Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multicast Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 208
196
Multi-Service IronWare Multicast Configuration Guide
53-1003032-02
IPv6 Multicast Listener Discovery snooping
2
Notice that the receiver for group ff0e::5 is directly connected to the device. As a result, the device
does not see a join message on behalf of the client. However, because IP Multicast Traffic
Reduction also is enabled, the device uses the MLD Group Membership report from the client to
select the port for forwarding traffic to group ff0e::5 receivers.
The IPv6 Multicast Traffic Reduction feature and the PIM-SM traffic snooping feature together build
a list of groups and forwarding ports for the VLAN. The list includes PIM-SM groups learned through
join messages as well as MAC addresses learned through MLD reports. In this case, even though
the device never sees a join message for the receiver for group ff0e::5, the device nonetheless
learns about the receiver and forwards group traffic to the receiver.
The device stops forwarding IPv6 multicast traffic on a port for a group if the port receives a prune
message for the group.
Notice that the ports connected to the source and the receivers are all in the same port-based
VLAN on the device. This is required for the PIM-SM traffic snooping feature. The feature also
requires the source and the downstream router to be on different IP subnets, as shown in
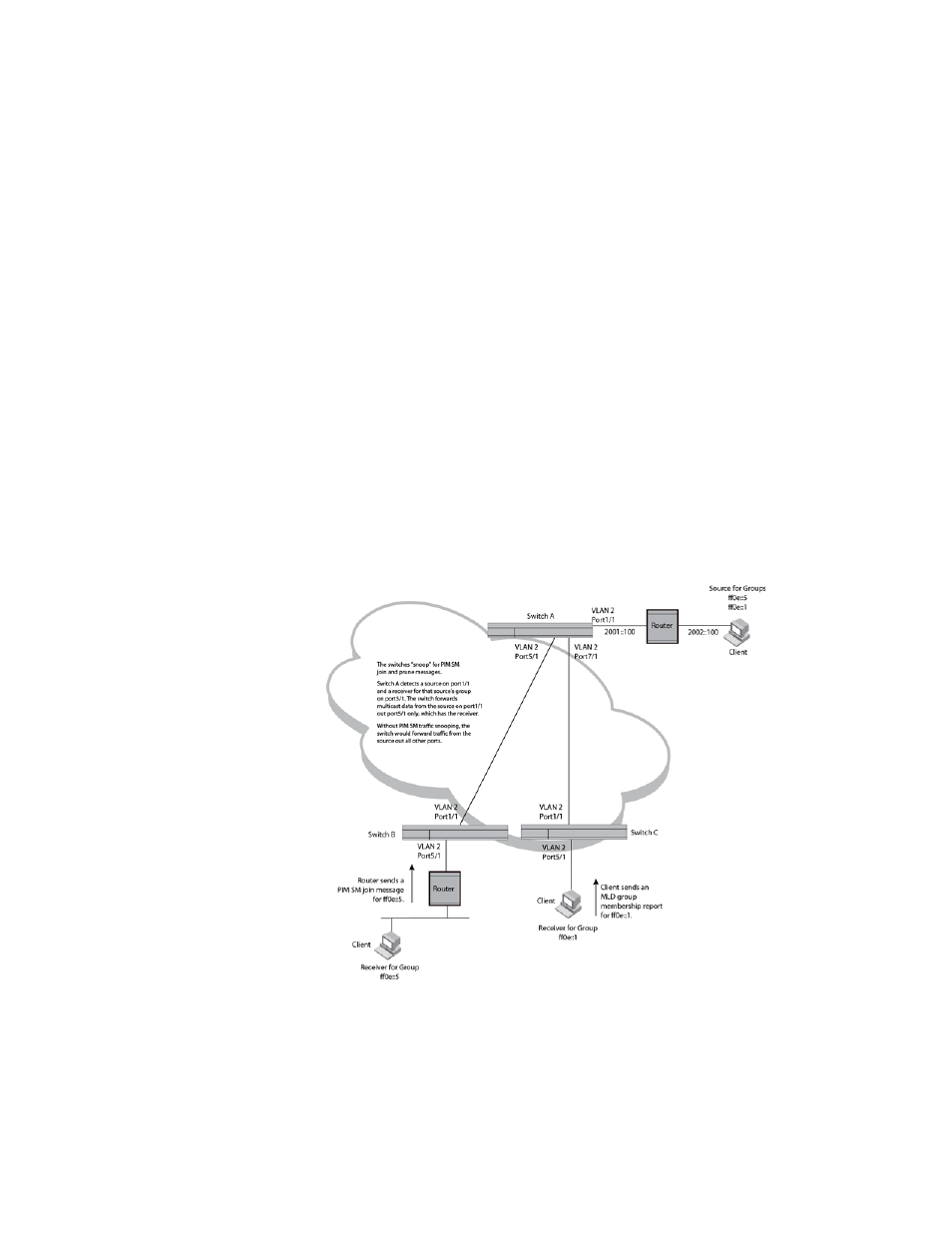
shows another example application for PIM-SM traffic snooping. This example shows
devices on the edge of a global Ethernet cloud. Assume that each device is attached to numerous
other devices.
FIGURE 22
PIM-SM IPv6 traffic reduction in global Ethernet environment
The devices on the edge of the global Ethernet cloud are configured for IP Multicast Traffic
Reduction and PIM-SM traffic snooping. Although this application uses multiple devices, the
feature has the same requirements and works the same way as it does on a single device.
