Scsi routing overview, Figure 31: scsi routing overview, 31 scsi routing overview – HP StorageWorks IP Storage Router User Manual
Page 61
Software Overview
61
IP Storage Router SR2122-2 User Guide
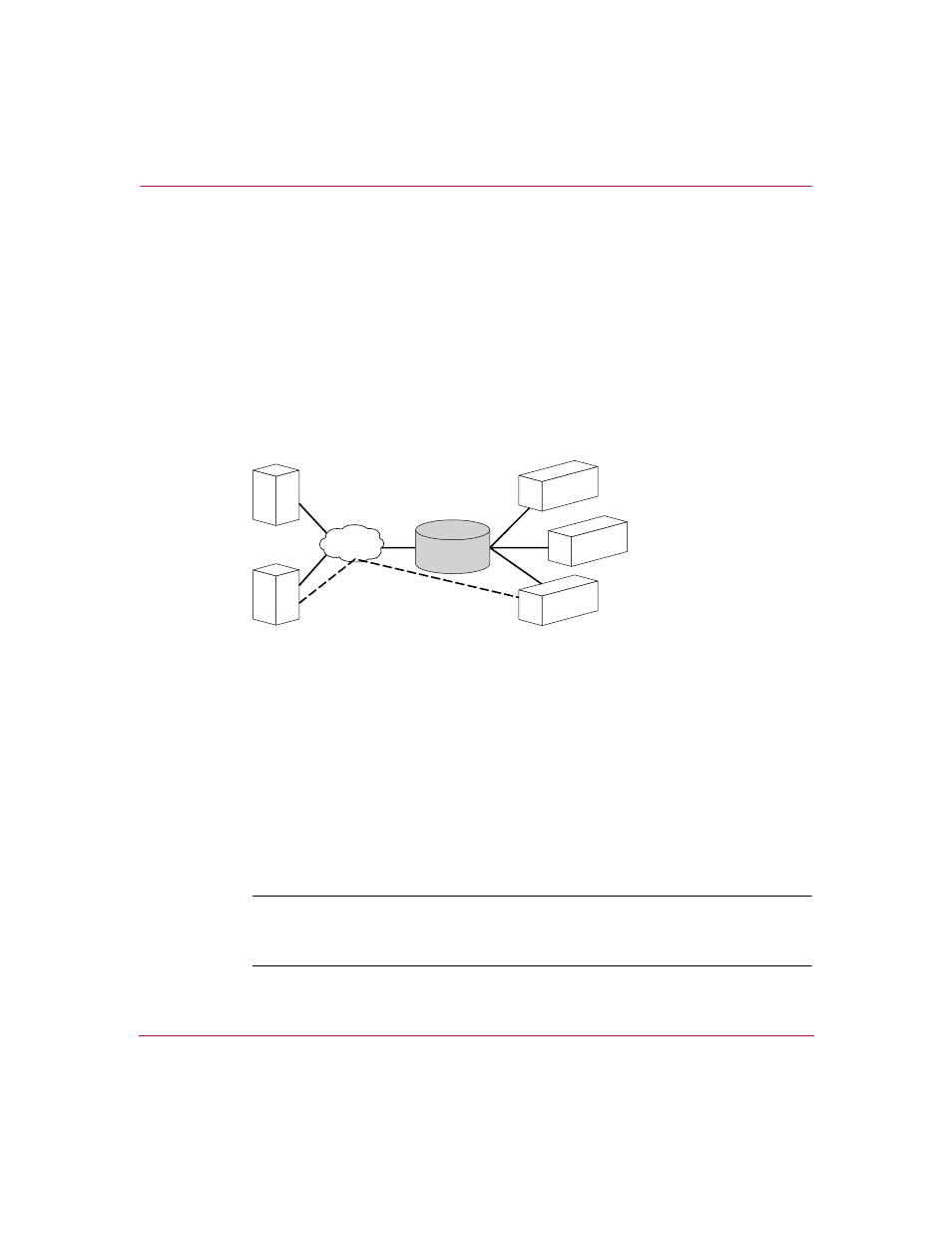
SCSI Routing Overview
SCSI routing provides IP hosts with access to FC storage devices as if the storage
devices were directly attached to the hosts, with access to devices being managed
primarily in the storage router. An iSCSI target (also called logical target) is an
arbitrary name for a group of physical storage devices. The iSCSI targets are
created and mapped to physical storage devices attached to the storage router. The
SR2122-2 presents the iSCSI targets to IP hosts (iSCSI initiators) as if the
physical storage devices were directly attached to the hosts. With SCSI routing,
storage devices are not aware of each IP host; the storage devices are aware of the
storage router and respond to it as if it were one FC host.
Figure 31: SCSI routing overview
To configure an IP Storage Router 2122-2 for SCSI routing, you should have a
basic understanding of the following concepts:
■
Routing SCSI Requests and Responses
■
■
SCSI Routing Mapping and Access Control
■
Available Instances of SCSI Routing
Note:
Along with FC storage, FC host connections and FC switch connections are
allowed; however, most of the illustrations in this manual show only storage connections
for the purpose of describing the storage router features.
IP hosts
IP
HP SR2122-2
An IP host accesses
FC storage as if it
were directly attached
to the storage
FC storage
15021
