
—
49.6 μs —
Note:
T/C clk
represents the period of the clock used during the declaration of the I/O object.
Programming Considerations
For edgelog input, the io_in( ) function requires a pointer to a data buffer, into
which the series of unsigned long values are stored, and a count argument, which
controls the number of values to be stored. The values stored represent the units
of clock period between input signal edges, rising or falling. The io_in( ) function
returns an unsigned short int that contains the actual number of edge-to-edge
periods stored. No input events are associated with an edgelog input object.
During the io_in( ) function call, the measurement process stops whenever the
maximum period is exceeded. In this case, the value returned will not be equal to
the count argument passed.
If a preload value is specified, it must be added to the value returned by io_in( ).
The resulting addition may cause an overflow, but this is normal.
This I/O model uses both of the Neuron timer/counters.
Neuron C Resources
The following functions are provided specifically for use with the edgelog I/O
object:
• io_edgelog_preload( )
Changes the maximum value for each period measurement. The maximum
value may range from 1 to 65535; the default value is 65535. This function is
only used for an edgelog device that is
not
declared with the single_tc option
keyword.
• io_edgelog_single_preload( )
