Pruning a multicast tree – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multicast Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 104
92
Multi-Service IronWare Multicast Configuration Guide
53-1003032-02
DVMRP overview
1
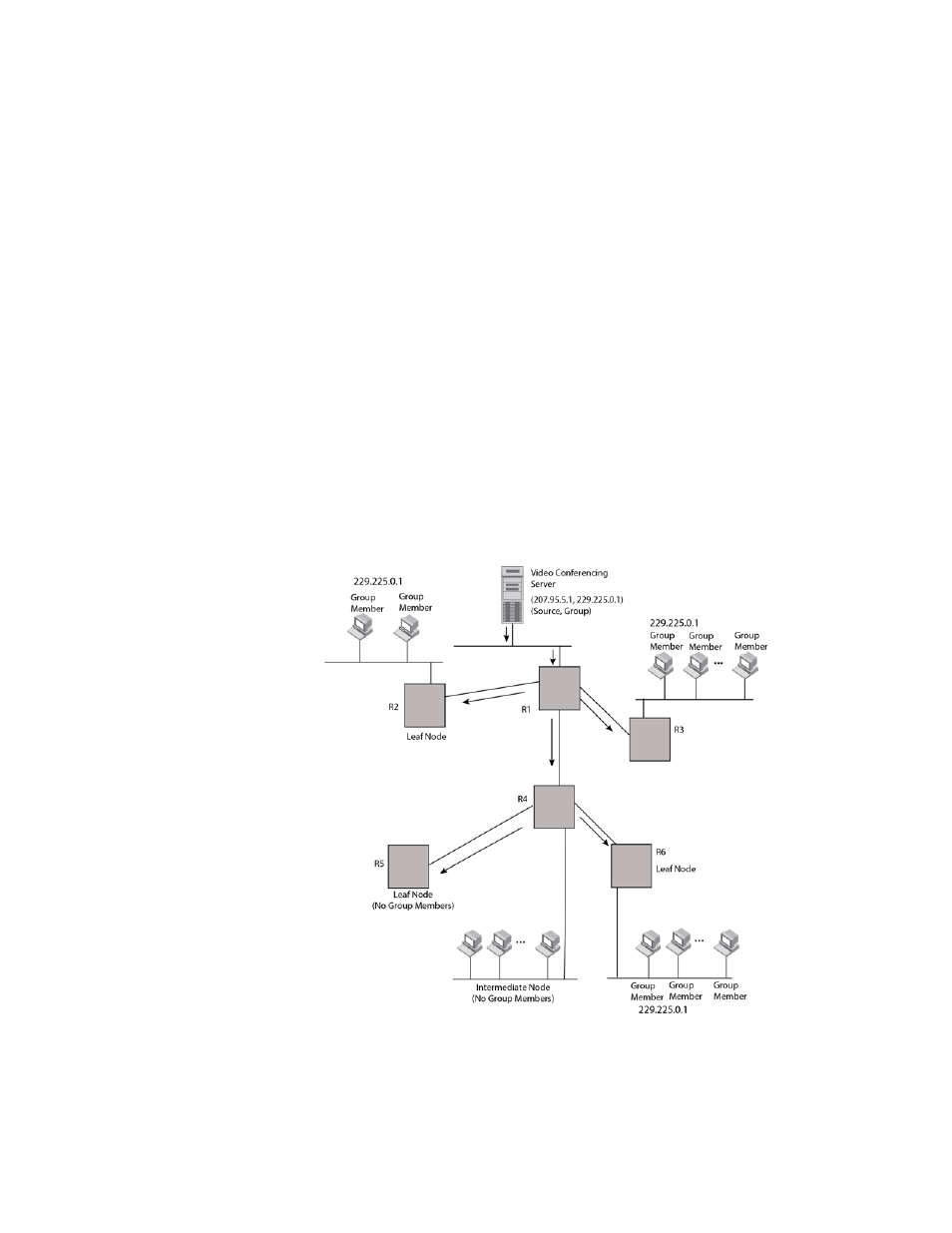
In
, the root node (R1) is forwarding multicast packets for group 229.225.0.2 that it
receives from the server to its downstream nodes, R2, R3, and R4. Router R4 is an intermediate
router with R5 and R6 as its downstream routers. Because R5 and R6 have no downstream
interfaces, they are leaf nodes.
The receivers in this example are those workstations that are resident on routers R2, R3, and R6.
Pruning a multicast tree
After the multicast tree is constructed, pruning of the tree will occur after IP multicast packets
begin to traverse the tree.
As multicast packets reach leaf networks (subnets with no downstream interfaces), the local IGMP
database checks for the recently arrived IP multicast packet address. If the local database does
not contain the address (the address has not been learned), the router prunes (removes) the
address from the multicast tree and no longer receives multicasts until the prune age expires.
In
, Router 5 is a leaf node with no group members in its local database. Consequently,
Router 5 sends a prune message to its upstream router. This router will not receive any further
multicast traffic until the prune age interval expires.
FIGURE 13
Downstream broadcast of IP multicast packets from source host
FIGURE 14
Pruning leaf nodes from a multicast tree
