Internet group management protocol (igmp) – Allied Telesis AT-WL2411 User Manual
Page 89
AT-WL2411 Installation and User’s Guide
89
An IP Tunnels configuration is shown in Figure 36.
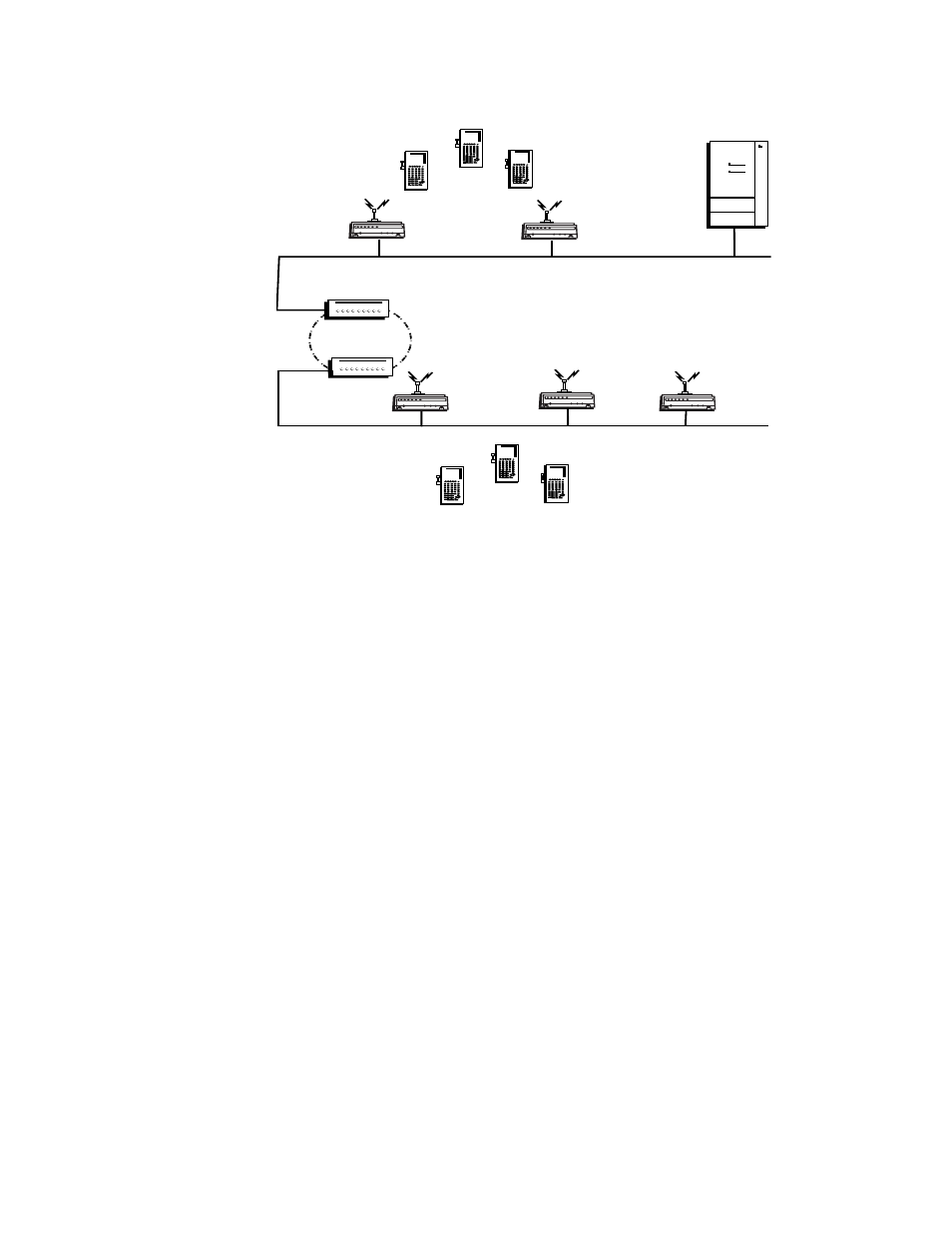
Figure 36 IP Tunnels Configuration
A non-root access point can concurrently receive hello messages on its
Ethernet port, its radio port, and its IP tunnel port. However, an access
point can use only one port to attach to the network. Port priorities are
structured so that an Ethernet connection is always selected first and an
IP tunnel connection is always selected before a radio connection.
Setting the secondary LAN bridge priority to zero disables the bridging
of wireless traffic to remote IP subnets. It allows end devices that are
connected to access points on a remote IP subnet to communicate with
hosts on the home subnet without bridging wireless traffic to the
remote IP subnet. This is always done for IP communication since the
wireless traffic is always from the home subnet and not from the remote
subnet. The secondary LAN bridge priority will allow you to select the
bridging mode for non-IP traffic such as NNL.
Internet Group
Management
Protocol (IGMP)
IGMP lets you originate multiple IP tunnels using a single IP multicast
address. Note that IGMP is independent of IP; it can be used to facilitate
multicast for IP or any other application.
IP routers only forward multicast packets to those subnets that have IP
hosts that participate in the respective IP multicast group. An IP host
uses IGMP to notify IP routers that it wants to participate in an IP
multicast group. Access points can act as IP hosts and participate in an IP
UAP 1
(root)
IP router
UAP 2
UAP 3
(Designated
Bridge)
UAP 5
Primary LAN
home subnet
Secondary LAN
remote subnet
Wireless
stations
21XXT028.eps
IP router
UAP 4
IP network
Wireless
stations
Host
