HP XP Racks User Manual
Page 60
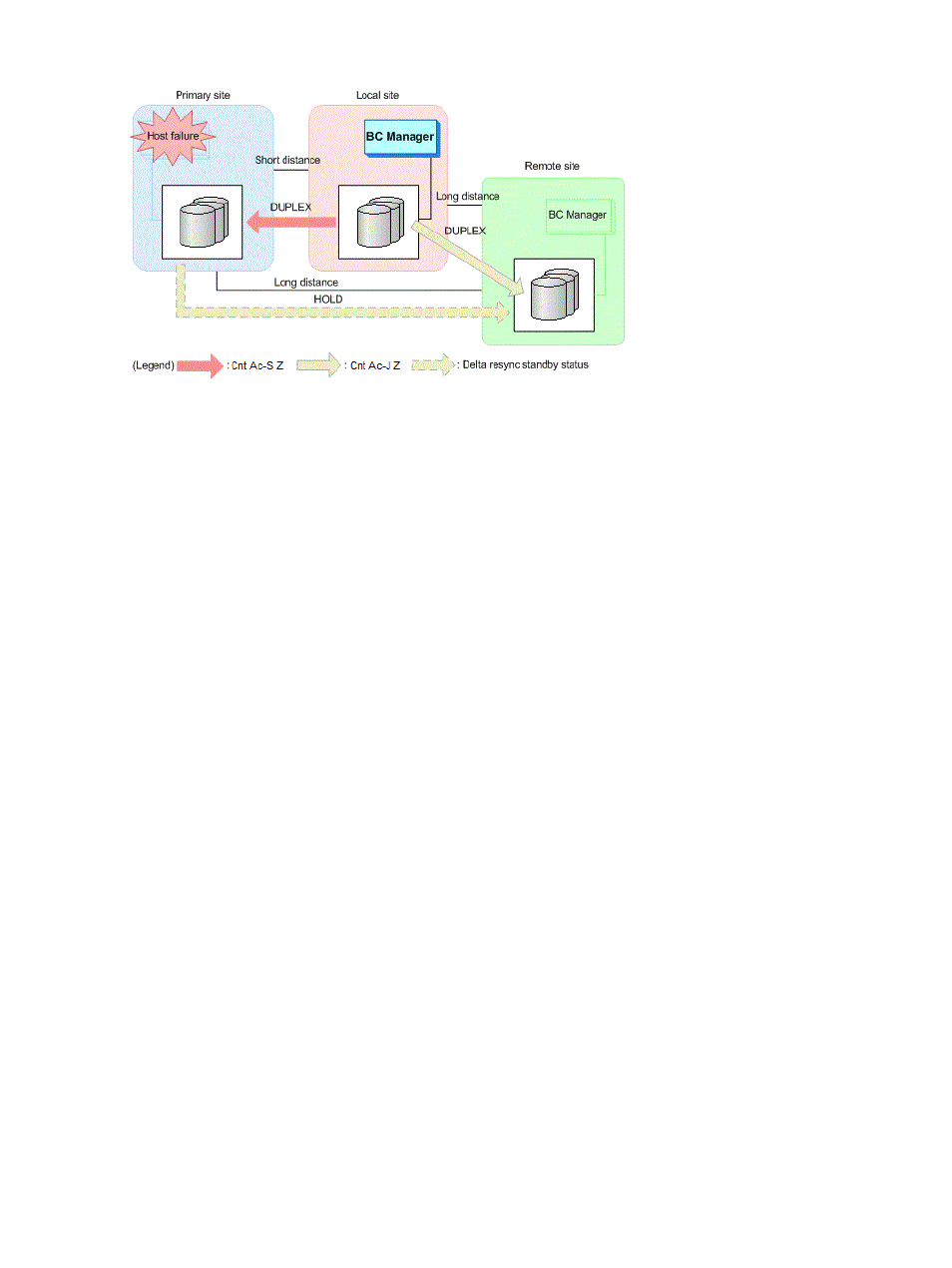
Figure 21 Example of a Delta Resync configuration (after a Delta Resync is performed)
2DC Configuration with HyperSwap and Continuous Access Journal
A 2DC configuration with HyperSwap and Continuous Access Journal Z can continue operating
even after a HyperSwap is performed.
The HyperSwap functionality reverses the relationship between a P-VOL and an S-VOL by using
TPC-R when the primary storage system and local storage system are connected to the same host
and a failure occurs during access to the primary storage system. HyperSwap enables the I/O
destination volume to be switched during a primary storage system failure or maintenance without
stopping operations.
With this configuration, Delta Resyncs are executed after a HyperSwap, allowing operations to
restart temporarily under a 2DC configuration after the HyperSwap with very little downtime.
To define a 2DC configuration with HyperSwap and Continuous Access Journal Z, create a PPRC
copy pair for which HyperSwaps are enabled. Next, in Business Continuity Manager, define that
copy pair as a Continuous Access Synchronous Z copy pair with the HyperSwap attribute. Also,
create a Continuous Access Journal Z copy pair between the primary storage system and remote
storage system, and then create a Continuous Access Journal Z copy pair in the delta-resync standby
status between the local storage system and remote storage system. If a copy pair is a Continuous
Access Synchronous Z copy pair with the HyperSwap attribute, the only operations that Business
Continuity Manager can perform on it are monitoring or dissolving it.
and
show a configuration before and after a HyperSwap
is performed.
60
Business Continuity Manager with replication products
