Gain adjustment – Panasonic MINAS E-series User Manual
Page 141
141
[Gain Adjustment]
Gain Adjustment
Method of Checking Resonance Frequency of a Mechanical System
(1) Using “PANATERM
®
”, setup support software, display frequency characteristics.
(2) Set parameters and measurement conditions. Values are just benchmarks.
• Set Pr11 (1st velocity loop gain) to about 25. (By reducing gain, make resonance frequency easily
identifiable.)
• Set amplitude to approximately 50 (r/min). (This is because torque cannot be saturated.)
• Set offset about 100 (r/min). (By increasing speed detection information, rotate the motor in a given
direction.)
• When the polarity is positive (+), the motor rotates in CCW direction. When it is negative (-), the motor
rotates in CW direction.
• Set sampling rate to 1. (Settings range from 0 to 7.)
(3) Execute frequency characteristics analysis.
• Before starting the measurement, ensure that limit of movement must not be exceeded.
Target rotation volume (rotation) is:
Offset (r/min) x 0.017 x (sampling rate + 1).
When you increase offset, you will obtain good measurement result. However, rotation volume will grow.
• When you measure, set Pr22 (Real time auto tuning set-up) to 0.
• You will have good measurement result when you set offset greater than setting of amplitude and so that the
motor always turns in one direction.
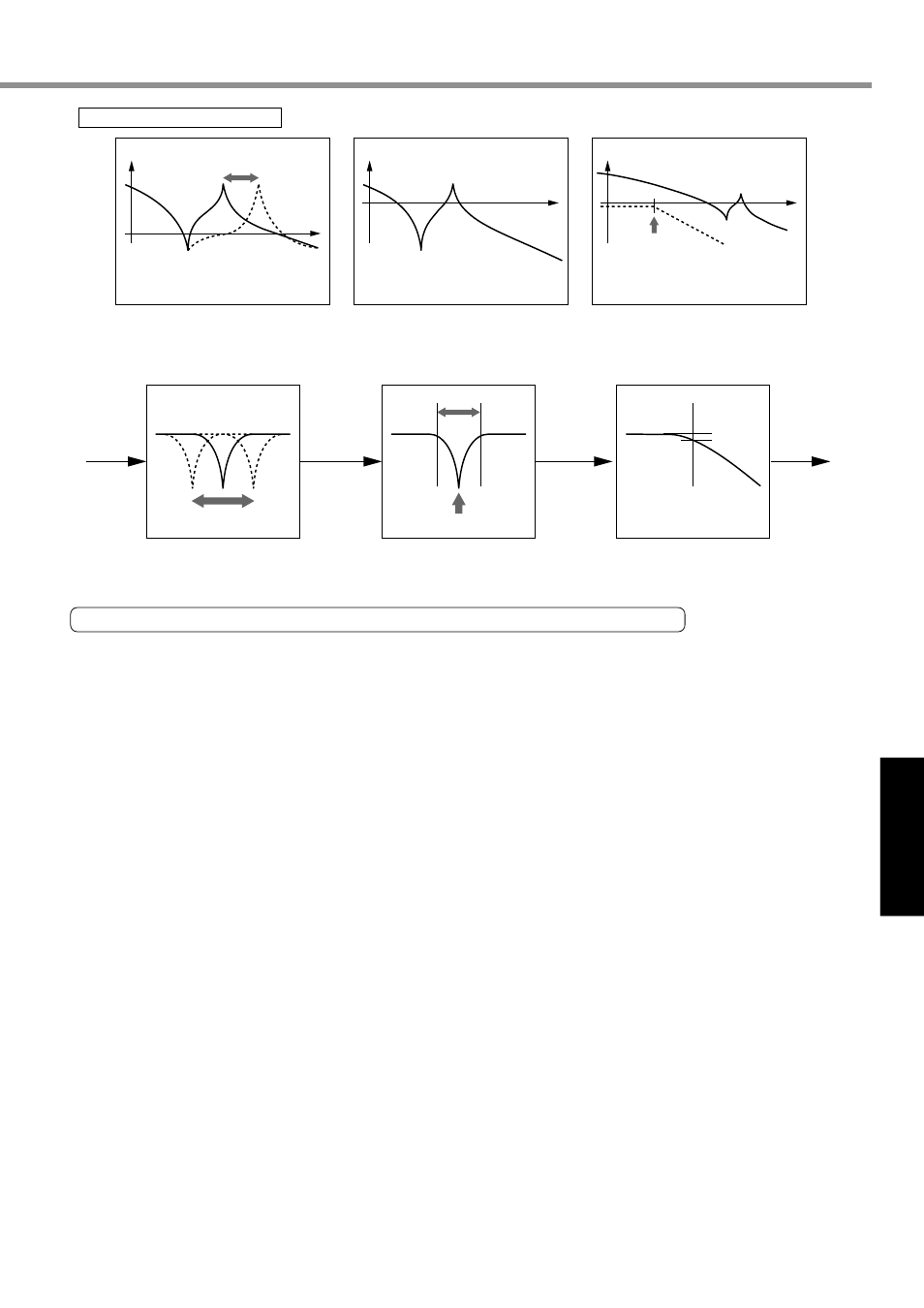
Torque
command
Gain
Frequency
Adaptive filter
Automatic frequency tracking
Frequency
Speed response
Width
Notch filter
Possible to suppress a large
resonance point frequency of
which does not change
Cutoff frequency
–3dB
Torque filter
Torque command
after filtering
Examples of adaptive devices
Devices resonance points of which
vary depending on individual
differences/aging
Gain
Frequency
Gain
Frequency
Tracking a resonance point
and instantly suppressing
Devices having a resonance point
frequency of which does not change
Devices having resonance peak in
frequency spectrum remote from
speed response
Reducing resonance peak in
high frequency spectrum
altogether
