Checking the volume group -76 – HP XP P9500 Storage User Manual
Page 144
When accessing a device that is to be managed after HDLM installation,
the setting name used until now cannot be used for access because the
logical device file name for the HDLM device that HDLM creates is used.
4
.
Unmount the disks.
If the disks to be managed by HDLM were mounted by specifying SCSI
devices, unmount them.
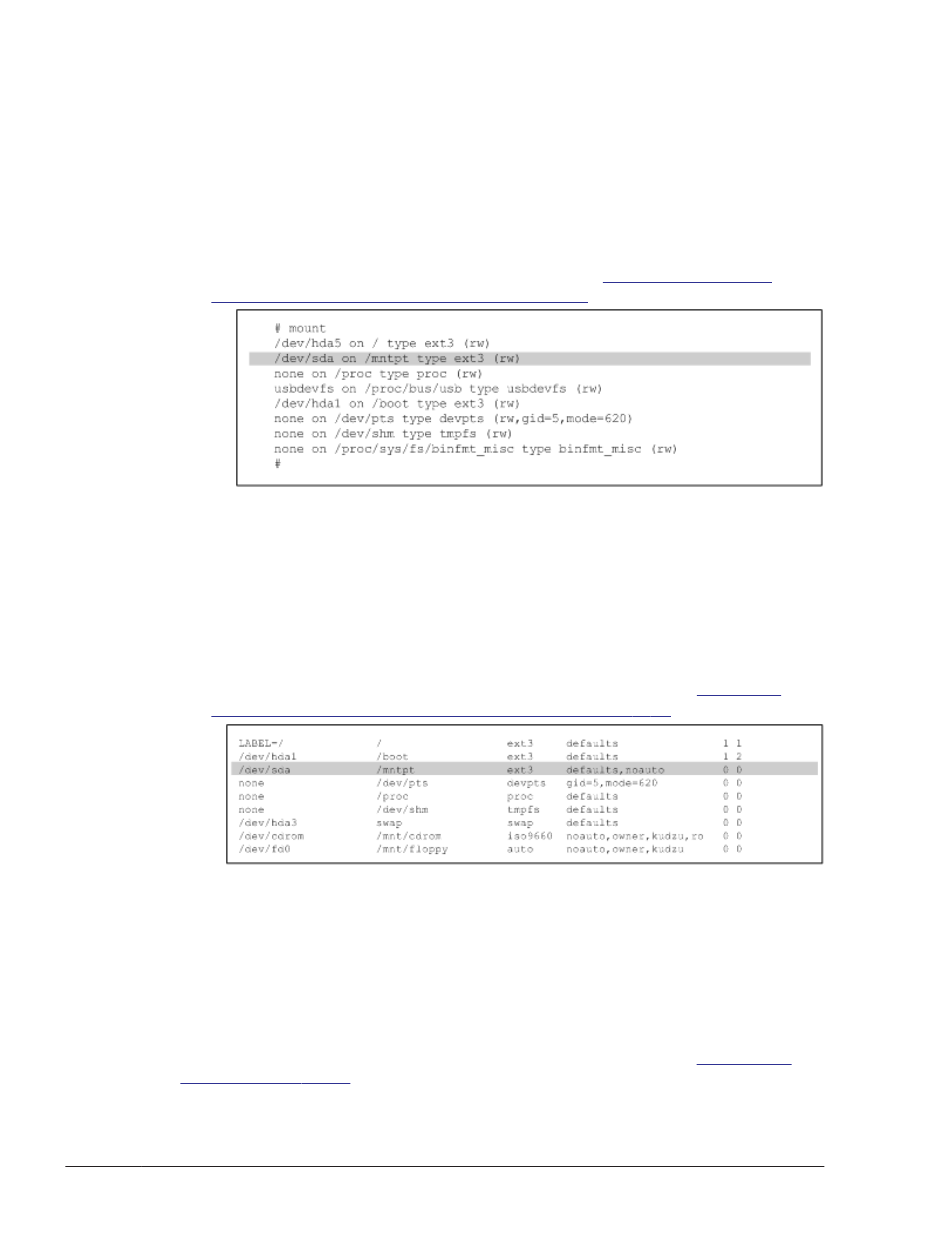
First, check the current settings. Execute the following command:
# mount
The current settings will be output as shown in
Results of the mount Command on page 3-76
Figure 3-2 Execution Results of the mount Command
The shaded portion shows the SCSI device to be managed by HDLM.
Execute the following command on this SCSI device to unmount it:
# umount /mntpt
5
.
If the disks are set to be mounted automatically when the host starts,
delete this setting from the /etc/fstab file.
An example of how to edit the /etc/fstab file is shown in
Example of How to Edit the /etc/fstab File on page 3-76
.
Figure 3-3 Example of How to Edit the /etc/fstab File
Comment out the shaded portions by placing a hash mark (#) at the
beginning of each line. The Linux functionality that adds LABEL= to a SCSI
device is not supported in HDLM. Do not use this functionality.
Checking the Volume Group
If you have already created a physical volume, volume group, or logical
volume by using LVM, you can use the procedure described in
only when all of the conditions below are satisfied.
3-76
Creating an HDLM Environment
Hitachi Dynamic Link Manager User Guide (for Linux(R))
