Continuous access synchronous remote commands – HP XP RAID Manager Software User Manual
Page 131
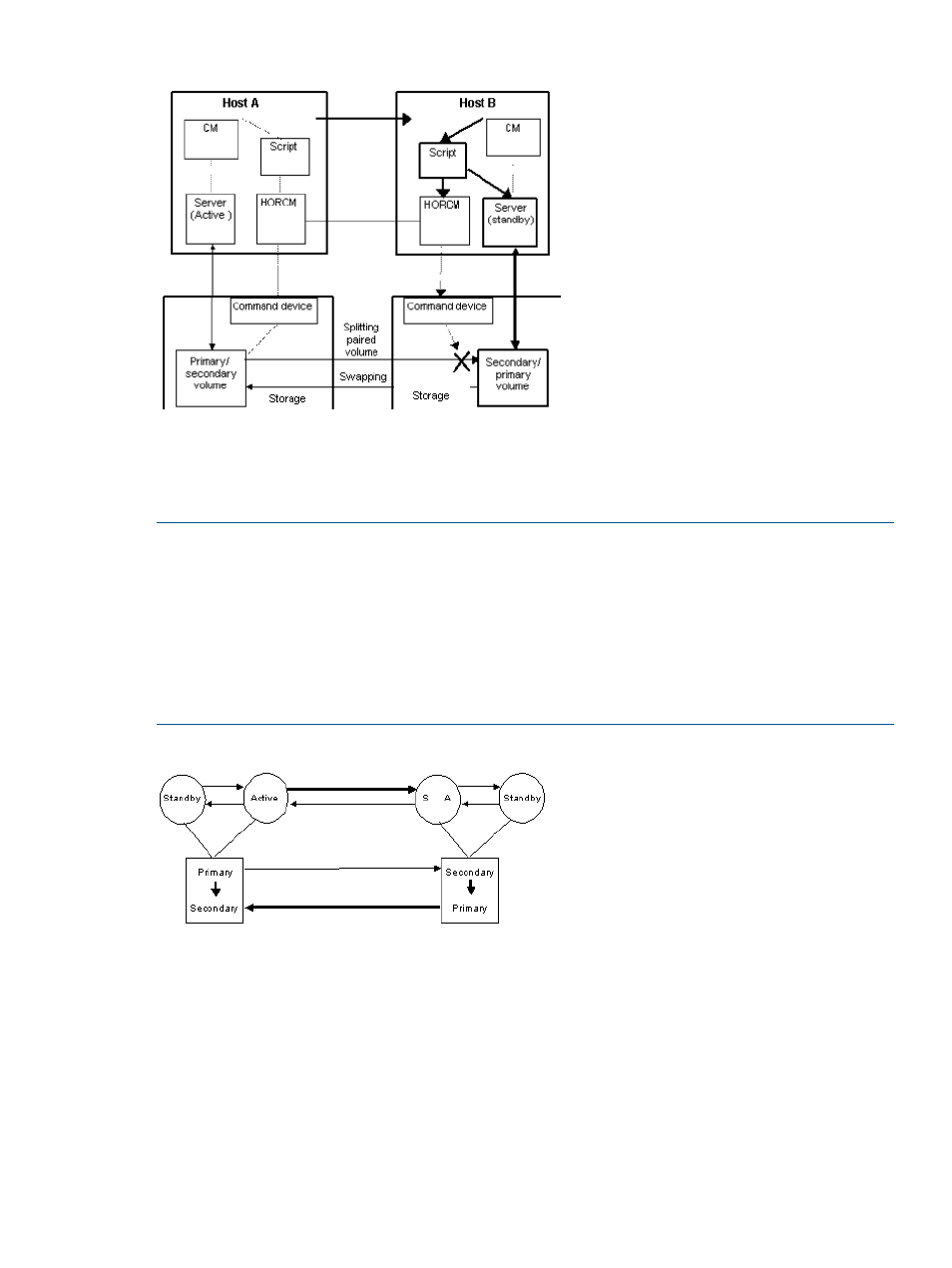
Figure 50 Server failover system configuration
In an HA environment, a package is a group of applications that are scripted to run on the
secondary host in the event of a primary host failure. When using the HA software (e.g.,
MC/ServiceGuard), the package can be transferred to the standby node as an operation executed
by the system administrator (see
).
NOTE:
If the operation is performed when RAID Manager and Continuous Access Synchronous
are being used, the volume is switched from primary to secondary as if an error had occurred,
even though data consistency is assured. When restoral of the original node occurs along with its
original package (group of applications), it is necessary to copy the data on the secondary volume
onto the primary volume; this operation can take as much time as the initial copy operation for the
pair. In actual operation, no package can be transferred when Continuous Access Synchronous
is being used. The secondary package is switched to the primary package, and vice versa, when
the primary volume is switched to the secondary volume. Therefore, the primary and secondary
Continuous Access Synchronous volumes should be switched depending on the package state.
Figure 51 Package transfer on high availability (HA) software
Continuous Access Synchronous remote commands
illustrates a Continuous Access Synchronous remote configuration. The RAID
Manager Continuous Access Synchronous remote commands assist the system operation with
volume backups among UNIX servers and their operating system management functions. The
Continuous Access Synchronous remote pair commands are also used to copy volumes in server
failover configurations and to restore the volumes to their original state after a server failover has
been recovered.
•
Pair creation command: Creates a new volume pair. Volume pairs can be created in units of
volume or group.
•
Pair splitting command: Splits a volume pair and allows read and write access to the secondary
volume.
Continuous Access Synchronous operations
131
