Table2.7 raid 5 overview, Raid 5 overview – Avago Technologies MegaRAID SATA 150-4 (523) User Manual
Page 38
2-16
Introduction to RAID
Copyright © 2003–2006 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
2.5.2.3
RAID 5
RAID 5 includes disk striping at the block level and parity. In RAID 5, the
parity information is written to several drives. RAID 5 is best suited for
networks that perform a lot of small input/output (I/O) transactions
simultaneously.
RAID 5 addresses the bottleneck issue for random I/O operations.
Because each drive contains both data and parity, numerous writes can
take place concurrently. In addition, robust caching algorithms and
hardware-based, exclusive-or assist make RAID 5 performance
exceptional in many different environments.
provides an overview of RAID 5.
2.5.2.4
RAID 10
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. RAID 10 consists of
striped data across mirrored spans. RAID 10 breaks up data into smaller
blocks, then mirrors the blocks of data to each RAID 1 set. Each RAID 1
set then duplicates its data to its other drive. The size of each block is
determined by the stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation
of the RAID set. Up to 8 spans can be supported by RAID 10.
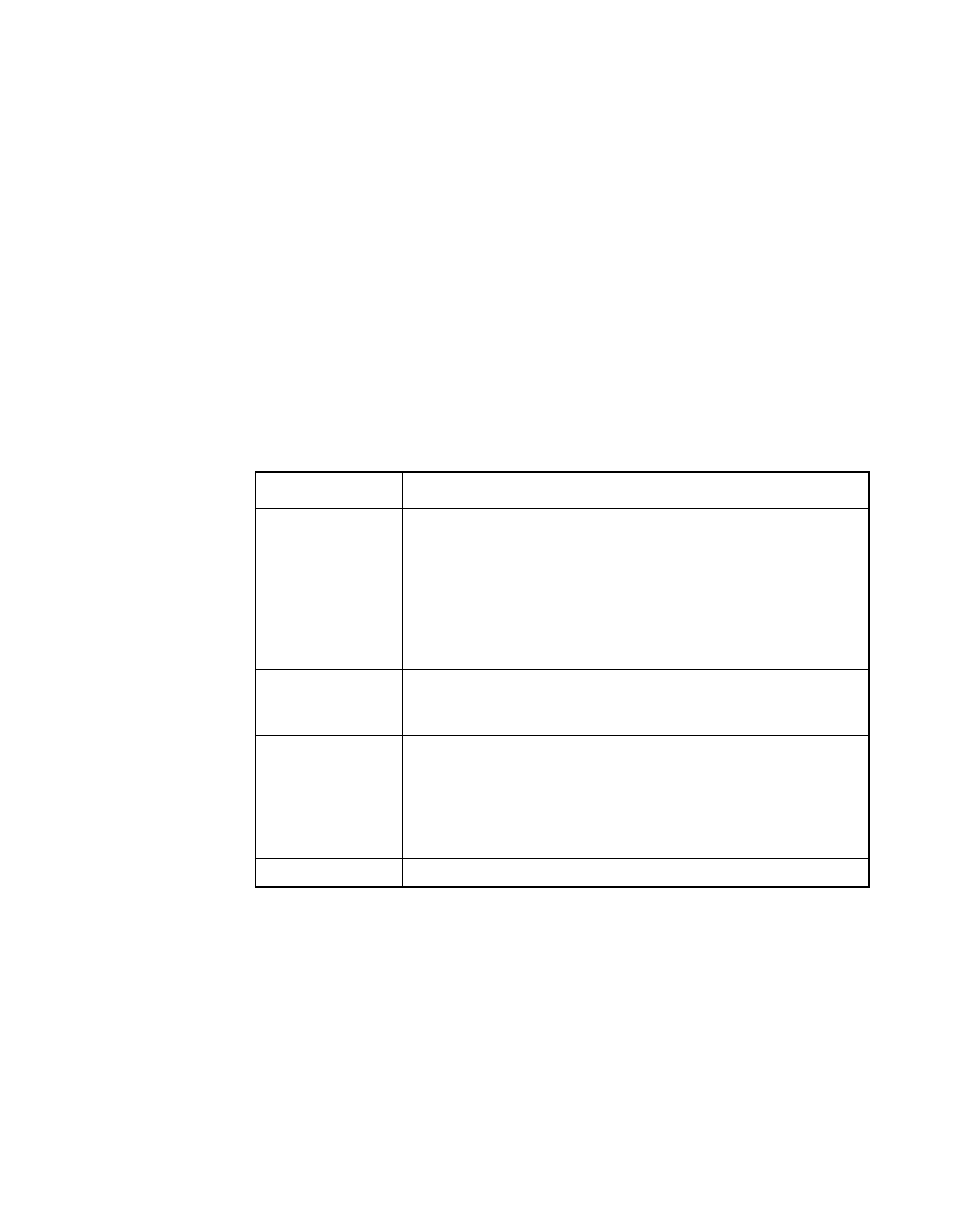
Table 2.7
RAID 5 Overview
Feature
Description
Uses
Provides high data throughput, especially for large files. Use
RAID 5 for transaction processing applications because
each drive can read and write independently. If a drive fails,
the RAID controller uses the parity drive to recreate all
missing information. Use also for office automation and
online customer service that requires fault tolerance. Use for
any application that has high read request rates but low write
request rates.
Strong Points
Provides data redundancy, high read rates, and good
performance in most environments. Provides data
redundancy with lowest loss of capacity.
Weak Points
Not well-suited to tasks requiring numerous writes. Suffers
more impact if no cache is used (clustering). Disk drive
performance is reduced if a drive is being rebuilt.
Environments with few processes do not perform as well
because the RAID overhead is not offset by the performance
gains in handling simultaneous processes.
Drives
3 to (14 drives x the number of channels).
