Gain adjustment, Objective of gain adjustment, Types of gain adjustment – Panasonic MINAS E-series User Manual
Page 128
128
Real time auto gain tuning
Adaptive filter
Normal auto gain tuning
Cancellation of automatic gain tuning
Manual gain tuning (basic)
Manual gain tuning (application)
Gain switching function
Suppression of mechanical
resonance
Anti-vibration control
P.130
P.131
P.132
P.135
P.136
P.138
P.138
P.140
P.142
Estimates the load inertia of a machine at real-time, and
automatically sets the optimum gain based on the result of
estimation.
Reduces resonance point vibration, by estimating the resonance
frequency from vibration component that appears in the motor
speed and automatically sets the notch filter.
Actuates the motor in a command pattern generated by the driver,
estimates the load inertia based on the torque required, and
automatically sets the appropriate gain.
Cautions need to be followed when you disable real time auto gain
tuning or the adaptive filter.
Manually adjust when you cannot execute the auto gain tuning due
to constraints such as operating pattern/load conditions, etc., or
when you wish to ensure ultimate responsiveness appropriate to
the individual loads.
If you cannot satisfy the specifications through the basic
adjustment, you can aim to improve performance by using the
following applied functions:
You can execute the gain switching with internal data or external
signal as a trigger. This shows the effects of reduced vibration
under suspension, shortened stabilization time, improved
command trackability, etc.
You are not able to set a high gain when the mechanical stiffness
is low or when vibration or noise is generated due to resonance
that results from the twist of the shaft. In such case, you can
suppress the resonance by using a torque filter or notch filter.
Reduces vibration at edge of the device, by removing the
components of the vibration frequency by the position command.
Functions
Descriptions
Refer
to:
Automatic adjustment
Manual adjustment
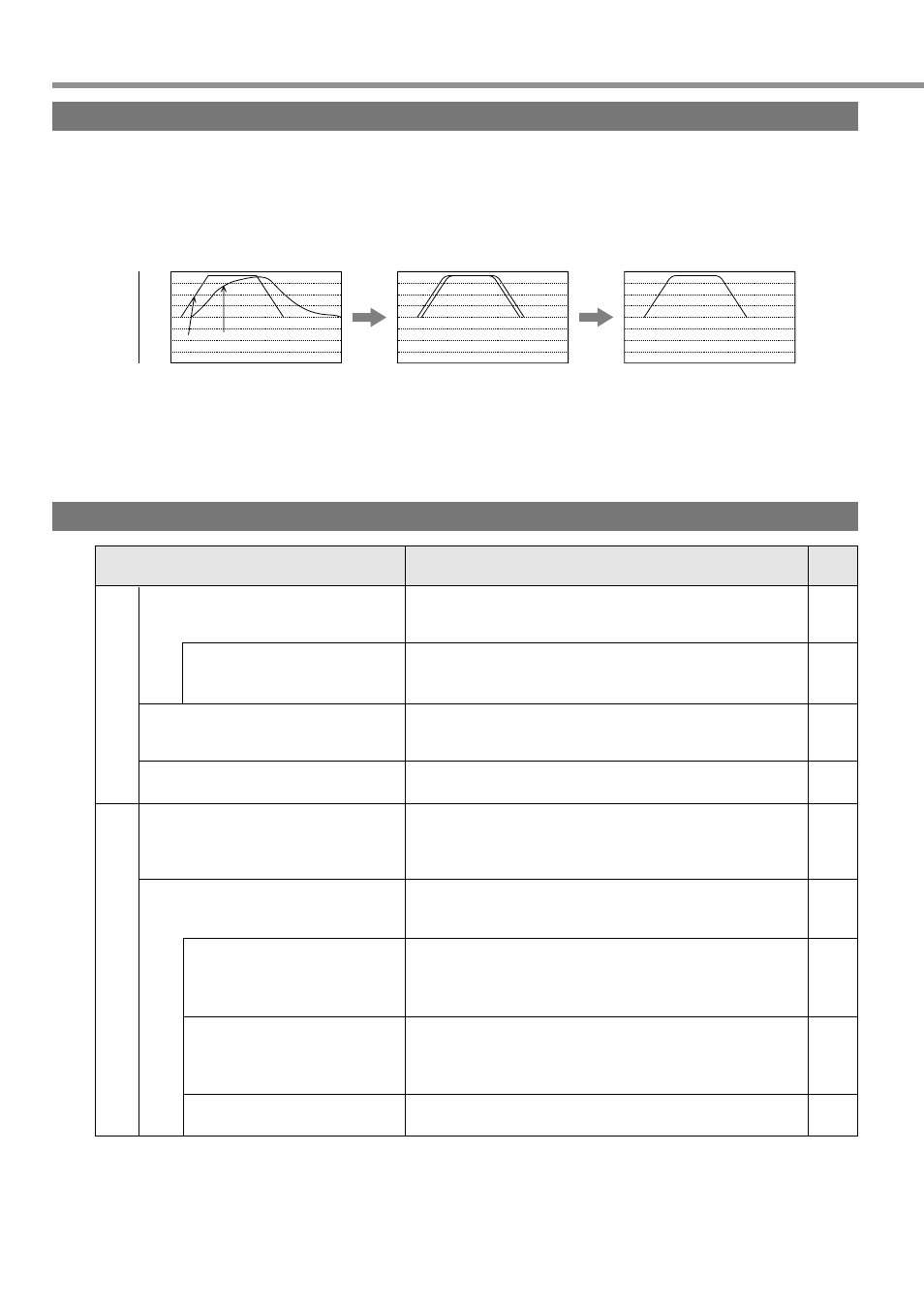
Objective of Gain Adjustment
It is necessary that the motor runs with the least delay time and in response to a command from the driver. Hence,
we need to adjust the gain of the motor to perform command, in order to maximize the performance of the machine.
Position loop gain
: 20
Velocity loop gain
:100
Velocity loop integration time constant : 50
Velocity feed forward
:
0
Inertia ratio
:100
Position loop gain
:100
Velocity loop gain
: 50
Velocity loop integration time constant : 50
Velocity feed forward
:
0
Inertia ratio
:100
Position loop gain
: 100
Velocity loop gain
: 50
Velocity loop integration time constant : 50
Velocity feed forward
: 500
Inertia ratio
: 100
Gain setting: low
Gain setting: High
+ Feed forward setting
+2000
-2000
0
0.0
375
250
125
0.0
375
250
125
0.0
375
250
125
(r/min)
+2000
-2000
0
(r/min)
Command speed
Actual motor speed
Gain Adjustment
Types of Gain Adjustment
• Pay adequate attention to safety.
• In case of oscillation (i.e., abnormal noise/vibration), promptly cut off the power or activate Servo-OFF.
