Jmotion command descriptions – Yaskawa MP930 User Manual
Page 34
2.1 Specifications
2 -9
J
Motion Command Descriptions
Table 2.7 describes the motion commands.
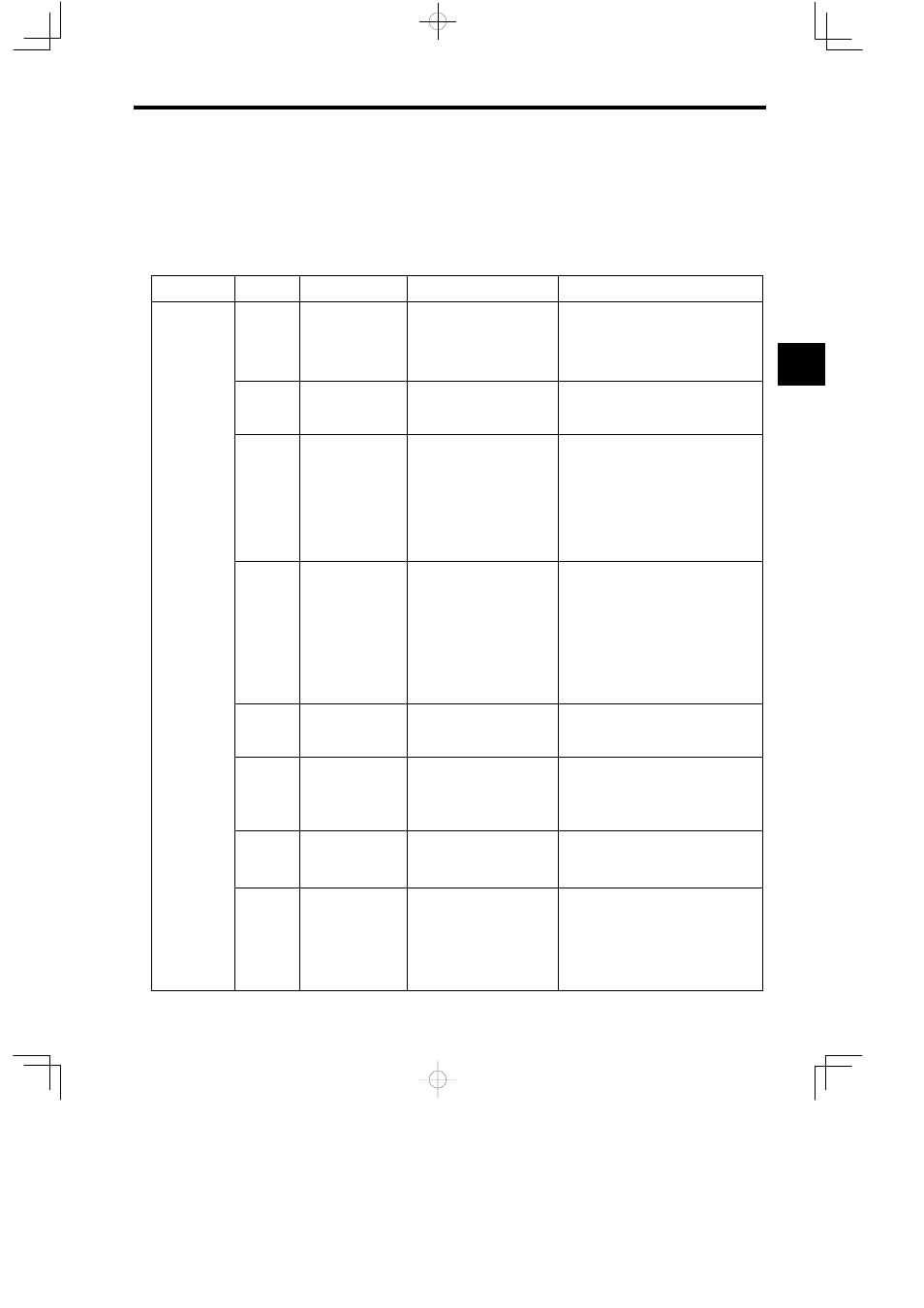
Table 2.7 Motion Command Description
Classification Command
Name
Programming Format
Function/Meaning
Axis Move
Commands
MOV
POSITIONING
MOV [axis1] − [axis2] − ⋅⋅⋅;
(Up to 14 axes can be desig-
nated.)
Executes positioning at rapid traverse
speed for up to 14 axes simultaneously.
In programming, replace “−” with the nu-
merical data for each axis.
MVS
LINEAR INTER-
POLATION
MVS [axis1] − [axis2] − ⋅⋅⋅F−;
(Up to 14 axes can be desig-
nated.)
Executes linear travel at interpolation feed
speed F for up to 14 axes simultaneously.
MCW
MCC
CLOCKWISE CIR-
CULAR INTER-
POLATION
COUNTERCLOCK-
WISE CIRCULAR
INTERPOLATION
MCW [axis1] − [axis2] − R−
F−; MCC [axis1] − [axis2] −
U− V− T− F−;
Executes circular interpolation at tangential
speed F for two axes simultaneously fol-
lowing radius R (or designated center point
coordinates).
With the center point coordinate designa-
tion, multiple circles can be designated
with T−. (T− can also be omitted.)
MCW
MCC
CLOCKWISE HE-
LICAL INTER-
POLATION
COUNTERCLOCK-
WISE HELICAL IN-
TERPOLATION
MCW [axis1] − [axis2] −U−V−
[axis3] −T− F−;
MCC [axis1] − [axis2]
−R−[axis3] −F−;
Moves three axes simultaneously in a com-
bination of circular interpolation and linear
interpolation outside of the circular inter-
polation plane. Speed F will be the circular
interpolation tangential speed.
With the center point coordinate designa-
tion, the number of turns can be designated
with T−. (T− can also be omitted.)
ZRN
ZERO POINT RE-
TURN
ZRN [axis1] − [axis2] − ⋅⋅⋅;
(Up to 14 axes can be desig-
nated.)
Returns each axis to its zero point.
SKP
SKIP
SKP [axis1]− [axis2]− ⋅⋅⋅ SS−;
(Up to 14 axes can be desig-
nated.)
If the SKIP signal turns ON during a linear
interpolation operation, skips the remain-
ing movement and proceeds to the next
block.
MVT
SET TIME POSI-
TIONING
MVT [axis1]− [axis2]− ⋅⋅⋅ T−;
(Up to 14 axes can be desig-
nated.)
Executes positioning by clamping the feed
speed so that travel can be completed at the
designated time.
EXM
EXTERNAL POSI-
TIONING
EXM [axis1]− D−;
When an external positioning signal is in-
put while external positioning is being
executed, only the travel distance desig-
nated by “D−” is positioned with an incre-
mental value, and then the next command
is executed.
2
