Host machines that can be paired – HP XP RAID Manager Software User Manual
Page 22
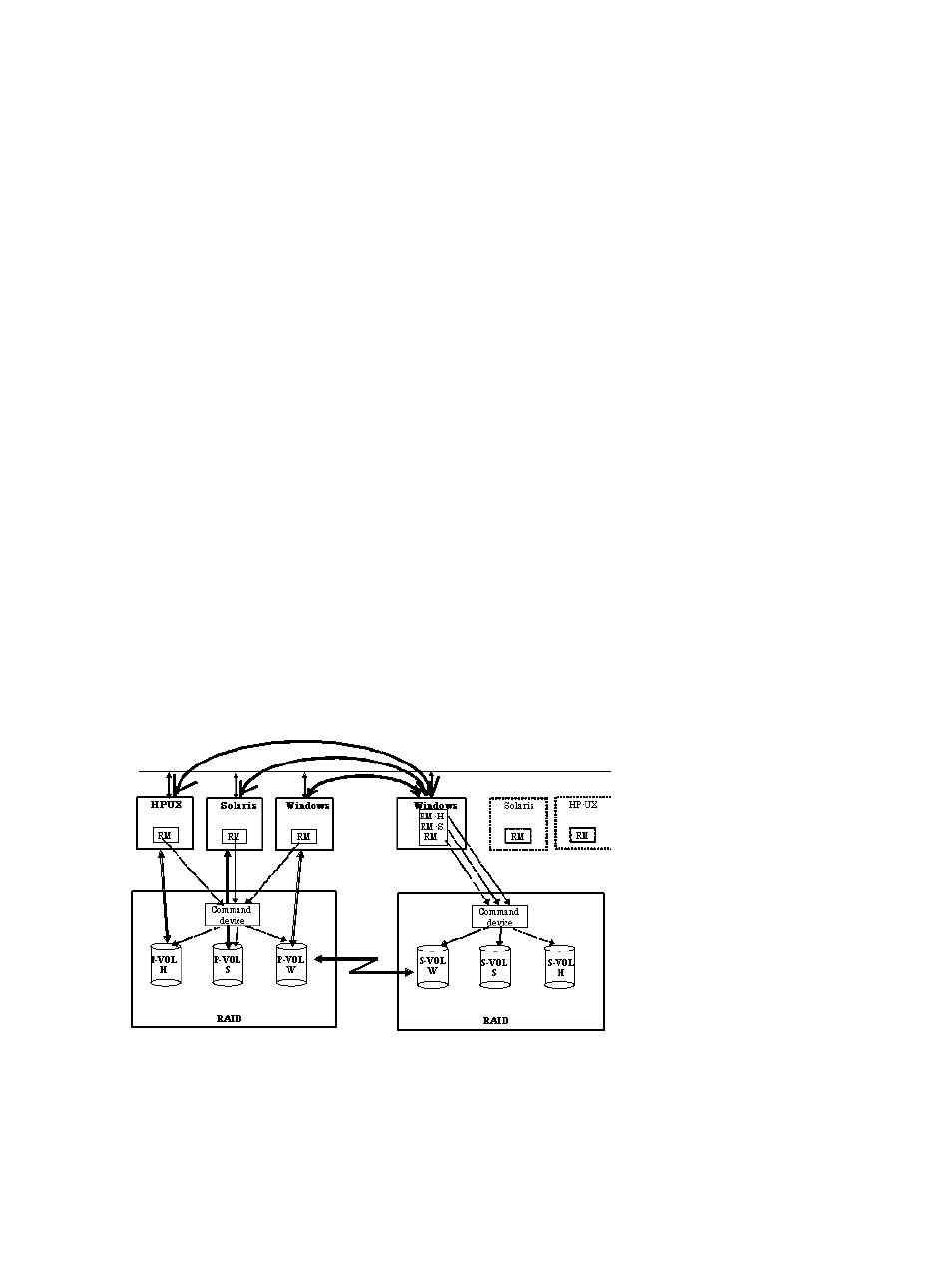
by different hosts. This guards against storage system failure as well as host failure. The RAID
Manager instances of separate hosts are connected via the LAN so that they can maintain
awareness of each other. Each RAID storage system has a command device that communicates
with each RAID Manager instance independently. Each storage system contains the primary
volumes of its connected RAID Manager instance and the secondary volumes of the other RAID
Manager instance (located on a different host in this case).
Host machines that can be paired
When you perform a pair operation, the version of RAID Manager should be the same on the
primary and secondary sites. As a particular application uses HORC, users sometimes use a HORC
volume as the data backup volume for the server. In this case, RAID Manager requires that the
RAID Manager instance correspond to each OS platform that is located on the secondary site for
the pair operation of data backup on the primary servers of each OS platform.
However, it is possible to prepare only one server at a secondary site by supporting RAID Manager
communications among different OSs (including the converter for little-endian vs big-endian).
represents RAID Manager’s communication among different OSs, and
shows the supported communication (32-bit, 64-bit, MPE/iX) among different
OSs. Please note the following terms that are used in the example:
•
RM-H: Value of HORCMFCTBL environment variable for an HP-UX RAID Manager instance
on Windows
•
RM-S: Value of HORCMFCTBL environment variable for a Solaris RAID Manager instance on
Windows
Restriction: RAID Manager for MPE/iX cannot communicate with 64-bit HORCM.
Restriction: RAID Manager’s communications among different operating systems is supported on
HP-UX, Solaris, AIX, Linux, and Windows (this is not supported on Tru64 UNIX/Digital UNIX).
Also, RAID Manager does not require that the HORCMFCTBL environment variable be set—except
for RM-H and RM-S instances (to ensure that the behavior of the operating system platform is
consistent across different operating systems).
Figure 11 RAID Manager communication among different operating systems
22
RAID Manager software environment
