Table2.5 raid 0 overview, Table2.6 raid 1 overview, Raid 0 overview – Avago Technologies MegaRAID SATA 150-4 (523) User Manual
Page 37: Raid 1 overview
RAID Levels
2-15
Copyright © 2003–2006 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
By breaking up a large file into smaller blocks, the RAID controller can
use several drives to read or write the file faster. RAID 0 involves no
parity calculations to complicate the write operation. This makes RAID 0
ideal for applications that require high bandwidth but do not require fault
tolerance. RAID 0 also denotes an independent or single drive.
provides an overview of RAID 0.
2.5.2.2
RAID 1
In RAID 1, the RAID controller duplicates all data from one drive to a
second drive. RAID 1 provides complete data redundancy, but at the cost
of doubling the required data storage capacity.
provides an overview of RAID 1.
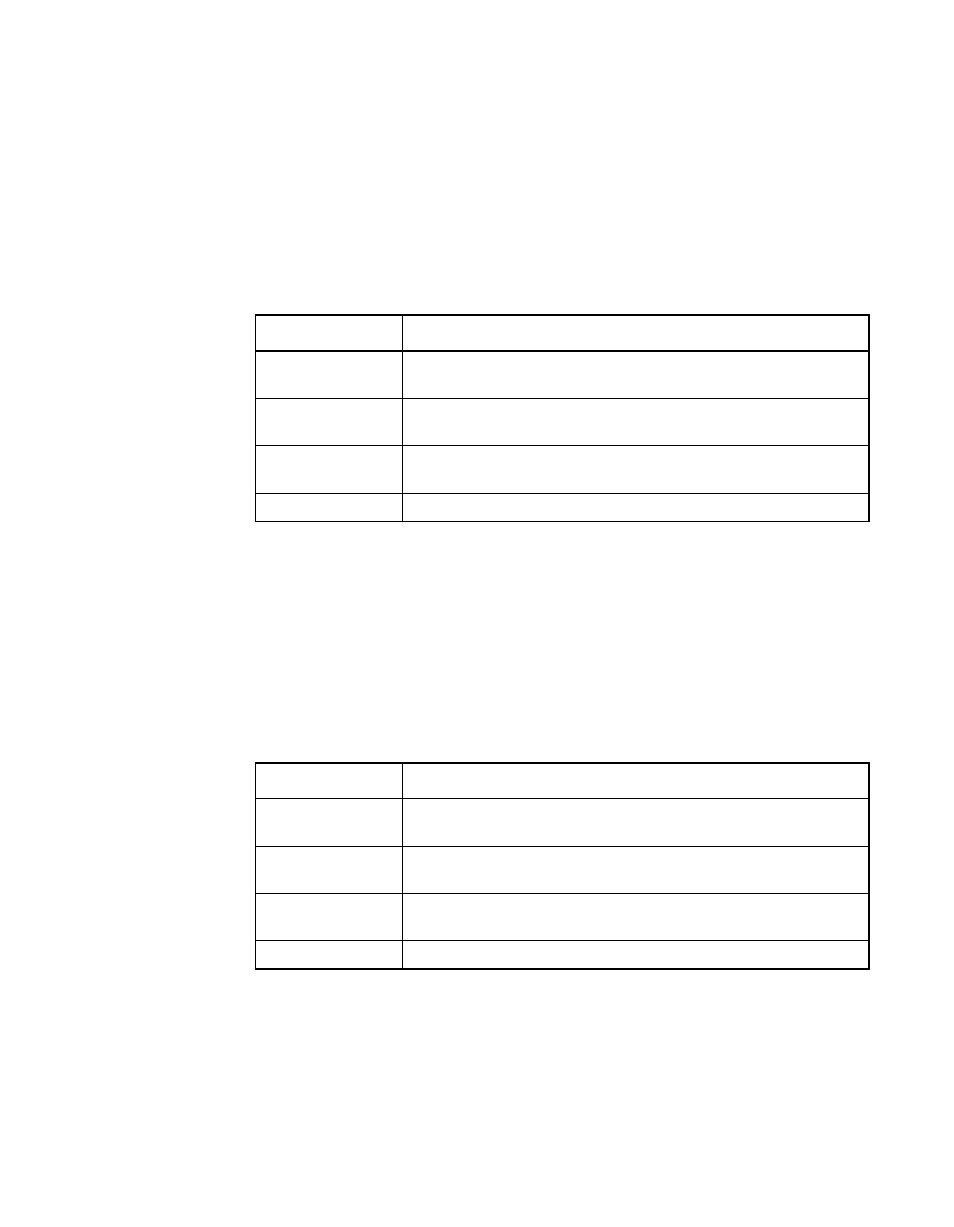
Table 2.5
RAID 0 Overview
Feature
Description
Uses
Provides high data throughput, especially for large files. Any
environment that does not require fault tolerance.
Strong Points
Provides increased data throughput for large files. No
capacity loss penalty for parity.
Weak Points
Does not provide fault tolerance or high bandwidth. All data
lost if any drive fails.
Drives
1 to (14 drives x the number of channels).
Table 2.6
RAID 1 Overview
Feature
Description
Uses
Appropriate for small databases or any other environment
that requires fault tolerance but small capacity.
Strong Points
Provides complete data redundancy. RAID 1 is ideal for any
application that requires fault tolerance and minimal capacity.
Weak Points
Requires twice as many disk drives. Performance is impaired
during drive rebuilds.
Drives
2
