Ethernet network addressing, Energy metering, Metered parameters – Rockwell Automation 1408-EMxx PowerMonitor 1000 Unit User Manual
Page 31
Rockwell Automation Publication 1408-UM001D-EN-P - September 2013
31
PowerMonitor 1000 Unit Features Chapter 2
Ethernet Network Addressing
The IP address is a 32-bit binary number, which consists of the network address
(NetID) and the machine address (HostID). The Subnet mask
defines the
boundary between the NetID and HostID and each 0 represents the HostID.
In this example, the NetID is 192.1.1.0 and the HostID is 0.0.0.207. The
relationship between NetID and HostID depends on the IP address class, the
discussion of which is beyond the scope of this document (the example uses a
Class C IP address). Devices on the same subnet can communicate directly;
devices on different subnets may communicate with each other only through a
gateway or router.
The Gateway IP address defines the address of the gateway or router on the unit’s
subnet that is used to route messages to other subnets for wide-area networking.
The default is 128.1.1.1.
Energy Metering
This function applies to catalog numbers 1408-EM1, 1408-EM2, and 1408-
EM3.
Metered Parameters
The power monitor calculates and returns the totalized energy values including
the following:
•
GWh forward, GWh reverse, and GWh net
•
kWh forward, kWh reverse, and kWh net
•
GVARh forward, GVARh reverse, and GVARh net
•
kVARh forward, kVARh reverse, and kVARh net
•
GVAh and kVAh
Each time the kWh value rolls over to zero the GWh value increments by one.
The other pairs of values operate in the same way.
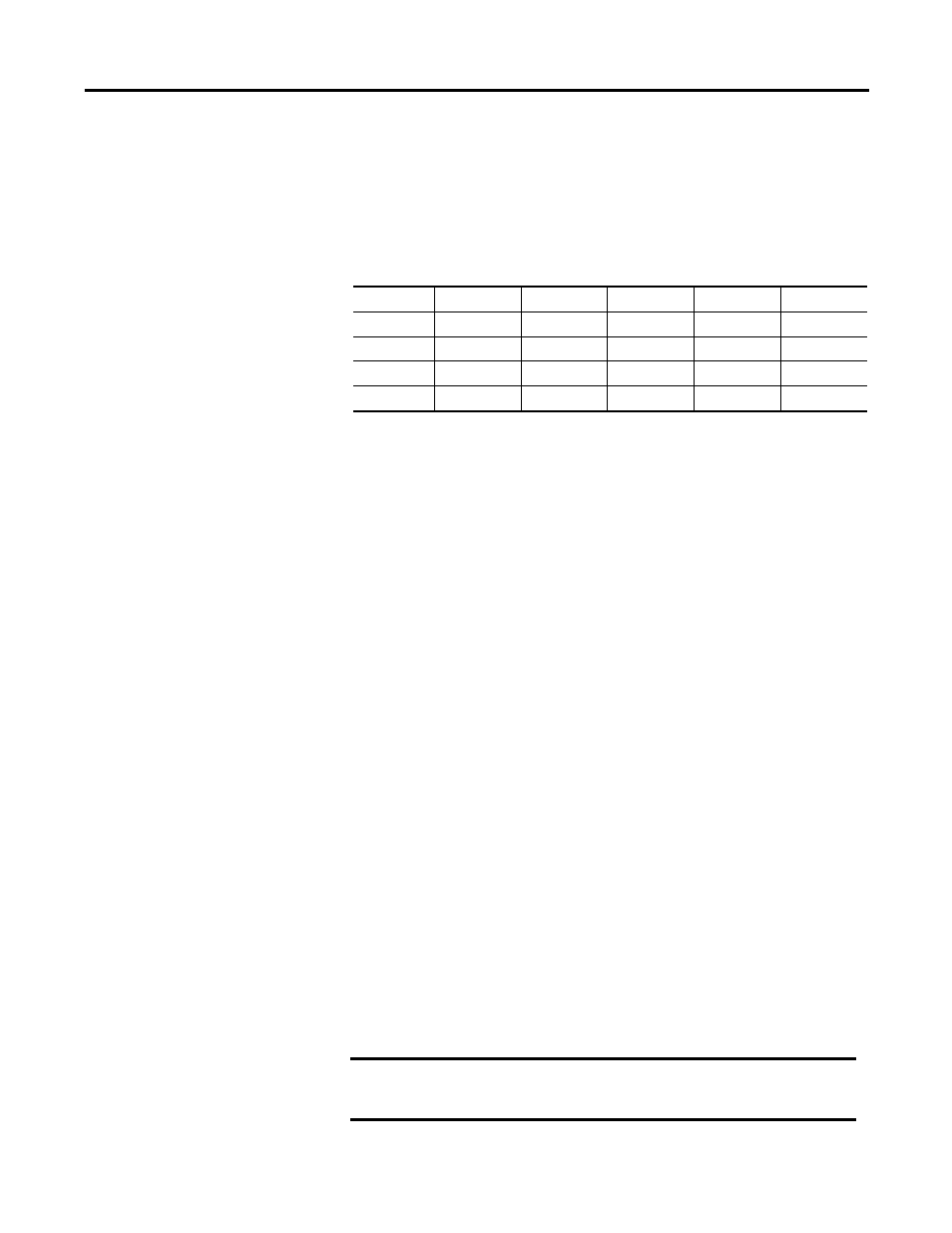
Table 1 - Ethernet Network Addressing Example
IP address
(decimal):
192
1
1
207
(binary):
11000000
00000001
00000001
11001111
Subnet mask (decimal):
255
255
255
0
(binary):
11111111
11111111
11111111
00000000
----
Net ID
----
-Host ID-
EXAMPLE
A large energy value could be displayed as 123,456,789,234.567 kWh
where 123,456 is the GWh metering result and 789,234.567 is the kWh
metering result.
