13 programming examples, Example: ellipse, Programming examples – HEIDENHAIN TNC 640 (34059x-02) User Manual
Page 341: Programming examples 9.13
Programming examples 9.13
9
TNC 640 | User's Manual
HEIDENHAIN Conversational Programming | 5/2013
341
9.13
Programming examples
Example: Ellipse
Program sequence
The contour of the ellipse is approximated by many
short lines (defined in Q7). The more calculation
steps you define for the lines, the smoother the curve
becomes.
The milling direction is determined with the starting
angle and end angle in the plane :
Machining direction is clockwise:
Starting angle > end angle
Machining direction is counterclockwise:
Starting angle < end angle
The tool radius is not taken into account.
0 BEGIN PGM ELLIPSE MM
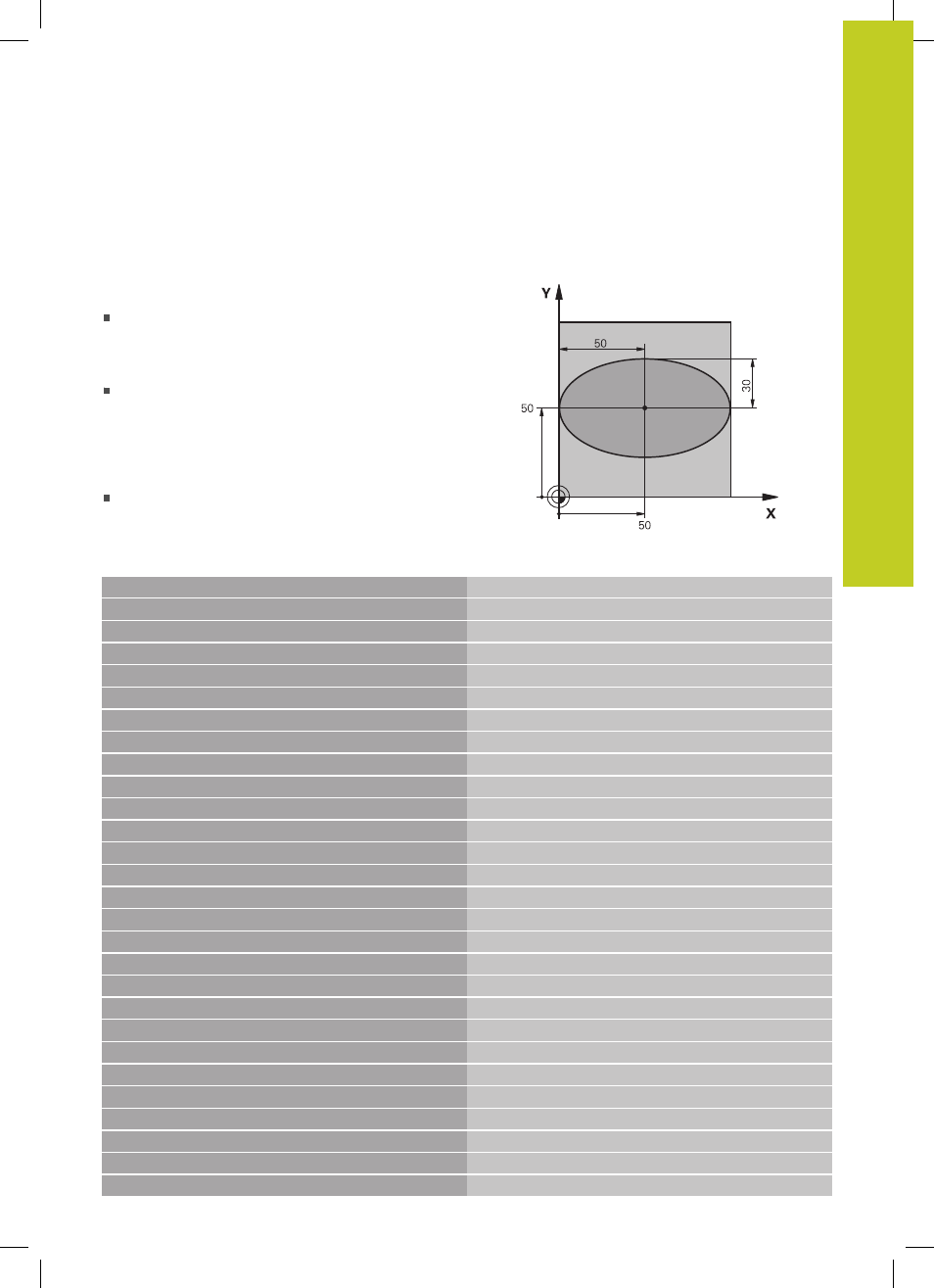
1 FN 0: Q1 = +50
Center in X axis
2 FN 0: Q2 = +50
Center in Y axis
3 FN 0: Q3 = +50
Semiaxis in X
4 FN 0: Q4 = +30
Semiaxis in Y
5 FN 0: Q5 = +0
Starting angle in the plane
6 FN 0: Q6 = +360
End angle in the plane
7 FN 0: Q7 = +40
Number of calculation steps
8 FN 0: Q8 = +0
Rotational position of the ellipse
9 FN 0: Q9 = +5
Milling depth
10 FN 0: Q10 = +100
Feed rate for plunging
11 FN 0: Q11 = +350
Feed rate for milling
12 FN 0: Q12 = +2
Set-up clearance for pre-positioning
13 BLK FORM 0.1 Z X+0 Y+0 Z-20
Definition of workpiece blank
14 BLK FORM 0.2 X+100 Y+100 Z+0
15 TOOL CALL 1 Z S4000
Tool call
16 L Z+250 R0 FMAX
Retract the tool
17 CALL LBL 10
Call machining operation
18 L Z+100 R0 FMAX M2
Retract the tool, end program
19 LBL 10
Subprogram 10: Machining operation
20 CYCL DEF 7.0 DATUM SHIFT
Shift datum to center of ellipse
21 CYCL DEF 7.1 X+Q1
22 CYCL DEF 7.2 Y+Q2
23 CYCL DEF 10.0 ROTATION
Account for rotational position in the plane
24 CYCL DEF 10.1 ROT+Q8
25 Q35 = (Q6 -Q5) / Q7
Calculate angle increment
26 Q36 = Q5
Copy starting angle
27 Q37 = 0
Set counter
