Example – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multicast Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 98
86
Multi-Service IronWare Multicast Configuration Guide
53-1003032-02
MSDP Anycast RP
1
NOTE
The anycast RP address *must* not be the IGP router-id.
•
Enable PIM-SM on all interfaces on which multicast routing is desired.
•
Enable an IGP on each of the loopback interfaces and physical interfaces configured for
PIM-SM.
•
Configure loopback interfaces with unique IP addresses on each of the RPs for MSDP peering.
This loopback interface is also used as the MSDP originator-id.
•
The non-RP PIM-SM routers may be configured to use the anycast RP address statically or
dynamically (by the PIMv2 bootstrap mechanism).
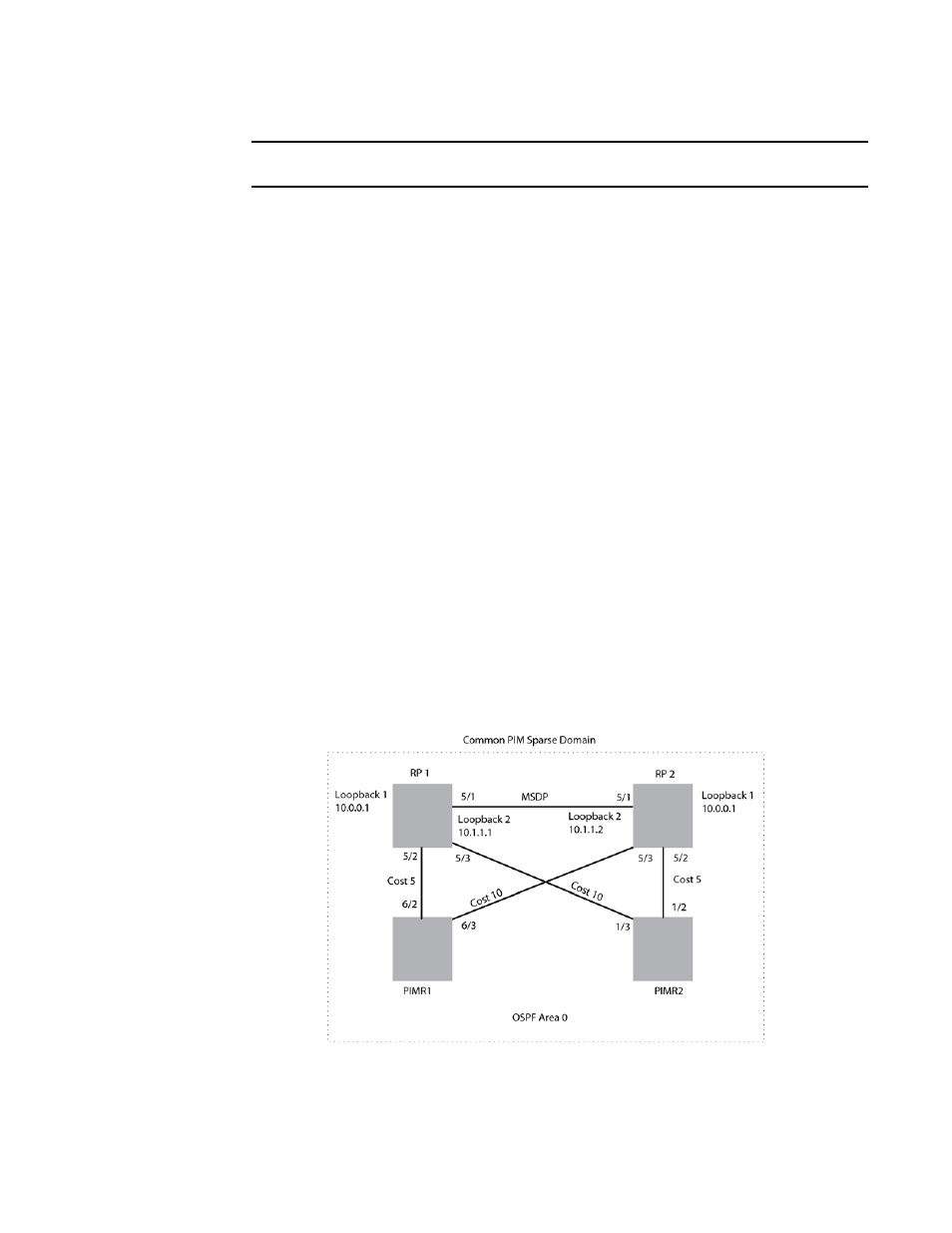
Example
The example shown in
is a simple MSDP Anycast-enabled network with two RPs and two
PIM-SM routers. Loopback 1 in RP 1 and RP 2 have the same IP address. Loopback 2 in RP1 and
Loopback 2 in RP2 have different IP addresses and are configured as MSDP peering IP addresses
in a mesh configuration.
In the PIM configuration for PIM-SM routers PIMR1 and PIMR2 the RP address is configured to be
the anycast RP address that was configured on the Loopback 1 interfaces on RP1 and RP2. OSPF
is configured as the IGP for the network and all of the devices are in OSPF area 0.
Since PIMR1 has a lower cost path to RP1 and PIMR2 has a lower cost path to RP2 they will
register with the respective RPs when both are up and running. This shares the load between the
two RPs. If one of the RPs fails, the higher-cost path to the IP address of Loopback 1 on the RPs is
used to route to the still-active RP.
The configuration examples demonstrate the commands required to enable this application.
FIGURE 11
Example of a MDSP Anycast RP network
