Configuring point-to-point bridges – Allied Telesis AT-WL2411 User Manual
Page 118
AT-WL2411 Installation and User’s Guide
118
Configuring Point-to-Point Bridges
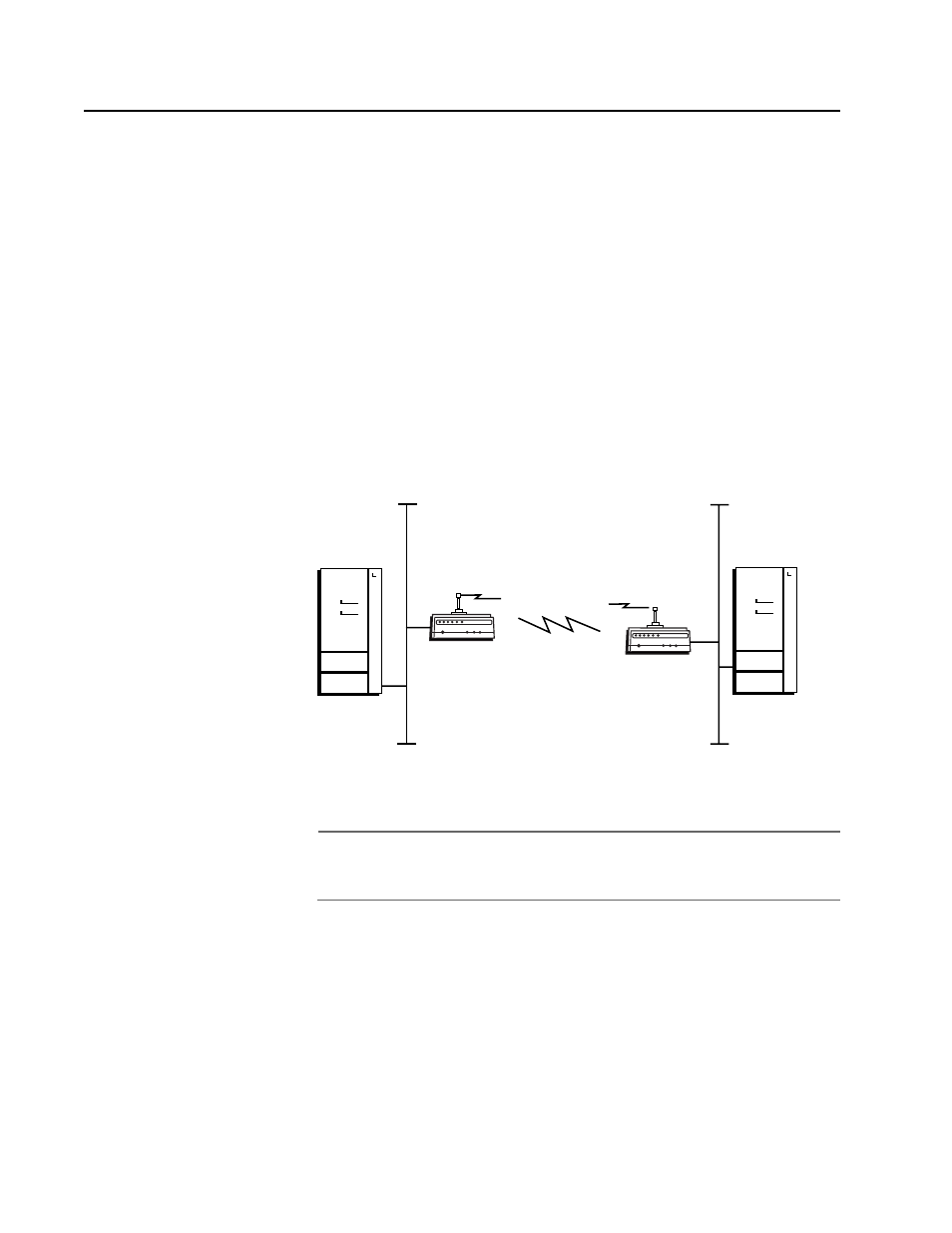
In your environment, you may have point-to-point bridges, which send
data from wireless end devices on a secondary LAN to a primary LAN.
This data is sent via a wireless hop. Wireless hops are formed when data
from wireless end devices move from one access point to another access
point through the radio ports.
These access points can be acting simultaneously as access points and
bridges or they can be acting as a bridge that is communicating to other
access points. If these access points are acting as access points and
bridges and if they connect 802.11b networks, each access point must
contain two of the same radios. If they connect 902 MHz networks or if
they are simply acting as a bridge, each access point only needs one
radio.
Figure 51 illustrates a point-to-point bridge configuration.
Figure 51 Point-to-Point Bridging
Note
Before you can create wireless hops, the radios in the access points
must be communicating with each other.
To create wireless hops, one radio in the point-to-point bridge on the
primary LAN must be configured as a master and one radio in the bridge
on the secondary LAN must be configured as a station. If you have two
radios in the bridge, one radio must be configured as a master and the
other as a station. The master radio in the bridge on the primary LAN
must have the Wireless Hops parameter enabled so that it honors
connections from station radios. The master radio transmits hello
packets, which allow the bridge on the secondary LAN to attach to the
spanning tree in the same way that wired access points do.
Host
21XXT013
.eps
Ethernet
Ethernet
Host
