The analog comparator, Atmega163(l) – Rainbow Electronics ATmega163L User Manual
Page 88
ATmega163(L)
88
The Analog Comparator
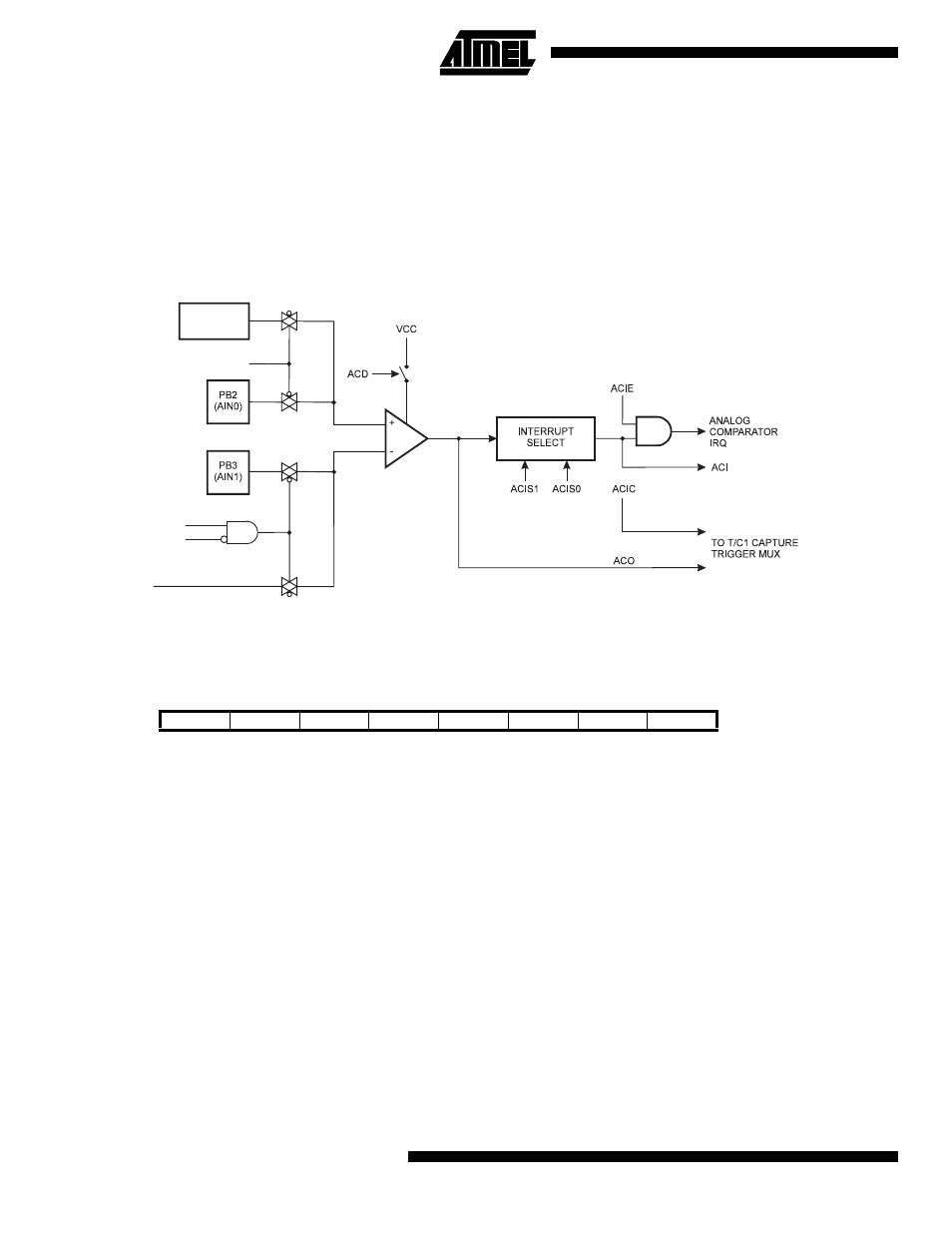
The analog comparator compares the input values on the positive pin PB2 (AIN0) and negative pin PB3 (AIN1). When the
voltage on the positive pin PB2 (AIN0) is higher than the voltage on the negative pin PB3 (AIN1), the Analog Comparator
Output, ACO, is set (one). The comparator’s output can be set to trigger the Timer/Counter1 Input Capture function. In
addition, the comparator can trigger a separate interrupt, exclusive to the Analog Comparator. The user can select Interrupt
triggering on comparator output rise, fall or toggle. A block diagram of the comparator and its surrounding logic is shown in
Figure 56.
Figure 56. Analog Comparator Block Diagram
Notes:
1. See Figure 57 on page 91.
The Analog Comparator Control And Status Register - ACSR
•
Bit 7 - ACD: Analog Comparator Disable
When this bit is set(one), the power to the analog comparator is switched off. This bit can be set at any time to turn off the
analog comparator. This will reduce power consumption in active and idle mode. When changing the ACD bit, the Analog
Comparator Interrupt must be disabled by clearing the ACIE bit in ACSR. Otherwise an interrupt can occur when the bit is
changed.
•
Bit 6 - ACBG: Analog Comparator Bandgap Select
When this bit is set and the BOD is enabled (BODEN fuse is programmed), a fixed bandgap voltage of nominally 1.22V
replaces the positive input to the Analog Comparator. When this bit is cleared, AIN0 is applied to the positive input of the
Analog Comparator.
•
Bit 5 - ACO: Analog Comparator Output
ACO is directly connected to the comparator output.
•
Bit 4 - ACI: Analog Comparator Interrupt Flag
This bit is set (one) when a comparator output event triggers the interrupt mode defined by ACIS1 and ACIS0. The Analog
Comparator Interrupt routine is executed if the ACIE bit is set (one) and the I-bit in SREG is set (one). ACI is cleared by
hardware when executing the corresponding interrupt handling vector. Alternatively, ACI is cleared by writing a logic one to
the flag.
Bit
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
$08 ($28)
ACD
ACBG
ACO
ACI
ACIE
ACIC
ACIS1
ACIS0
ACSR
Read/Write
R/W
R/W
R
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Initial value
0
0
N/A
0
0
0
0
0
ACBG
BANDGAP
REFERENCE
ADC MULTIPLEXER
OUTPUT
ACME
ADEN
1)
