Index, Pretrigger function – Yokogawa DAQWORX User Manual
Page 15
1-9
IM WX13-01E
Before Using the
AddT
rigger Software
1.1 Overview of Functions
1
2
3
4
5
Index
6
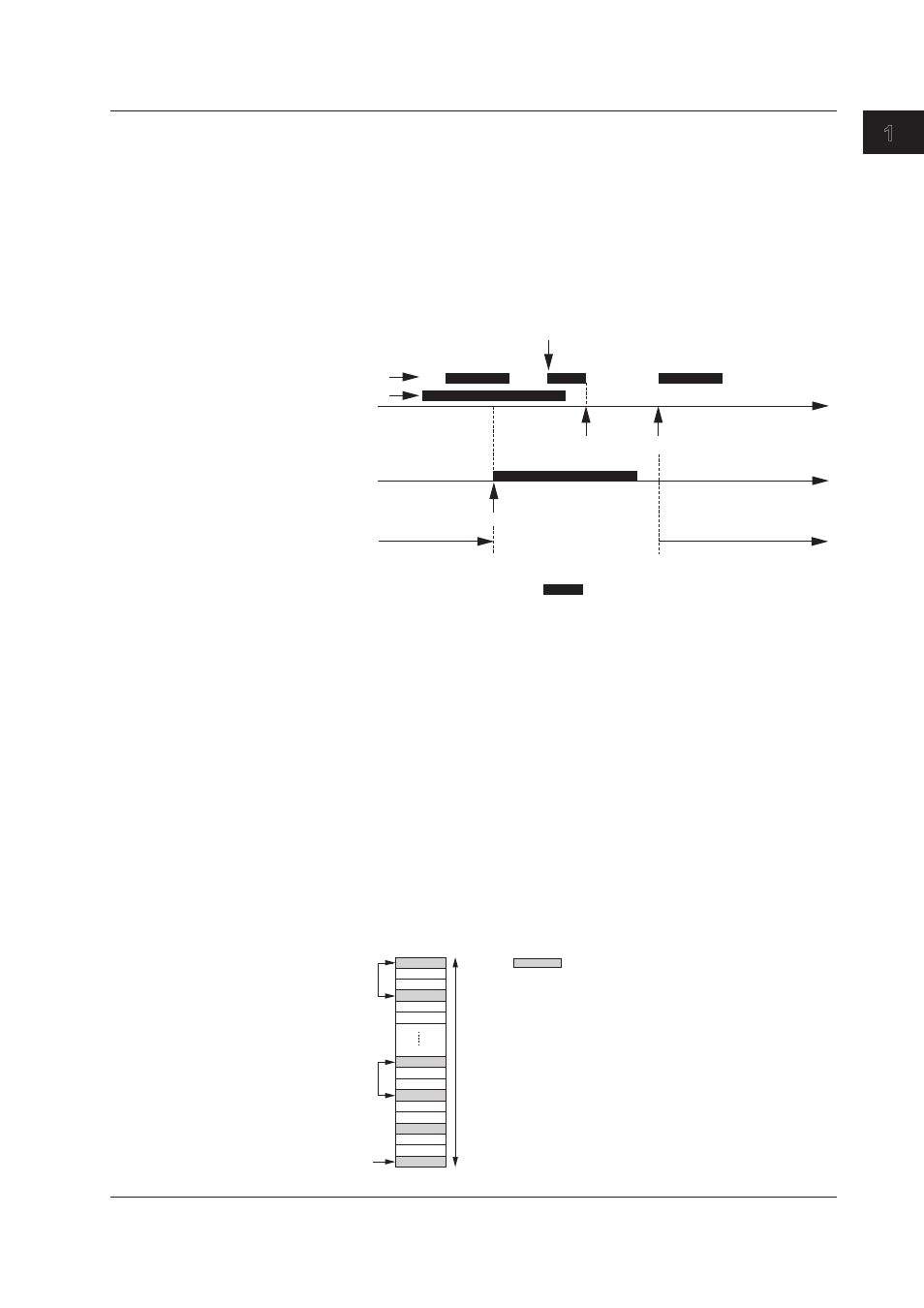
Example: when the start condition is to scan for 2 alarms and the stop
condition is to scan for 1 alarms (OR condition).
Logging stops at the point stop condition alarm 1 occurs. At that point (B) the start
conditions are being met (alarm 1 or 2 is occurring) but logging does not start. The
start condition’s alarm 1 is cleared and reactivated between points B and C’, but
logging does not start because start condition’s alarm 2 is still occurring during that
time, and the start condition continues to be met. Both start condition alarms are
cleared for the first time at point C, making the start conditions no longer met. Logging
finally starts thereafter at point D, when the start condition is met again. (See the
following figure for the letters referred to in the text above.)
Start
Condition
Time
Stop
Condition
Alarm 1
Alarm 1
Alarm 2
Logging period
Logging period
Logging stops
Period during which alarms are occurring
Logging starts
C
C’
B
D
A
Pretrigger Function
If the start condition is an alarm trigger or level trigger, you can use a pretrigger function.
The pretrigger function allows you to save only the specified number of data prior to the
trigger start point. The number of data specified does not include the trigger point itself.
The pretrigger function can be set in the range from 0 to 1799 data points. If you specify
0 data points, the pretrigger function is effectively disabled.
Number of Pretrigger Data Specified and the Recording Rate
When data is saved to a file, it is first thinned at the specified recording rate. The number
of data specified for the pretrigger represents the number of data after thinning. The
internal memory can save up to 1800 data acquired from the monitor server (see page
1-2, “AddTrigger Structure”). Because of this, the valid range for the data that can be
specified for the pretrigger varies depending on the recording rate. That range is from 0
to (1800 ÷ the recording rate) - 1.
For example, the recording rate in the figure below is 3, so the valid range is from 0 to
599.
Recording rate
Recording rate
Start trigger
1800 data
Data to be logged
