Inter-disk controller logical paths – HP XP Racks User Manual
Page 114
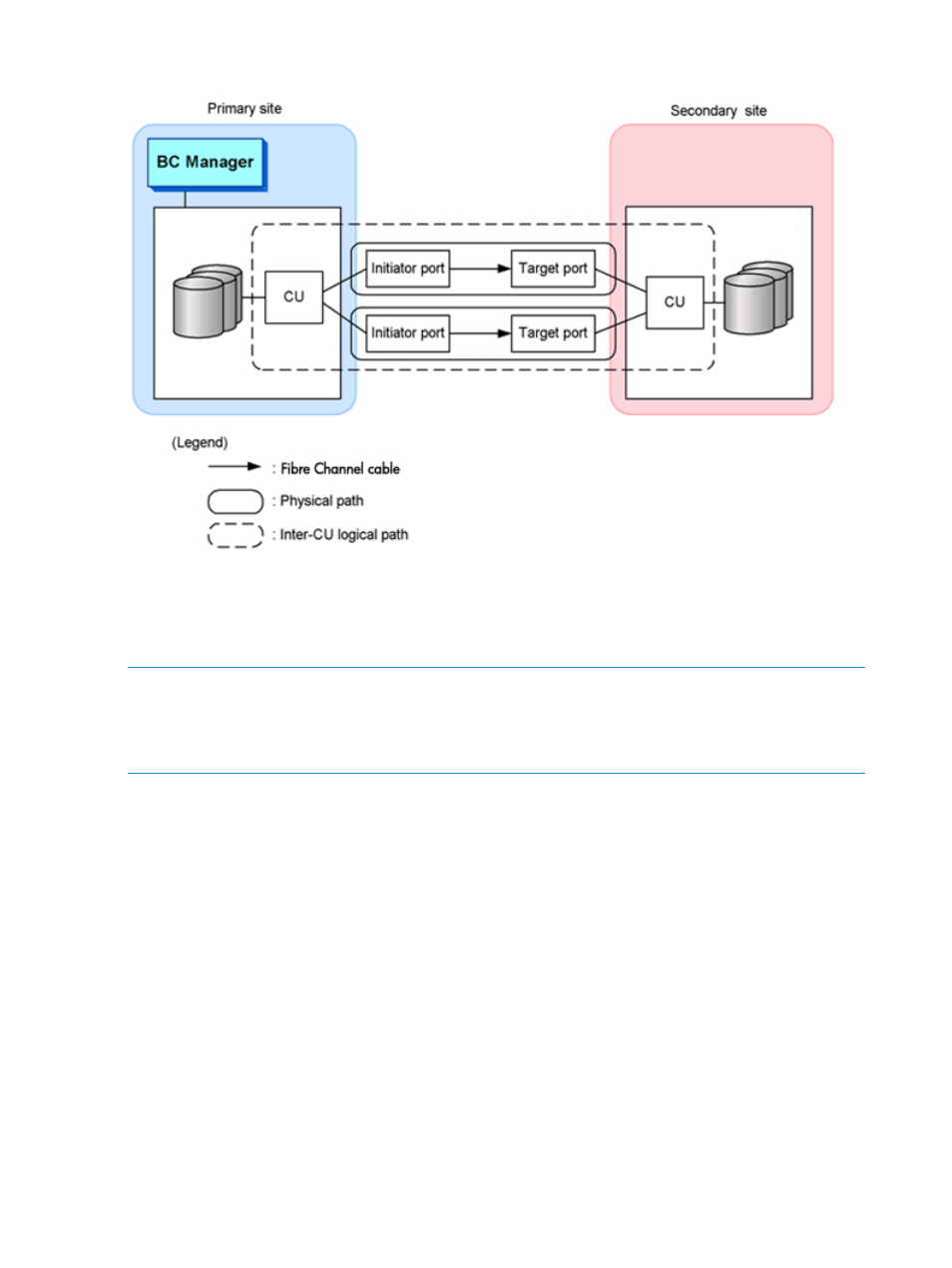
Figure 65 Overview of the inter-control unit logical path (forward direction)
When the Reverse Resync function is used, an inter-control unit logical path from the secondary
site to the primary site (reverse direction) is also necessary. To establish a reverse direction
inter-control unit logical path, the route list needs to be set and the command device needs to be
registered.
NOTE:
When using the following models, you cannot establish or delete an inter-control unit
logical path from the secondary site to the primary site (reverse direction) by using the command
device.
•
XP12000/XP10000 Disk Arrays that do not support Continuous Access Journal Z functions
Inter-disk controller logical paths
An inter-disk controller logical path is a logical path provided between an XP12000/XP10000,
an XP24000/XP20000, XP P9500 disk array, and/or XP7 storage for Cnt Ac-J Z operations
between storage systems. It is a virtual communication path established between the primary
storage system and secondary storage system on a physical path, when an MCU within the primary
storage system and a RCU within the secondary storage system are connected by at least one FC
cable.
When an inter-disk controller logical path is established, communication is enabled between a
journal group that belongs to the primary storage system, and a journal group of the secondary
storage system.
Path group IDs can be specified to establish multiple inter-disk controller logical paths between the
same storage systems. If path group IDs are specified when defining journal groups, inter-disk
114
Understanding Business Continuity Manager functions
