Reading the signature bytes, Reading the calibration byte, Parallel programming characteristics – Rainbow Electronics ATmega163L User Manual
Page 131: Atmega163(l)
ATmega163(L)
131
3.
Set OE to ‘0’, BS2 to ‘1’ and BS1 to ‘1’. The status of the Fuse High bits can now be read at DATA (‘0’ means pro-
grammed).
Bit 2..1 = BOOTSZ1..0 Fuse bits
Bit 0 = BOOTRST Fuse bit
4.
Set OE to ‘0’, BS2 to ‘0’ and BS1 to ‘1’. The status of the Lock bits can now be read at DATA (‘0’ means pro-
grammed).
Bit 5 = Boot Lock Bit12
Bit 4 = Boot Lock Bit11
Bit 3 = Boot Lock Bit02
Bit 2 = Boot Lock Bit01
Bit 1 = Lock Bit2
Bit 0 = Lock Bit1
5.
Set OE to ‘1’.
Reading the Signature Bytes
The algorithm for reading the Signature bytes is as follows (refer to Programming the Flash for details on Command and
Address loading):
1.
A: Load Command ‘0000 1000’.
2.
C: Load Address Low Byte ($00 - $02).
3.
Set OE to ‘0’, and BS to ‘0’. The selected Signature byte can now be read at DATA.
4.
Set OE to ‘1’.
Reading the Calibration Byte
The algorithm for reading the Calibration byte is as follows (refer to Programming the Flash for details on Command and
Address loading):
1.
A: Load Command ‘0000 1000’.
2.
C: Load Address Low Byte, $00.
Set OE to ‘0’, and BS1 to ‘1’. The Calibaration byte can now be read at DATA.
3.
Set OE to ‘1’.
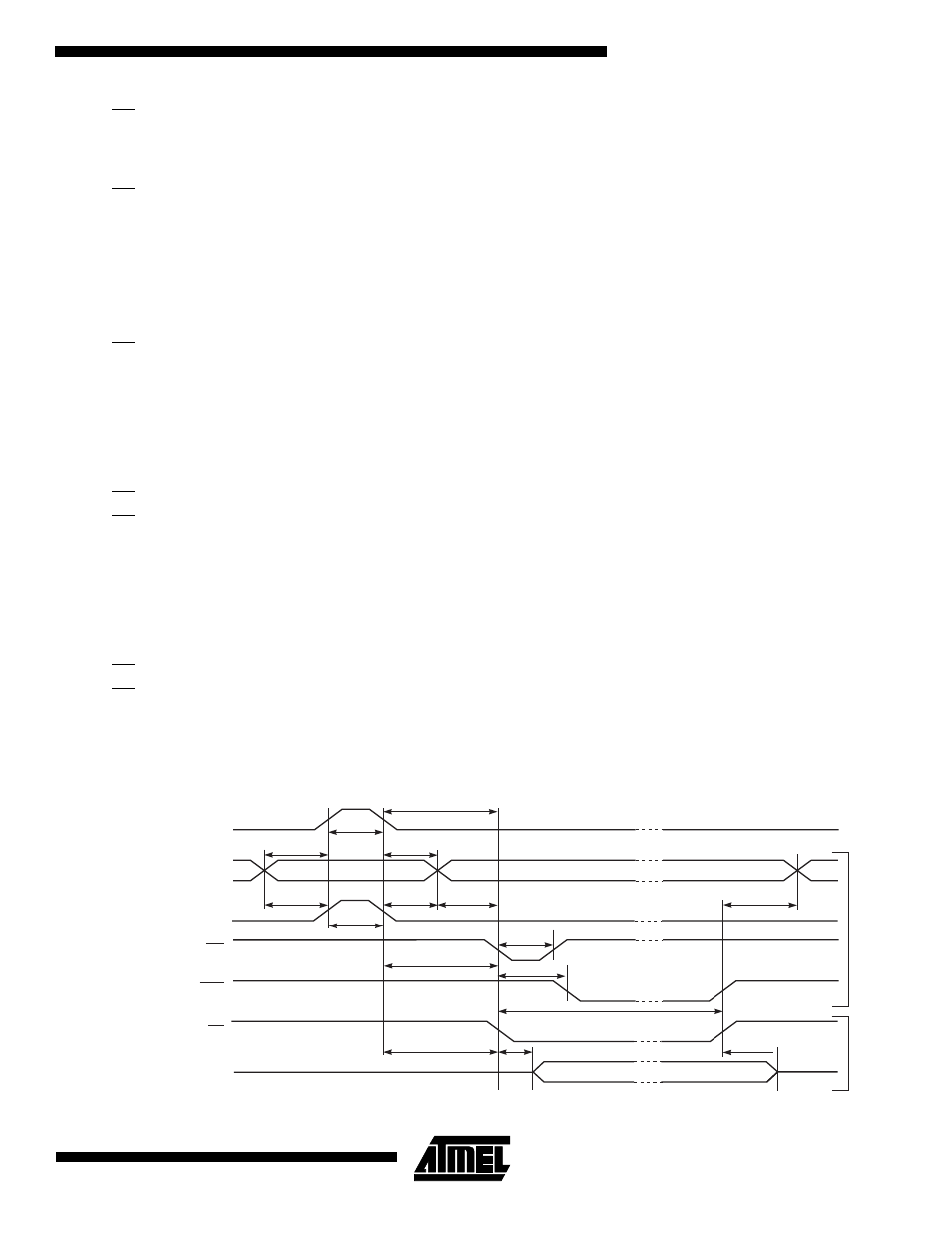
Parallel Programming Characteristics
Figure 85. Parallel Programming Timing
Data & Contol
(DATA, XA0/1, BS1, BS2)
DATA
W
rite
Read
XTAL1
t
XHXL
t
WLWH
t
DVXH
t
XLOL
t
OLDV
t
XLDX
t
PLWL
t
WLRH
WR
RDY/BSY
OE
PAGEL
t
PHPL
t
PLBX
t
BVPH
t
XLWL
t
RHBX
t
OHDZ
t
BVWL
WLRL
