Pim sparse router types – Brocade Multi-Service IronWare Multicast Configuration Guide (Supporting R05.6.00) User Manual
Page 164
152
Multi-Service IronWare Multicast Configuration Guide
53-1003032-02
IPv6 PIM Sparse
2
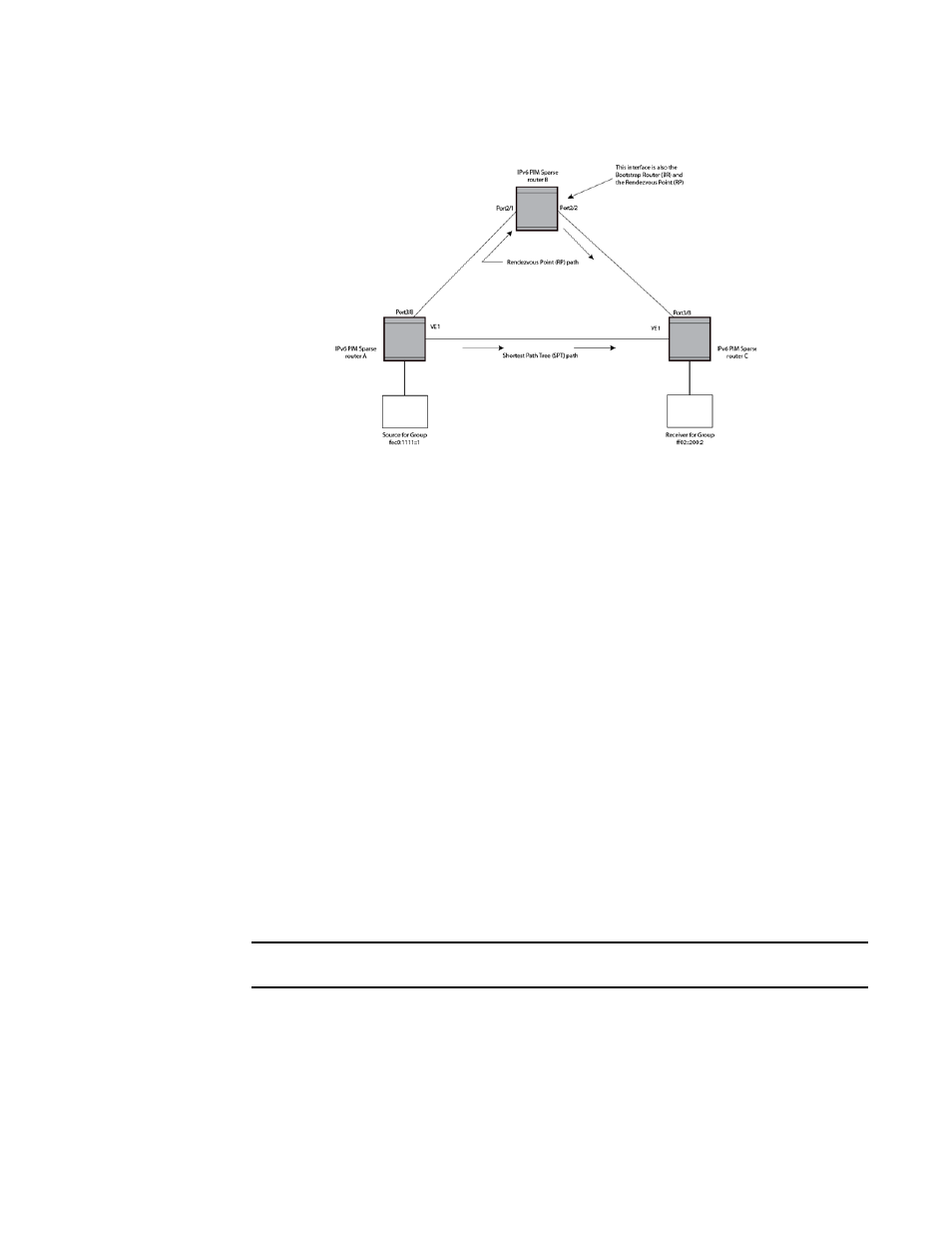
PIM Sparse router types
Routers that are configured with PIM Sparse interfaces also can be configured to fill one or more of
the following roles:
•
BSR – The Bootstrap Router (BSR) distributes RP information to the other PIM Sparse routers
within the domain. Each PIM Sparse domain has one active BSR. For redundancy, you can
configure ports on multiple routers as candidate BSRs. The PIM Sparse protocol uses an
election process to select one of the candidate BSRs as the BSR for the domain. The BSR with
the highest BSR priority (a user-configurable parameter) is elected. If the priorities result in a
tie, then the candidate BSR interface with the highest IP address is elected. In the example in
, PIM Sparse router B is the BSR. Port 2/2 is configured as a candidate BSR.
•
RP – The Rendezvous Points (RP) is the meeting point for PIM Sparse sources and receivers. A
PIM Sparse domain can have multiple RPs, but each PIM Sparse multicast group address can
have only one active RP. PIM Sparse routers learn the addresses of RPs and the groups for
which they are responsible from messages that the BSR sends to each of the PIM Sparse
routers. In the example in
, PIM Sparse router B is the RP. Port 2/2 is configured as a
candidate Rendezvous Point (RP).
To enhance overall network performance, the device uses the RP to forward only the first
packet from a group source to the group receivers. After the first packet, the device calculates
the shortest path between the receiver and the source (the Shortest Path Tree, or SPT) and
uses the SPT for subsequent packets from the source to the receiver. The device calculates a
separate SPT for each source-receiver pair.
NOTE
It is recommended that you configure the same ports as candidate BSRs and RPs.
