HP XP RAID Manager Software User Manual
Page 139
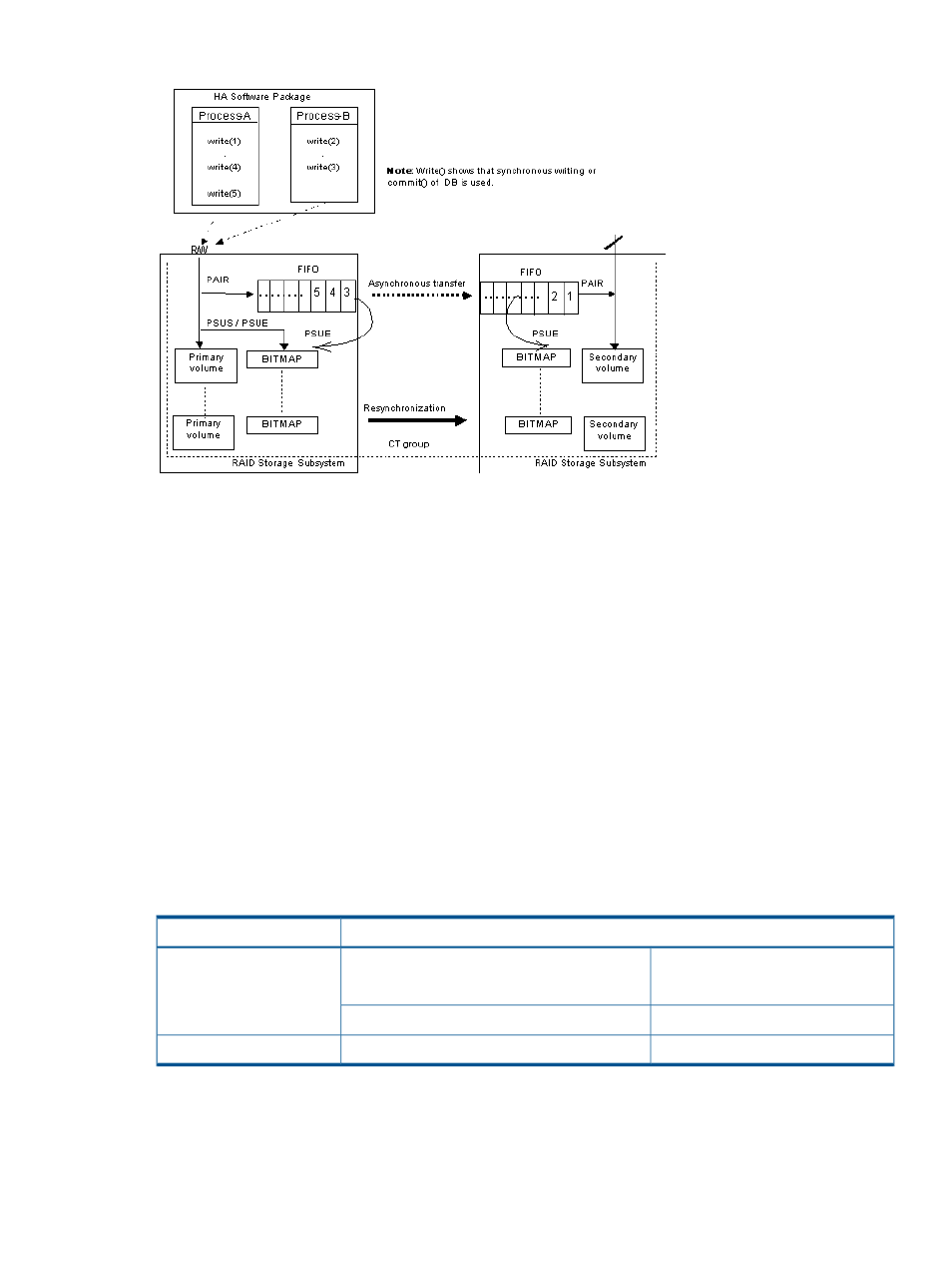
Figure 54 Continuous Access Asynchronous consistency groups
Restrictions
•
Group definition of Continuous Access Asynchronous/Continuous Access Journal/Continuous
Access Synchronous volume: All volumes in a group must be contained within the same storage
system. If two or more groups of RAID Manager include the same CT group (CTGID), then
pair operation of the group specification is handled in CT group entirety.
•
Registration of CTGID number and limitations: RAID Manager registers CTGID to RAID disk
array automatically when paired volumes are created by paircreate command, and groups
of configuration definition files are mapped to CTGID. The maximum number of CT groups is
256 for P9500, XP24000/20000 Disk Arrays, and 128 (CTGID0 – CTGID 127) for XP12000
Disk Array/XP10000 Disk Arrays, 64 for XP1024/XP128 (CTGID0 to CTGID63), and
16(CTGID0- CTGID15) for XP512/XP48 Disk Arrays. Continuous Access
Asynchronous/Continuous Access Journal pair command is terminated with EX_ENOCTG
when the maximum number of CT groups is exceeded.
•
Relationships between CTGID and Journal ID: CT group numbers 0-127 are used for Continuous
Access Asynchronous, Continuous Access Synchronous, and Continuous Access Journal. The
rest of the CT group numbers 128-255 are used only for Continuous Access Journal, and are
mapped to the journal.
Table 31 Assignment of consistency group IDs (CTGIDs)
Assignment
CTGID
CTG 0-127
Continuous Access Asynchronous
0 -127
Continuous Access Synchronous
JNG 0-127
Continuous Access Journal
JNG 128-255
Continuous Access Journal
128 - 255
•
At-time Split for Continuous Access Synchronous: The operation for making data consistency
is only supported by the following option:
pairsplit -g
pairsplit -g
Continuous Access Synchronous, Business Copy, and Continuous Access Journal operations
139
