2 maximizing performance, Table2.11 raid levels and performance, Maximizing performance – Avago Technologies MegaRAID SATA 150-4 (523) User Manual
Page 43: Raid levels and performance
RAID Configuration Strategies
2-21
Copyright © 2003–2006 by LSI Logic Corporation. All rights reserved.
2.6.2
Maximizing Performance
A RAID disk subsystem improves I/O performance. The RAID array
appears to the host computer as a single storage unit or as multiple
logical units. I/O is faster because drives can be accessed simultaneously.
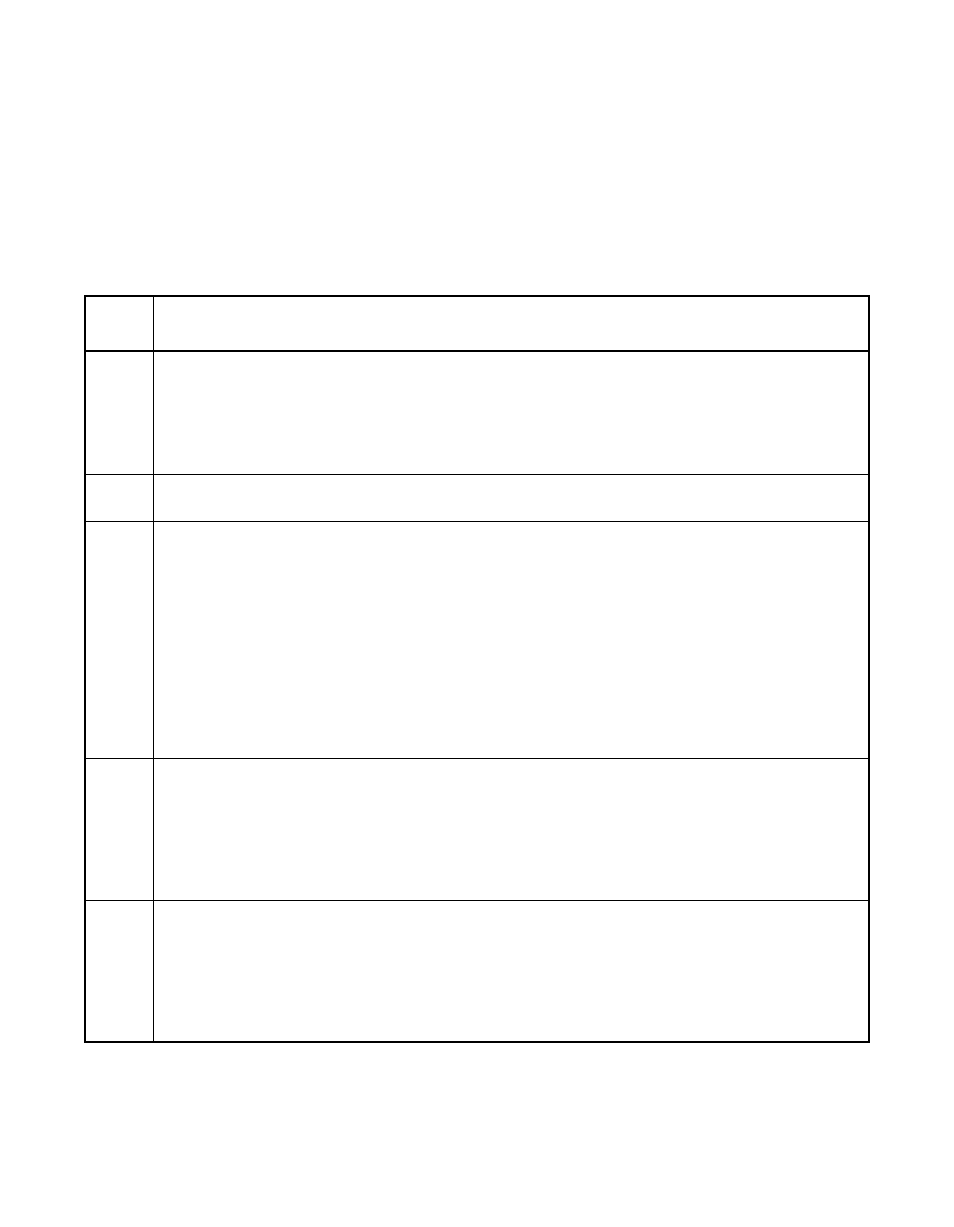
describes the performance for each RAID level.
Table 2.11
RAID Levels and Performance
RAID
Level
Performance
0
RAID 0 (disk striping) offers the best performance of any RAID level. RAID 0 breaks up data
into smaller blocks, then writes a block to each drive in the array. Disk striping writes data
across multiple disk drives instead of just one disk drive. It involves partitioning each drive
storage space into stripes that can vary in size from 8 Kbytes to 128 Kbytes. These stripes
are interleaved in a repeated sequential manner. Disk striping enhances performance
because multiple drives are accessed simultaneously.
1
With RAID 1 (disk mirroring), each drive in the system must be duplicated, which requires
more time and resources than striping. Performance is impaired during drive rebuilds.
5
RAID 5 (distributed parity) provides high data throughput, especially for large files. Use this
RAID level for any application that requires high read request rates, but low write request
rates, such as transaction processing applications, because each drive can read and write
independently. Since each drive contains both data and parity, numerous writes can take
place concurrently. In addition, robust caching algorithms and hardware based exclusive-or
assist make RAID 5 performance exceptional in many different environments.
Parity generation can slow the write process, making write performance significantly lower for
RAID 5 than for RAID 0 or RAID 1. Disk drive performance is reduced if a drive is being
rebuilt. Clustering can also reduce drive performance. Environments with few processes do
not perform as well because the RAID overhead is not offset by the performance gains in
handling simultaneous processes.
10
RAID 10 (disk spanning) works best for data storage that needs the enhanced I/O
performance of RAID 0 (striped arrays), which provides high data transfer rates. Spanning
increases the size of the logical volume and improves performance by doubling the number
of spindles. The system performance improves as the number of spans increases.
(The maximum number of spans is eight.) As the storage space in the spans is filled, the
system stripes data over fewer and fewer spans and RAID performance degrades to that of
a RAID 1 or RAID 5 array.
50
RAID 50 (disk spanning) works best when used with data that requires high reliability, high
request rates, and high data transfer. It provides high data throughput, data redundancy, and
very good performance. Spanning increases the size of the logical volume and improves
performance by doubling the number of spindles. The system performance improves as the
number of spans increases. (The maximum number of spans is eight.) As the storage space
in the spans is filled, the system stripes data over fewer and fewer spans and RAID
performance degrades to that of a RAID 1 or RAID 5 array.
