High voltage i/o ports, Atmega4hvd/8hvd – Rainbow Electronics ATmega8HVD User Manual
Page 56
56
8052B–AVR–09/08
ATmega4HVD/8HVD
13. High Voltage I/O Ports
All high voltage AVR ports have true Read-Modify-Write functionality when used as general
digital I/O ports. This means that the state of one port pin can be changed without unintention-
ally changing the state of any other pin with the SBI and CBI instructions. All high voltage I/O
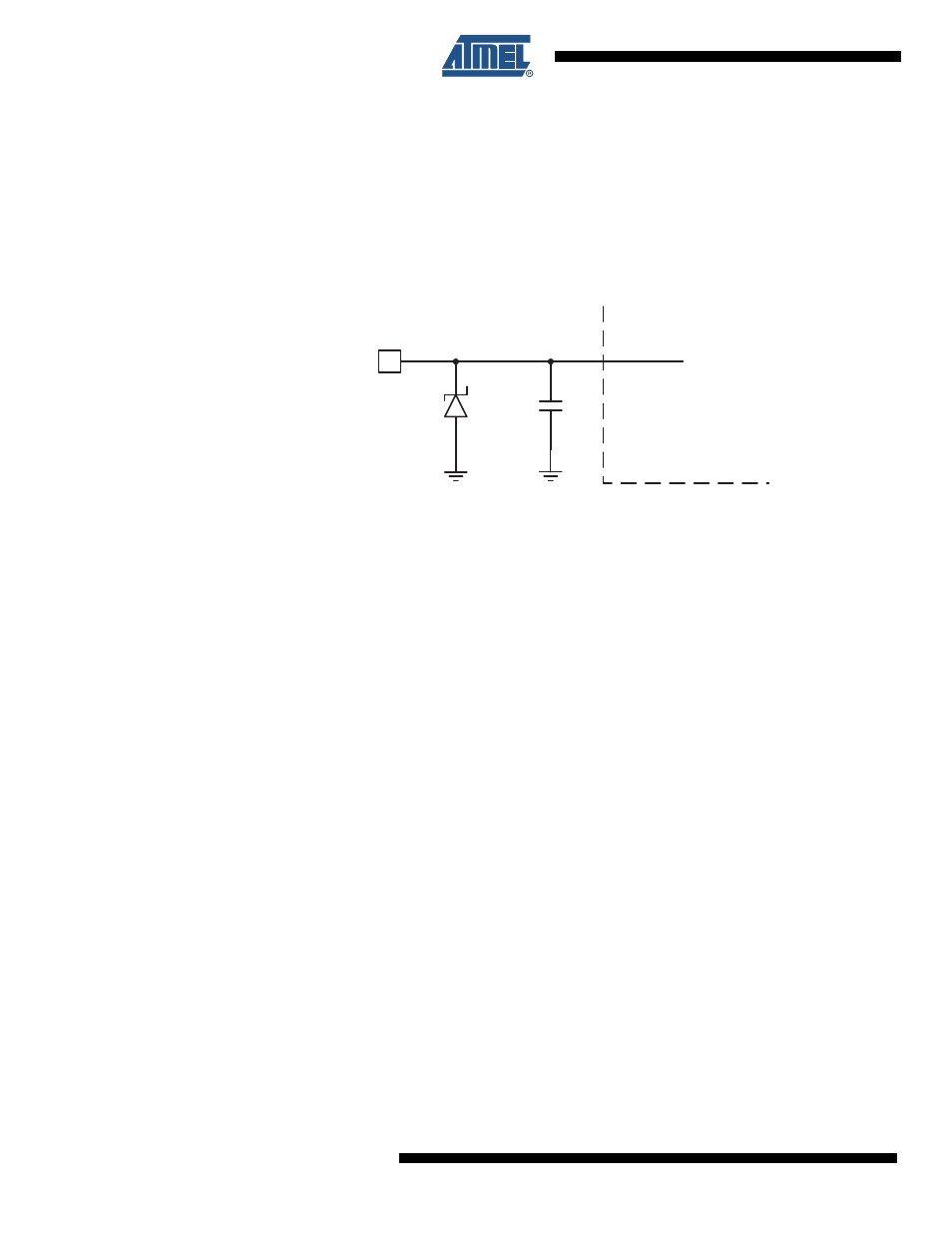
pins have protection Zener diodes to Ground as indicated in
Figure 13-1
. See
for a complete list of parameters.
Figure 13-1. High Voltage I/O Pin Equivalent Schematic
Note:
1. See
Figure 13-2 on page 57
for details.
All registers and bit references in this section are written in general form. A lower case “x” rep-
resents the numbering letter for the port, and a lower case “n” represents the bit number.
However, when using the register or bit defines in a program, the precise form must be used.
For example, PORTC3 for bit number three in Port C, here documented generally as PORTxn.
The physical I/O Registers and bit locations are listed in
”Register Description” on page 60
.
One I/O Memory address location is allocated for each high voltage port, the Data Register –
PORTx. The Data Register is read/write.
Using the I/O port as General Digital Output is described in
”High Voltage Ports as General
.
C
pin
Logic
Pxn
