HP Storage Mirroring Software User Manual
Page 376
374 of 739
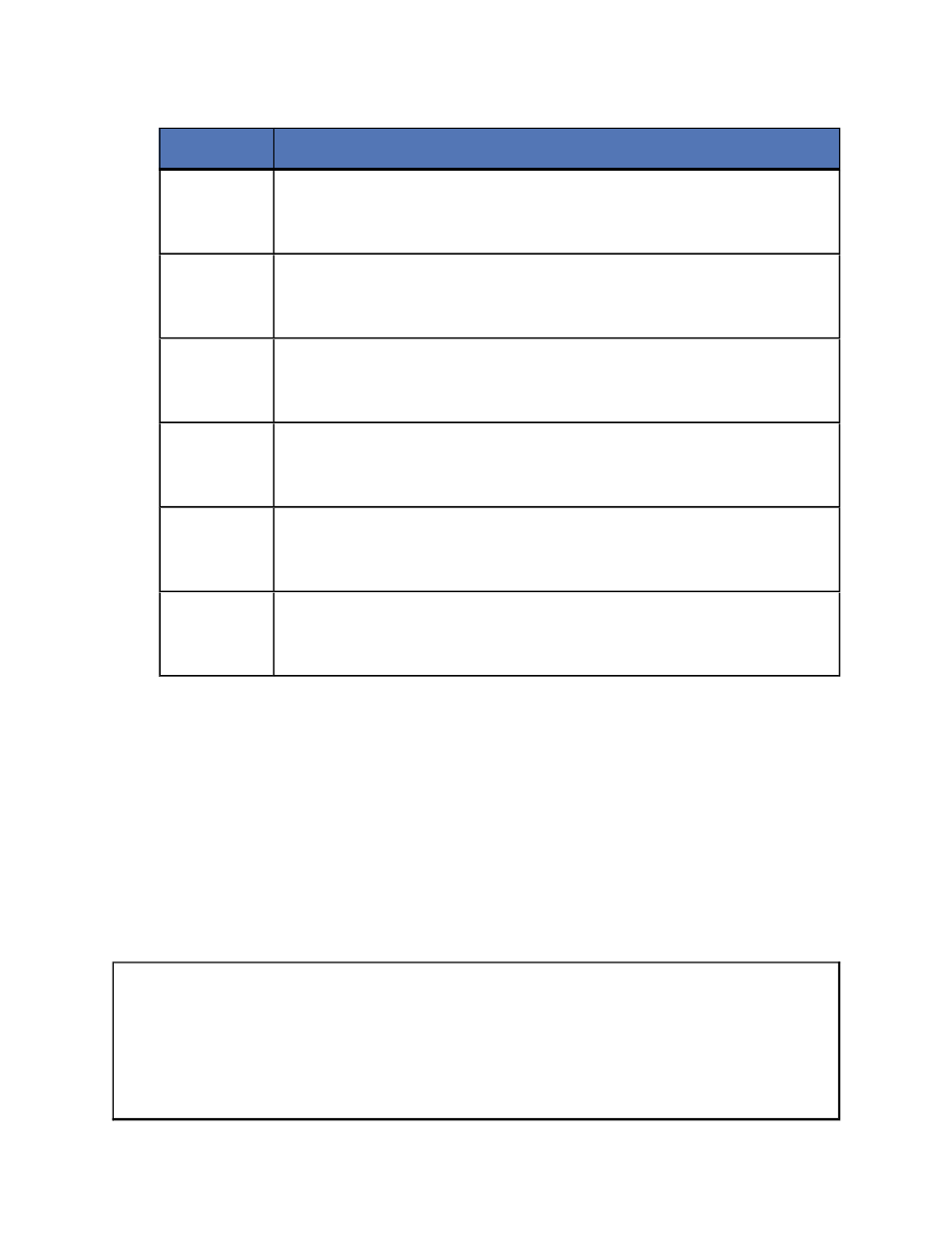
Variable
Description
www.xxx
The first two octets of the source’s IP address. For example, if the
source’s IP address is 192.168.1.108, this variable would be
192.168.
zzz.yyy
The last two octets, in reverse order, of the source’s IP address.
For example, if the source’s IP address is 192.168.1.108, this
variable would be 108.1.
source_
server’s_
FQDN
The fully qualified domain name of the source server
target_
server_IP_
address
The IP address on the source
aaa.bbb
The first two octets of the target’s IP address. For example, if the
target’s IP address is 116.123.2.47, this variable would be
116.123.
ddd.ccc
The last two octets, in reverse order, of the target’s IP address. For
example, if the target’s IP address is 116.123.2.47, this variable
would be 47.2.
For example, suppose you had the following environment.
●
Full qualified domain name of the source—Alpha.domain.com
●
Source IP address—192.168.1.108
●
Fully qualified domain name of the target—Beta.domain.com
●
Target IP address—116.123.2.47
●
Fully qualified domain name of the DNS server—DNSServer.domain.com
●
DNS zone—domain.com
You would add the following to your failover script to delete the host and reverse lookup
entries and add new entries associating the source to the target.
dnscmd DNSServer.domain.com /RecordDelete domain.com alpha A 192.168.1.108
/f
dnscmd DNSServer.domain.com /RecordDelete 192.168.in-addr.arpa 108.1 PTR
alpha.domain.com /f
dnscmd DNSServer.domain.com /RecordAdd domain.com alpha A 116.123.2.47
dnscmd DNSServer.domain.com /RecordAdd 116.123.in-addr.arpa 47.2 PTR
alpha.domain.com
