3 maximizing storage capacity, Table2.12 raid levels and capacity, Maximizing storage capacity – Avago Technologies MegaRAID SATA 150-4 (523) User Manual
Page 44: Raid levels and capacity
2-22
Introduction to RAID
Copyright © 2003–2006 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
2.6.3
Maximizing Storage Capacity
Storage capacity is an important factor when selecting a RAID level.
There are several variables to consider. Mirrored data and parity data
require more storage space than striping alone (RAID 0). Parity
generation uses algorithms to create redundancy and requires less
space than mirroring.
explains the effects of the RAID levels
on storage capacity.
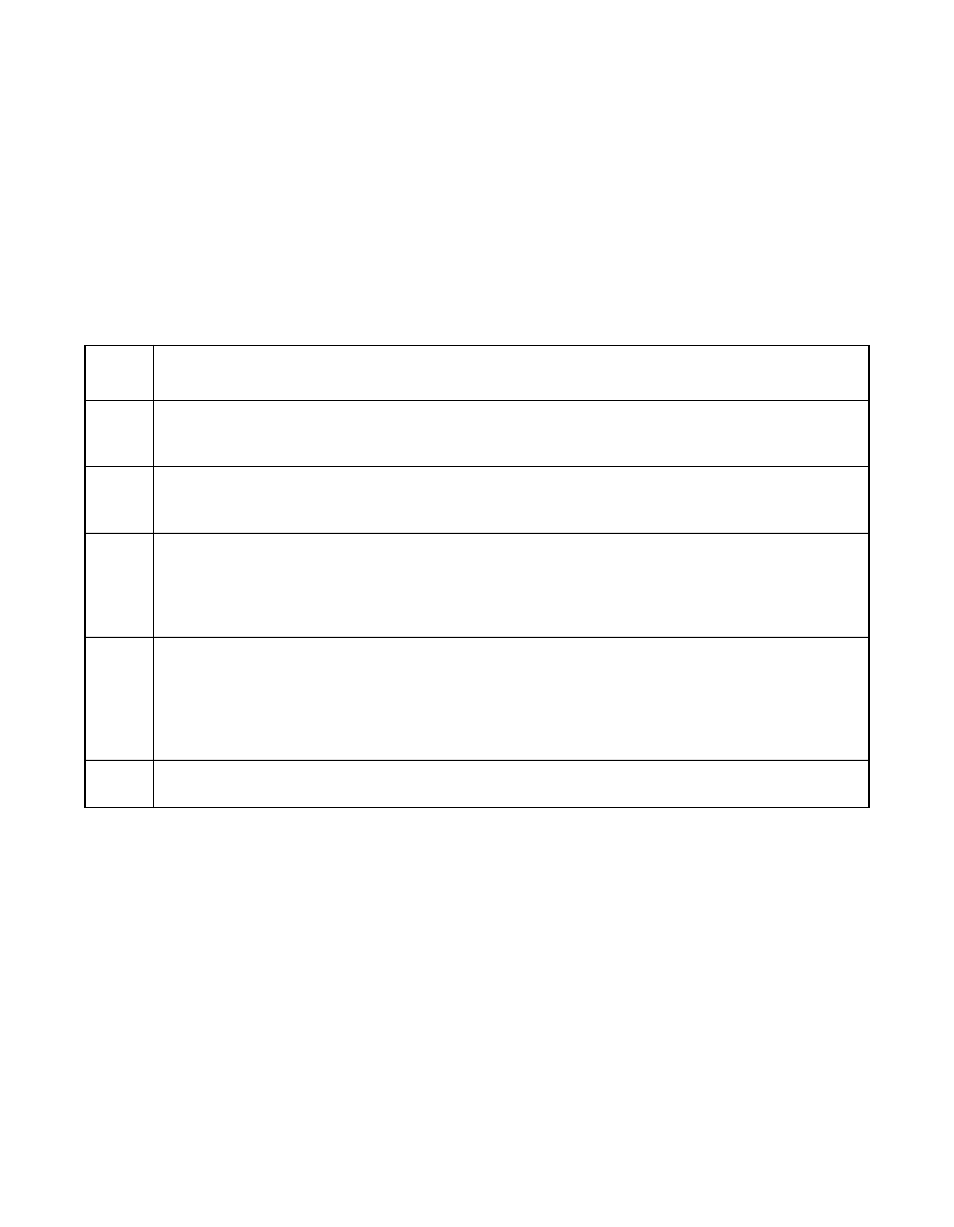
Table 2.12
RAID Levels and Capacity
RAID
Level
Capacity
0
RAID 0 (disk striping) involves partitioning each drive storage space into stripes that can vary
in size. The combined storage space is composed of stripes from each drive. RAID 0 provides
maximum storage capacity for a given set of physical disks.
1
With RAID 1 (disk mirroring), data written to one disk drive is simultaneously written to
another disk drive, which doubles the required data storage capacity. This is expensive
because each drive in the system must be duplicated.
5
RAID 5 (distributed parity) provides redundancy for one drive failure without duplicating the
contents of entire disk drives. RAID 5 breaks up data into smaller blocks, calculates parity by
performing an exclusive-or on the blocks, then writes the blocks of data and parity to each
drive in the array. The size of each block is determined by the stripe size parameter, which
is set during the creation of the RAID set.
10
RAID 10 (disk spanning) requires twice as many drives as all other RAID levels except RAID
1. RAID 10 works well for medium-sized databases or any environment that requires a higher
degree of fault tolerance and moderate to medium capacity. Disk spanning allows multiple
disk drives to function like one big drive. Spanning overcomes lack of disk space and
simplifies storage management by combining existing resources or adding relatively
inexpensive resources.
50
RAID 50 (disk spanning) requires two to four times as many parity drives as RAID
5.
This
RAID level works best when used with data that requires medium to large capacity.
