Series 5000 resolution and range – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 199
I/O Model Reference
189
7 25.6
μs 1678
ms
51.2
μs
3355 ms
To Calculate for Other Clock Rates:
• Resolution =
InputClock
n
t
ClockSelec
)
(
2
+
ClockSelect
= 0..7
n
= 1 for dualslope, edgelog, oneshot output, ontime, period input,
and triac output
n
= 2 for frequency output
InputClock
in MHz
Resolution
in seconds
• Maximum Range = 65535 x
Resolution
Resolution
in seconds
Maximum Range
in seconds
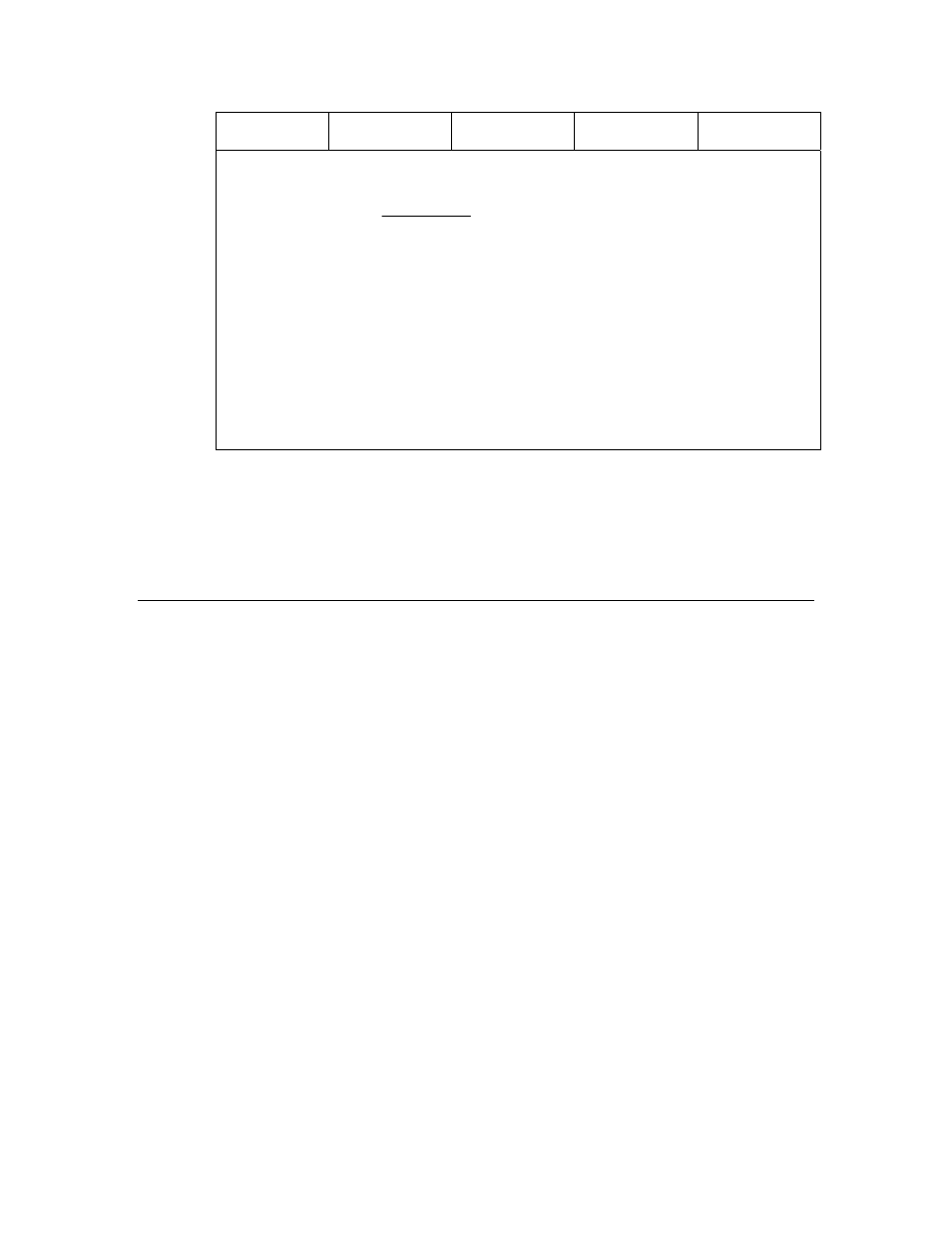
For each of the timer/counter I/O models, the range and resolution in Table 66
should be read as:
• Range of 13.1 ms in steps of 0.2 μs
• Range of 26.2 ms in steps of 0.4 μs
• And so on
Series 5000 Resolution and Range
For dualslope input, edgelog input, ontime input, and period input, and infrared
input, the timer/counter returns a value (or a table of values, in the case of
edgelog input) in the range 0 to 65535, representing elapsed times from 0 up to
the maximum range given in Table 67 on page 190.
For oneshot output, frequency output, and triac output, the timer/counter can be
programmed with a number in the range 0 to 65535. This number represents the
waveform ontime for oneshot output, the waveform period for frequency output,
and the control period from sync input to pulse/level output for the triac output.
The clock select value is specified with the clock keyword in the declaration of the
I/O object in the Neuron C application program, and can be modified at runtime
by using the io_set_clock() function.
The resolution and range values in Table 67 apply to all system clock settings,
that is, they do not scale with changes to the system clock.
If you specify an alternate clock value (using the io_set_clock() function with a
TCCLK_* macro value) that is lower than your device’s system clock setting, the
resolution and range values reflect the expected values specified in Table 67.
However, you cannot specify a value that defines a clock rate that is higher than
one-half of the device’s system clock. For example, if your system clock rate is 20
MHz, you can specify any TCCLK_* macro that defines a 10 MHz or lower clock
rate (that is, you cannot specify TCCLK_40MHz or TCCLK_20MHz – no error is
issued, but the effective value used in this case is TCCLK_10MHz).
