1 read operation, 1 scanning method – KEYENCE BL-600 Series User Manual
Page 96
Chapter 6 Functions for Reading Operation
86
6
6.1
Read Operation
This section describes the scanning methods of the BL-600 Series.
6.1.1 Scanning method
There are two methods to trigger the BL-600 Series to read bar codes: the “Level
signal” method and the “One-shot signal” method. Select an appropriate method
according to the application. Typically, the “Level signal” method is used.
The following examples for these two methods use the “6.2.1 Single label read
mode”.
➮ See page 88.
Level signal trigger
When the trigger input turns on, the BL-600 Series starts laser emission to read the
bar codes. The laser turns off after the number of the bar code reading reaches the
specified decoding match count.
➮ See page 43.
The BL-600 Series then sends the
read data.
Reference 1: The BL-600 Series can read up to 4 types of bar codes without
changing settings.
➮ See page 49.
Reference 2: Pressing the TEST switch lightly (for less than 2 seconds) serves as
a trigger input (The laser turns on once.).
➮ See page 8.
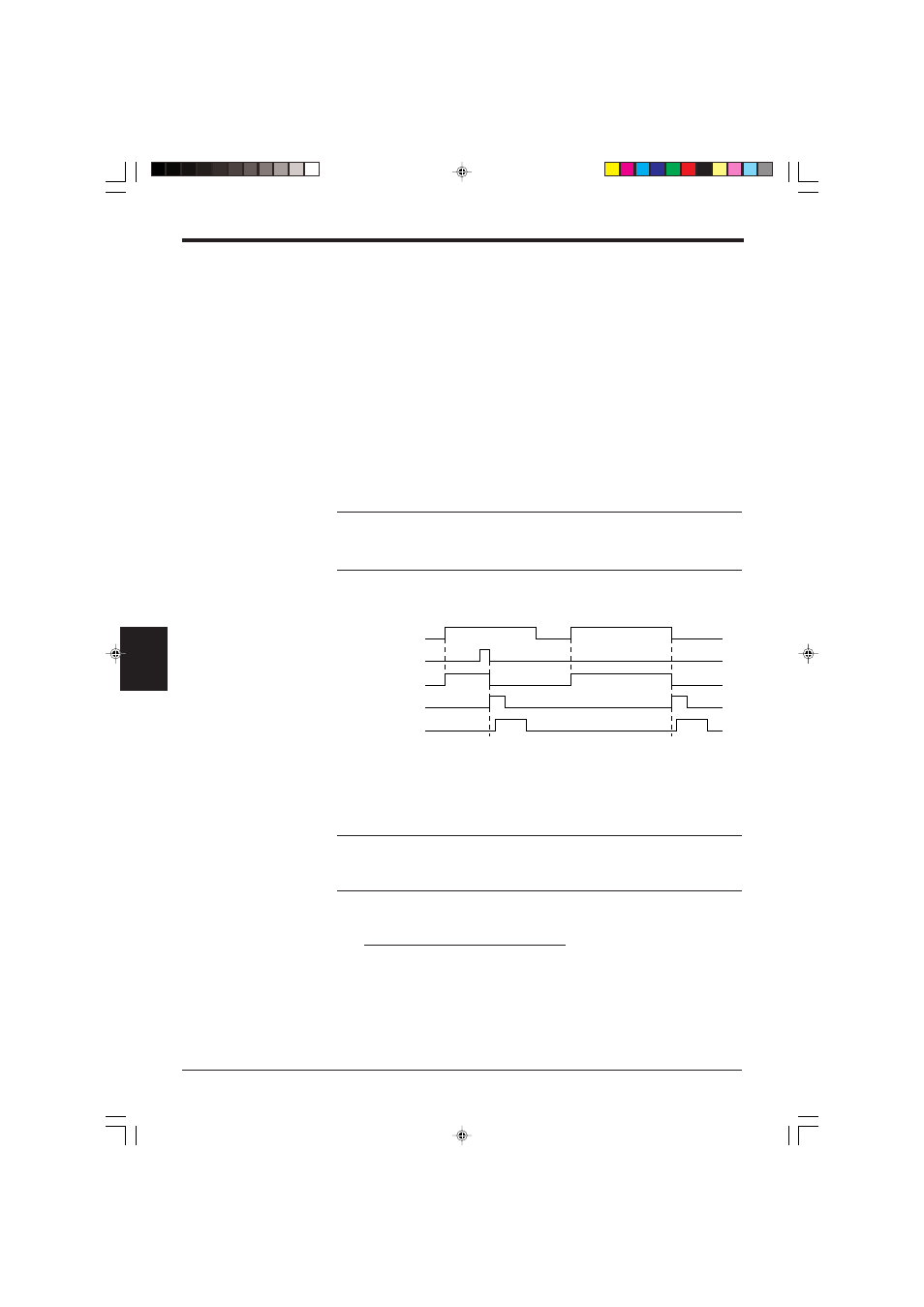
■ Timing diagram
*1 Set trigger input so that it stays on long enough for the laser beam to cover the
entire bar code.
*2 The BL-600 Series emits a laser after the trigger input exceeds the preset input
time.
➮ See the following note.
Note: The BL-600 Series has a built-in AGC (auto gain control) circuit. It requires a
maximum of 3 scans (6 ms) to adjust the gain. Therefore, the BL-600 Series
requires a maximum of 6 ms after the laser beam turns on before it begins to read
the data.
*3 The communication time can be obtained from the following expression:
*4 The length of time that the OK/NG output is on can be changed to any value
between the range of 10 ms to 2.55 s.
➮ See page 53.
*5 The OK/NG output turns on 5 ms after the bar code is read.
If the bar code cannot be read, the NG output is delayed by 5 ms plus the
specified input time.
Trigger input
Bar code
Laser beams
Communication time
OK/NG output
OK/NG
NG
*2
*1
*3
*4
*5
(Code length of data to be
sent + Header/number of
characters in delimiter)
X
Data bits + (1: If parity is used) + Start/stop bit
Baud rate
