Programming considerations – Echelon I/O Model Reference for Smart Transceivers and Neuron Chips User Manual
Page 187
I/O Model Reference
177
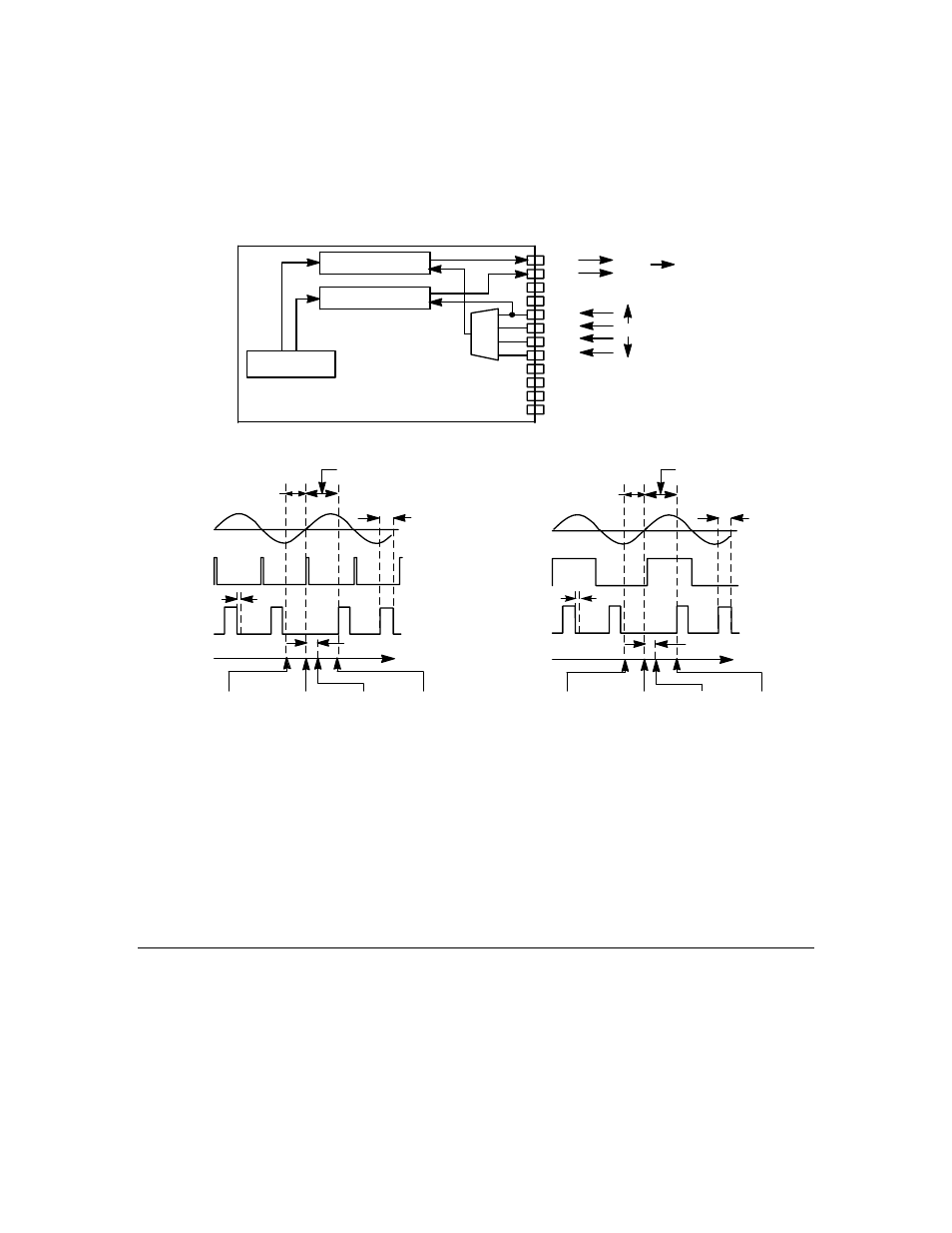
The output gate pulse is asserted after the control period and is deasserted at or
near the next sync input point. Although the input trigger signal (zero crossing)
is asynchronous relative to the internal clock, there is minimal jitter, t
jit
,
associated with the output gate pulse.
The actual active edge of the sync input and the triac gate output can be set by
using the clockedge or invert parameters, respectively.
trigger
output
Timer/Counter 1
Timer/Counter 2
sync
IO0
IO1
IO2
IO3
IO4
IO5
IO6
IO7
mux
to
triac
gate
from
zero
crossing
detector
IO10
IO9
IO8
t
ret
END OF
io_out()
t
gpw
NEW
GATE-PULSE
DELAY
FIRST GATE
PULSE WITH
NEW DELAY
HARDWARE
UPDATED
START
OF
io_out()
TIME
(OUTPUT)
ZERO
CROSSING
DETECTOR
AC
INPUT
CLOCK EDGE
(+)
t
ret
END OF
io_out()
NEW
GATE-PULSE
DELAY
FIRST GATE
PULSE WITH
NEW DELAY
HARDWARE
UPDATED
START
OF
io_out()
TIME
TRIAC GATE
(OUTPUT)
ZERO
CROSSING
DETECTOR
AC
INPUT
CLOCK EDGE
(+-)
t
jit
IO11
t
fout
t
jit
t
gpw
t
fout
TRIAC GATE
System Clock
Divide Chain
Figure 67. Stretched Triac Output and Timing
The hardware update does not happen until the occurrence of an external active
sync clock edge. The internal timer is then enabled, and a triac gate pulse is
generated after the user-defined period has elapsed. This sequence is repeated
indefinitely until another update is made to the triac gate pulse delay value.
t
fout
(min) refers to the delay from the initiation of the function call to the first
sampling of the sync input. In the absence of an active sync clock edge, the input
is repeatedly sampled for 10 ms (1/2 wave of a 50 Hz line cycle time), t
fout
(max),
during which the application processor is suspended.
Programming Considerations
Execution of this I/O object type is synchronized with the sync pin input and
might not return for up to 10 ms. That is, the application program could be
delayed for as long as 10 ms. Because of this synchronization, the frequency of
the sync pin input (and the frequency of the AC circuit being controlled) is
limited to the 50-60 Hz range.
