Avago Technologies MegaRAID SATA 150-4 (523) User Manual
Page 59
Configuration Utility Menu
3-11
Version 2.0
Copyright © 2003–2006 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
The View/Update Parameters submenu is accessible through the
View/Update Parameters option in the Logical Drive submenu.
describes the Advance submenu.
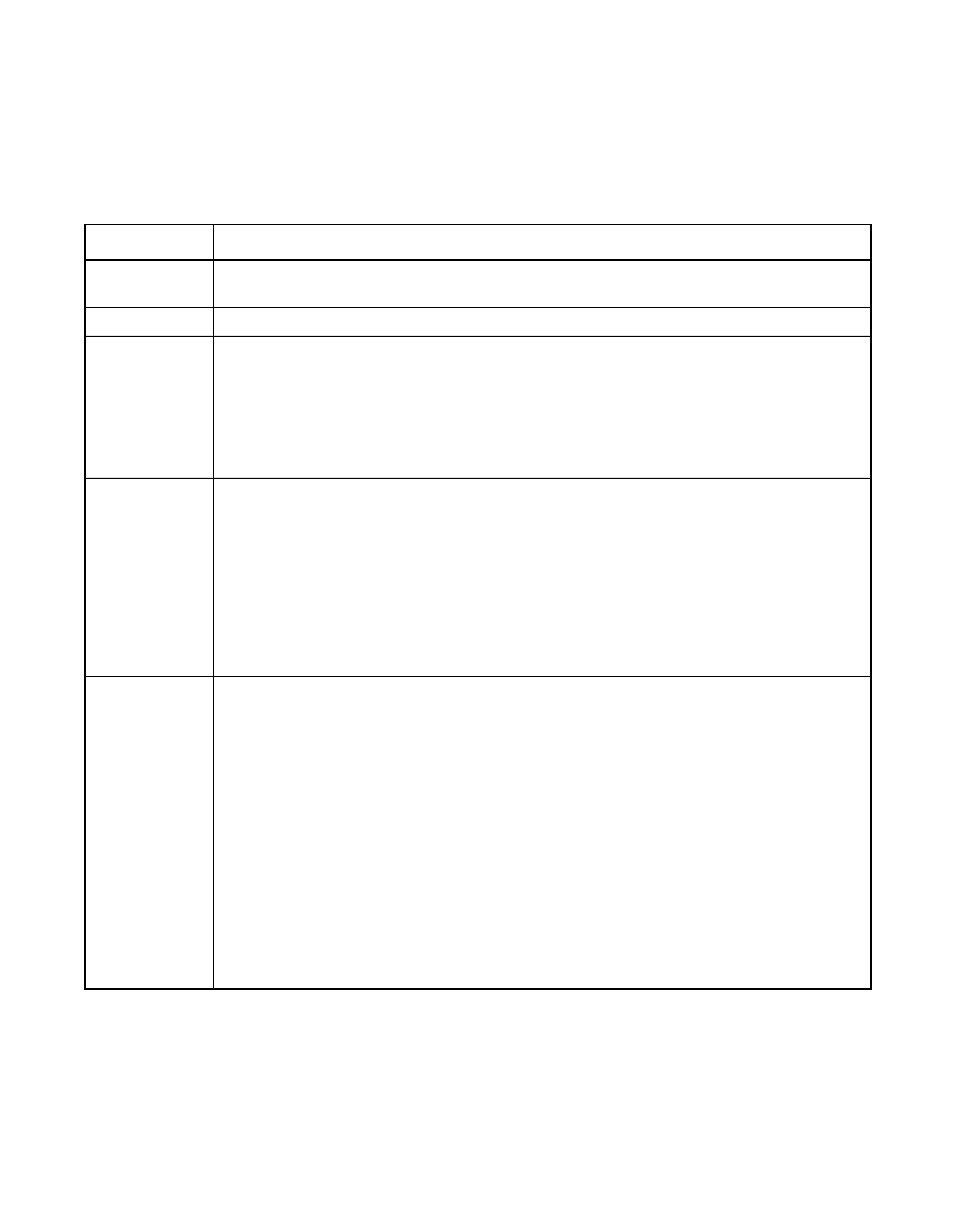
Table 3.5
Configuration Utility View/Update Parameters Submenu
Option
Description
RAID
Use this option to indicate the RAID level for the array. The number of physical drives
in a specific array determines the RAID levels that can be implemented with the array.
Size
Use this option to indicate the size of the logical drive in Mbytes.
Stripe Size
Use this option to specify the size of the segments written to each drive in a RAID 1,
5, 10, or 50 configuration. The default stripe size is 64 Kbytes. You can set the stripe
size to 8, 16, 32, 64, or 128 Kbytes.
A larger stripe size improves read performance, especially if your system performs
mostly sequential reads. However, if you are sure that your computer does random
read requests more often, select a small stripe size.
Write Policy
1
Use this option to set the caching method to write-through or write-back. The default
setting is write-through caching. In write-through caching, the controller sends a data
transfer completion signal to the host after the disk subsystem receives all the data in
a transaction.
In write-back caching, the controller sends a data transfer completion signal to the
host after the controller cache receives all the data in a transaction.
Write-through caching has a data security advantage over write-back caching, while
write-back caching has a performance advantage.
Read Policy
Use this option to enable the read-ahead cache feature for the logical drive. You can
set this parameter to Normal, Read-Ahead, or Adaptive. The default setting is Normal.
Normal caching specifies that the controller reads only the requested data and does
not read ahead for the current logical drive.
Read-Ahead caching specifies that the controller uses read-ahead caching for the
current logical drive. Read-Ahead caching allows the controller to read sequentially
ahead of requested data and to store the additional data in cache memory,
anticipating that the data is needed soon. Read-Ahead supplies sequential data faster,
but is not as effective when accessing random data.
Adaptive specifies that the controller begins using Read-Ahead caching if the two
most recent disk accesses occurred in sequential sectors. If all read requests are
random, the algorithm reverts to Normal; however, all requests are still evaluated for
possible sequential operation.
