Figure 42: vlan access overview, 42 vlan access overview – HP StorageWorks IP Storage Router User Manual
Page 76
Software Overview
76
IP Storage Router SR2122-2 User Guide
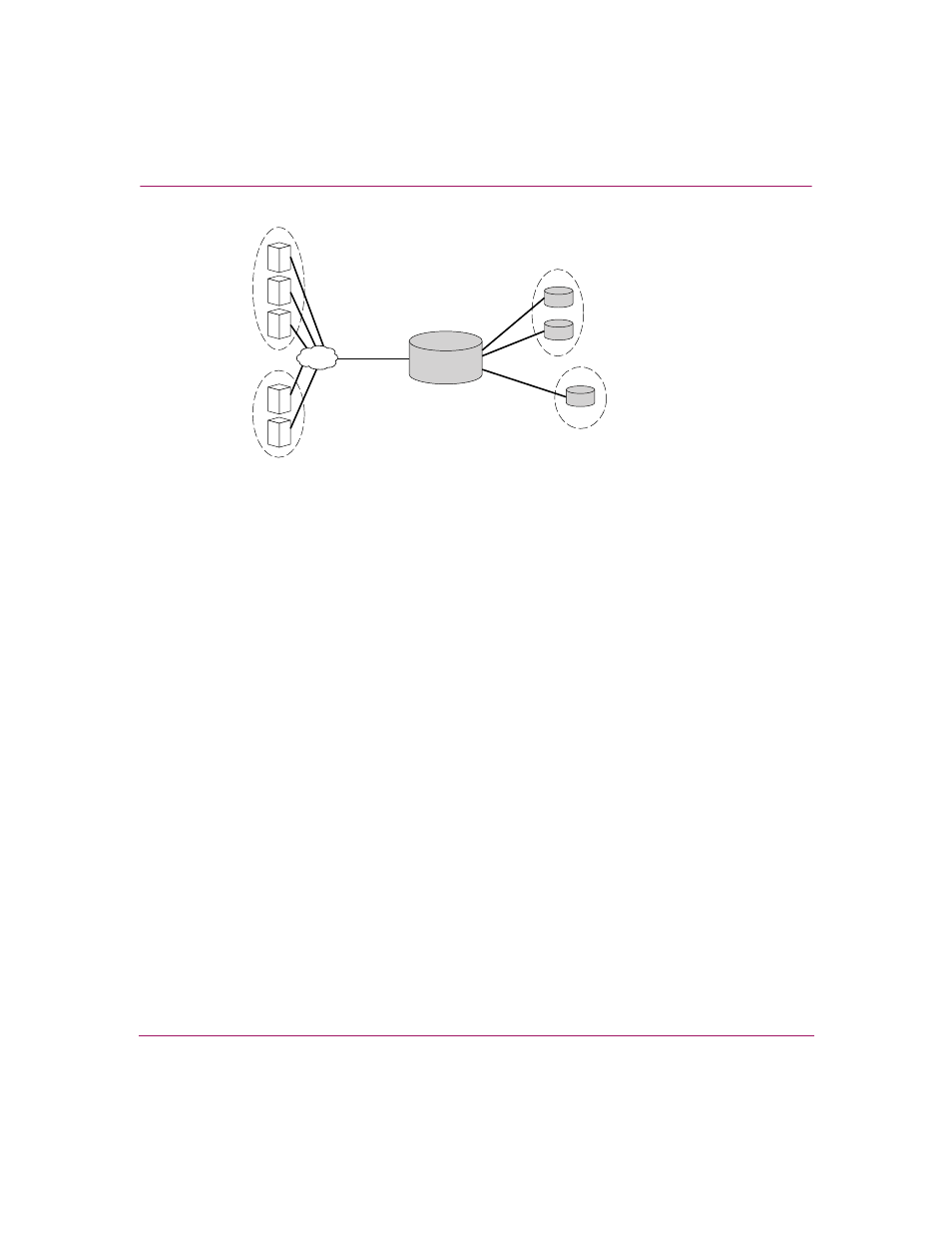
Figure 42: VLAN access overview
If the storage router is used in a switched network environment, configure the
storage router using the proprietary VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP). With VTP,
the storage router will exchange VTP packets with an externally attached switch
to dynamically learn about the VLANs that are accessible in the IP network. The
storage router then uses VTP to propagate VLAN information around the
switched network using layer 2 multicast packets.
If the storage router is used in a non-switched network environment, configure the
storage router for VLAN without using VTP. The storage router does not
exchange VTP packets to learn about the VLANs in the network. Instead, you
must manually assign VLANs in the network with a VLAN identifier (VID)
number. You can optionally assign each VLAN with a unique name and manually
set the MTU size.
If the storage router participates in a cluster, the VLAN information configured
for the storage router is propagated to all storage routers in the cluster.
The SR2122-2 uses IEEE 802.1Q standard for VLAN encapsulation. With 802.1Q
encapsulation, VLAN information is carried in packets sent and received through
the storage router Gigabit Ethernet interface. These packets contain the VID and
other VLAN information needed for VLAN members to participate in a VLAN.
A VLAN is granted access to storage devices via a SCSI routing instance
configured in the storage router. The iSCSI targets assigned to the SCSI routing
instance determine which storage devices the VLAN can access.
IP
hp SR2122-2
VLAN 200
VLAN 100
Configured with two SCSI
routing instances named
SR100 and SR200
Storage device accessible by
VLAN 200 via SCSI routing
instance SR200
Storage device accessible by
VLAN 100 via SCSI routing
instance SR100
802.1Q trunk
15038
