Alarms, Single set point ramping, Process and deviation alarms – Watlow EZ-ZONE RMH User Manual
Page 110: Alarm set points, Alarm hysteresis
Watlow EZ-ZONE
®
RMH Module
•
107
•
Chapter 6 Features
50 percent output
3 ON, 3 OFF
66 percent output
6 ON, 3 OFF
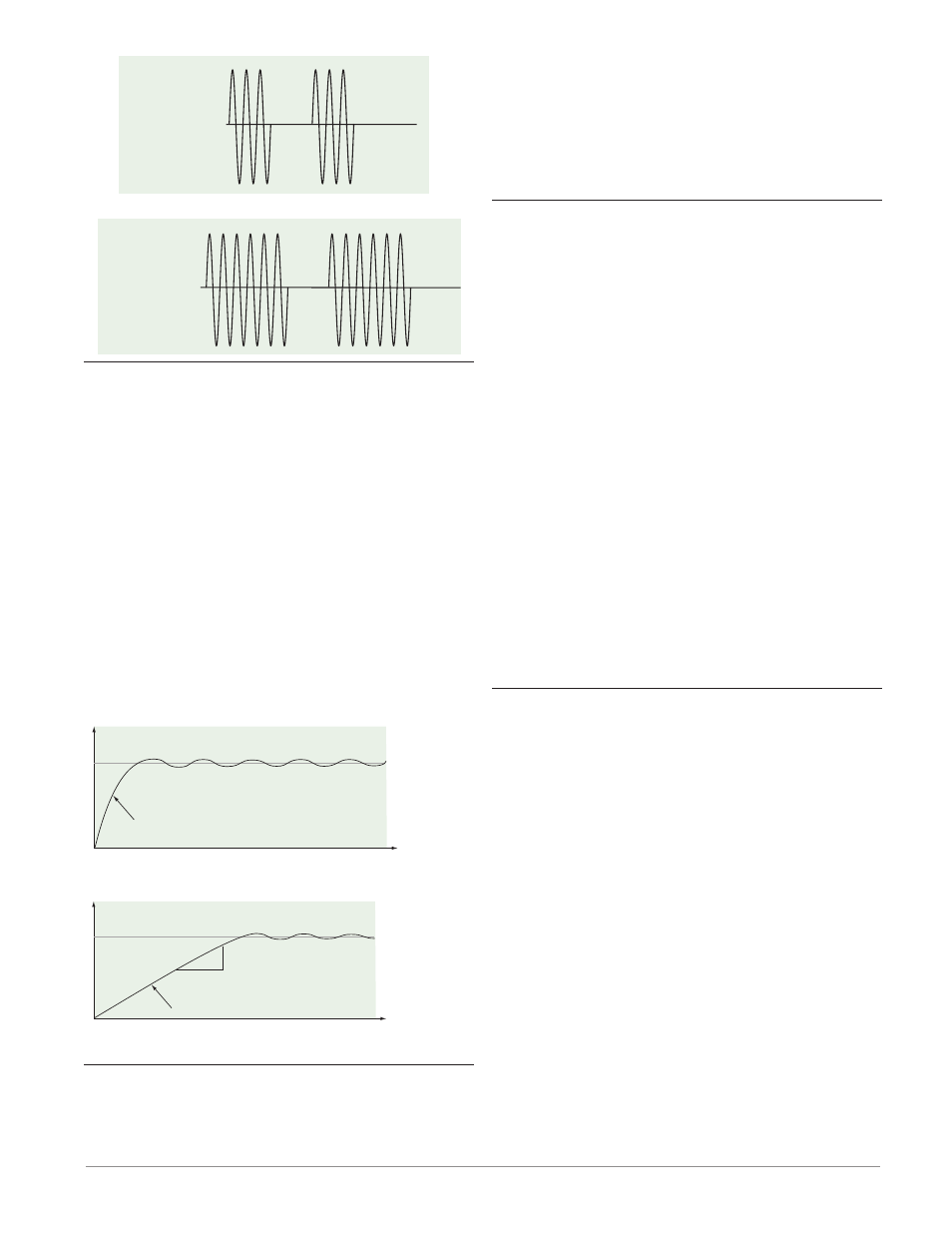
Single Set Point Ramping
Ramping protects materials and systems that can-
not tolerate rapid temperature changes. The value of
the ramp rate is the maximum degrees per minute or
hour that the system temperature can change.
Select Ramp Action [``rP] (Setup Page, Loop
Menu):
[`oFF]
ramping not active.
[`Str]
ramp at startup.
[StPt]
ramp at a set point change.
[both]
ramp at startup or when the set point
changes.
Select whether the rate is in degrees per minute or
degrees per hour with Ramp Scale [`r;SC]. Set the
ramping rate with Ramp Rate [`r;rt] (Setup Page,
Loop Menu).
Set Point
Time
Temperature
Heating System without Ramping
Temperature reaches Set Point quickly
Set Point
Time
Temperature
Heating System with Ramping
Temperature ramps to Set Point at a set rate
degrees
per minute
Alarms
Alarms are activated when the output level, process
value or temperature leaves a defined range. A user
can configure how and when an alarm is triggered,
what action it takes and whether it turns off auto-
matically when the alarm condition is over.
Configure alarm outputs in the Setup Page before
setting alarm set points.
Alarms do not have to be assigned to an output.
Alarms can be monitored and controlled through the
front panel or by using software.
Process and Deviation Alarms
A process alarm uses one or two absolute set points
to define an alarm condition.
A deviation alarm uses one or two set points that
are defined relative to the control set point. High
and low alarm set points are calculated by adding or
subtracting offset values from the control set point.
If the set point changes, the window defined by the
alarm set points automatically moves with it.
Select the alarm type with Type [`A;ty] (Setup
Page, Alarm Menu).
Alarm Set Points
The alarm high set point defines the process value
or temperature that will trigger a high side alarm.
The alarm low set point defines the temperature that
will trigger a low side alarm. For deviation alarms,
a negative set point represents a value below closed
loop set point. A positive set point represents a value
above closed loop set point. View or change alarm
set points with Low Set Point [`A;Lo] and High Set
Point [`A;hi] (Operations Page, Alarm Menu).
Alarm Hysteresis
An alarm state is triggered when the process value
reaches the alarm high or alarm low set point. Alarm
hysteresis defines how far the process must return
into the normal operating range before the alarm can
be cleared.
Alarm hysteresis is a zone inside each alarm set
point. This zone is defined by adding the hysteresis
value to the alarm low set point or subtracting the
hysteresis value from the alarm high set point. View
or change alarm hysteresis with Hysteresis [`A;hy]
(Setup Page, Alarm Menu).
