Virtual local area networks – Rockwell Automation 1734-AENTR EtherNet/IP Network Configuration User Manual User Manual
Page 145
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
145
Troubleshoot an EtherNet/IP Communication Module with Diagnostic Web Pages Chapter 10
Rockwell Automation Publication ENET-UM001L-EN-P - March 2014
145
Troubleshoot an EtherNet/IP Communication Module with Diagnostic Web Pages Chapter 10
IGMP snooping cannot control unicast or broadcast traffic. To learn how to
control unicast or broadcast traffic, see Virtual Local Area Networks on
.
This example assumes that the switch does not support IGMP snooping querier
function, so a router is required.
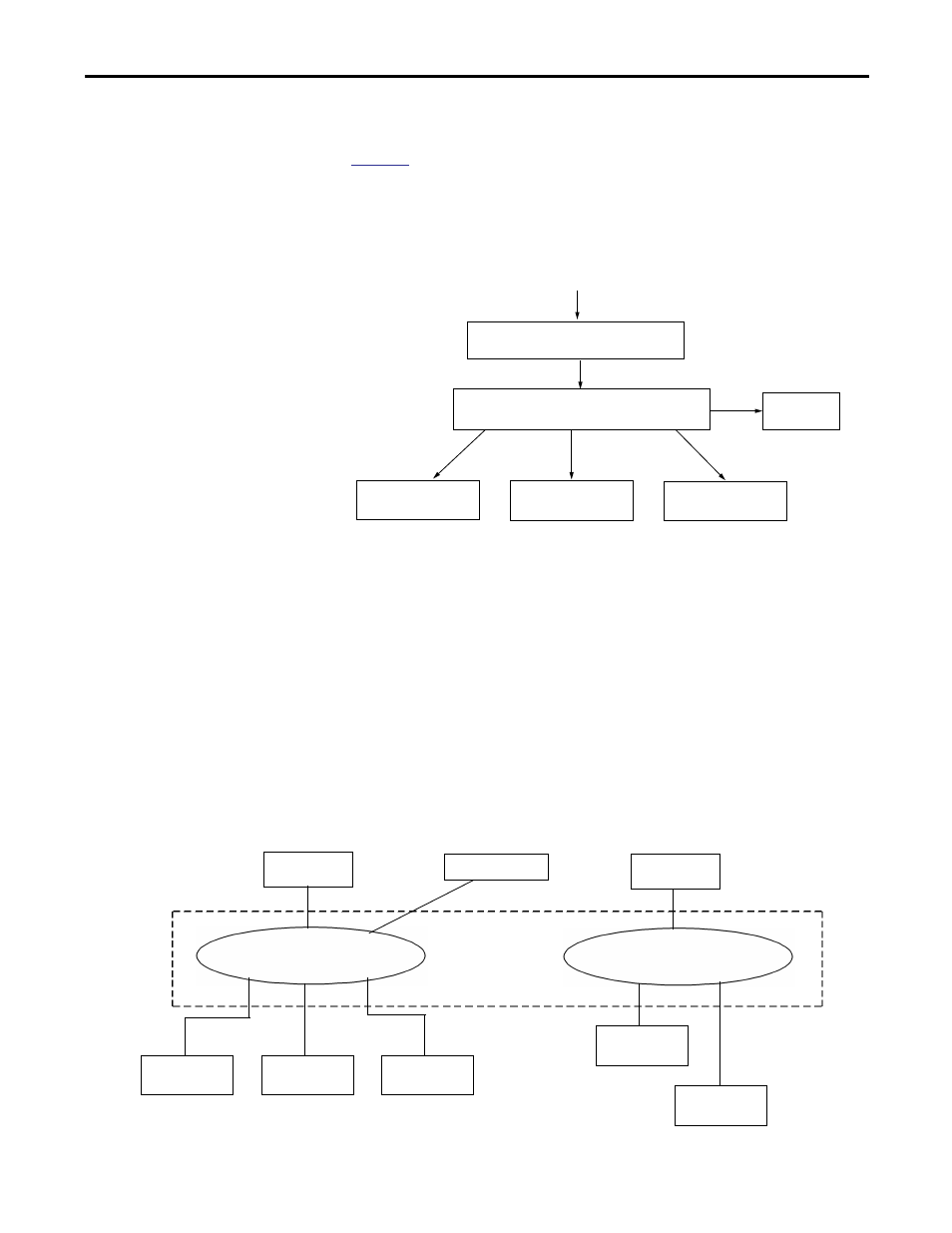
Figure 13 - IGMP Snooping Example
Virtual Local Area Networks
With a managed switch, you can establish virtual local area networks (VLAN) to
segregate various kinds of network traffic and also increase security between your
networks. You could create multiple isolated networks so that the traffic from
one network does not burden the other network.
As with IGMP snooping, VLAN can control multicast traffic. However, unlike
IGMP snooping, VLAN can also control and block this traffic:
• Unicast traffic
• Broadcast traffic
Figure 14 - Virtual Local Area Networks (VLAN)
Plant Network
Router sends out IGMP polls to determine
members of a multicast group.
Switch listens to the polls and responses and
identifies members of each multicast group.
Controller
(Consumer)
I/O
(Multicast Producer)
I/O
(Multicast Producer)
I/O
(Multicast Producer)
Controller A
Workstation
Controller B
VLAN A
VLAN 2
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Switch
- 1734-AENT EtherNet/IP Network Configuration User Manual 22-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Network Configuration User Manual 20-COMM-E EtherNet/IP Network Configuration User Manual 1794-AENT EtherNet/IP Network Configuration User Manual 1783-Etxx EtherNet/IP Network Configuration User Manual 1769-Lxxx EtherNet/IP Network Configuration User Manual 1756-Enxx EtherNet/IP Network Configuration User Manual
