Settings for using an hdlm device as a boot disk, See steps 1 to 16 in – HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 174
After completing the above procedure, you can perform an upgrade
installation of HDLM in a multi-path boot disk environment that uses a logical
volume (LVM2) on an HDLM device.
Settings for Using an HDLM Device as a Boot Disk
This subsection describes how to perform a new installation of HDLM in a
single-path boot disk environment that uses a SCSI device and how to set up
the environment.
Note that if the settings are incorrect, the OS might not start. For details
about what action to take if the OS cannot be started from an HDLM device,
Countermeasures for Unsuccessful Startup of the OS from an HDLM
The name of the boot loader configuration file used in these procedures
differs depending on the boot loader and OS. The names of the boot loader
configuration files are listed in
Table 3-53 Names of Boot Loader
Configuration Files on page 3-106
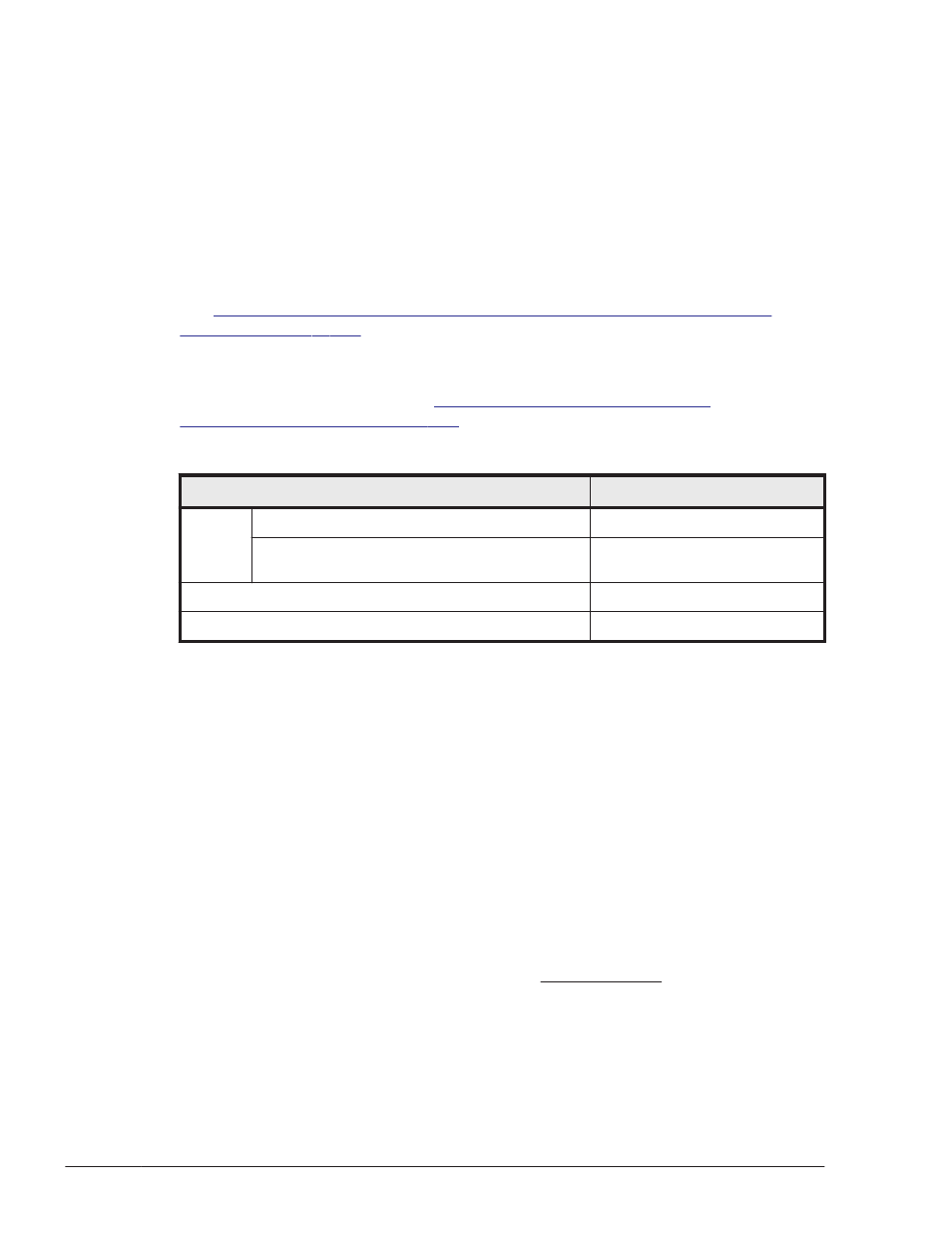
Table 3-53 Names of Boot Loader Configuration Files
Boot loader
Configuration file name
GRUB
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux
/etc/grub.conf
For SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 10 or SUSE
LINUX Enterprise Server 11
/boot/grub/menu.lst
LILO
/etc/lilo.conf
ELILO
/etc/elilo.conf
To install HDLM in a boot disk environment that uses a SCSI device,
and set up the environment:
1
.
Log in to Linux as a user with root permissions.
2
.
If the OS is SUSE LINUX Enterprise Server 10 SP3 or later, specify
multipath=off in the boot loader configuration file.
Make sure that multipath=off has been set in the kernel line of the
boot loader configuration file. The following example shows how to specify
multipath=off:
¢
When ELILO is used as the boot loader:
:
:
image = vmlinuz-2.6.16.60-0.54.5-default
label = 51
append = "splash=silent multipath=off"
description = Linux
initrd = initrd-2.6.16.60-0.54.5-default
root = /dev/disk/by-id/scsi-35001862001472c70-part12
multipath=off is set in the underlined section.
3-106
Creating an HDLM Environment
Hitachi Dynamic Link Manager User Guide (for Linux(R))
